Chinese Warlord Era
Chinese Warlord Era
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a period in the history of the Republic of China when control of the country was divided among former military cliques of the Beiyang Army and other regional factions.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
October 1922: Following resolution of the Shandong Problem, the Japanese Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory was returned to China on 10 December 1922.
November 1919: The occupation of Outer Mongolia by the Beiyang government of the Republic of China began in October.
January 1918: De facto evolution of the boundary of Tibet up to 1932.
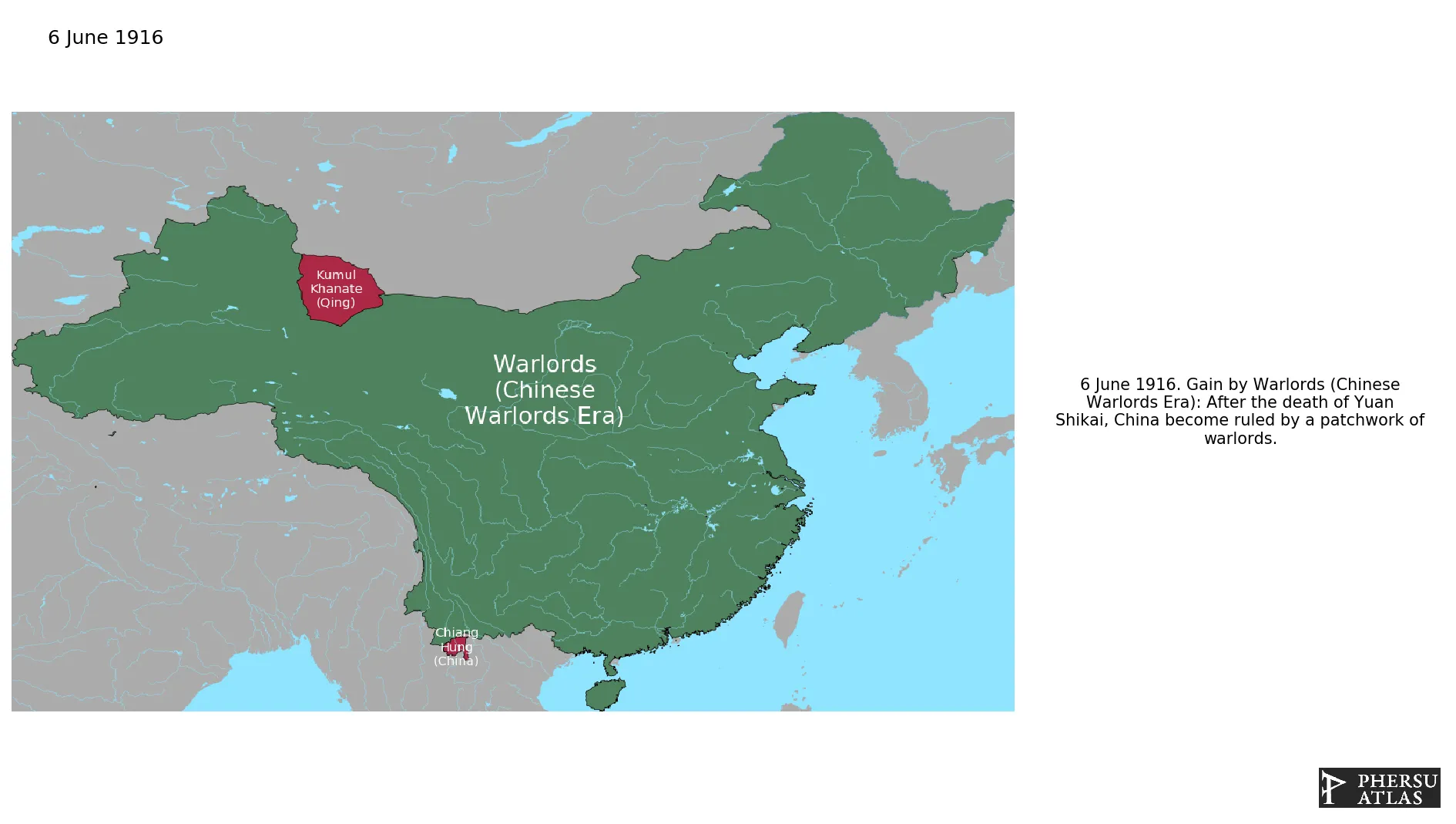
June 1916: After the death of Yuan Shikai, China become ruled by a patchwork of warlords.
December 1922: Jiaozhou Bay is returned to China by Japan.
Was a military campaign launched by the Kuomintang to conquer whole China from the many warlords that controlled its various regions.
June 1928: The NRA Third Collective Army marched into Beijing.
June 1928: Zhang Zongchang subordinate Xu Yuanquan subsequently surrendered Tianjin to the Chinese Republican First Collective Army.
July 1926: For simplicity we assume that at the the start of the Northern expedition only the Kuomintang represents the Republic of China due to ist unification aims.
July 1926: The Kuomintang captured Changsha on 11 July.
August 1926: The Kuomintang, led by Li Zongren and his Guangxi NRA Seventh Army, had taken Xianning.
November 1926: In early November, Kuomintang troops moved to capture the Yangtze ports of Jiujiang and Hukou.
November 1926: On 9 November 1926, Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang forces successfully retook control of Nanchang.
December 1926: Yingqin, a prominent military leader of the Kuomintang army, entered Fuzhou unopposed.
January 1927: By 29 January, the offensive had reached Lanxi and Jinhua, where a fierce battle resulted in a catastrophic defeat for Sun's forces.
February 1927: Sun's commander in the area, Meng Chao-yueh, decided to abandon Hangzhou to the Chinese Republican Army.
March 1927: The Warlords withdraw from Nanjing on 23 March, leaving the city undefended. Cheng arrived on the next day.
March 1927: The NRA went on to capture Anhui provincial capital Hefei and the smaller city of Bengbu.
April 1927: Launching a counteroffensive on 3 April, the NPA had been able to force the NRA back more than 161 kilometres to the Yangtze by 11 April.
May 1927: By 20 May, Li (Republic of China) had captured Bengbu.
May 1927: On 28 May, Li (Republic of China) took Suzhou.
April 1928: The Chinese Republican forces occupy Jining.
May 1928: The Kuomintang Third Army, led by General Xu Yongchang, was able to capture Zhangjiakou.
May 1928: Nankou Pass conquered by Kuomintang.
December 1928: Zhang Xueliang officially declared his allegiance to the nationalist government in Nanjing on 29 December 1928, marking the formal end of the Northern Expedition, and the reunification of China.
September 1926: The Republican Army offensive was forced into retreat as Sun arrived from Nanjing with reinforcements on 21 September.
July 1927: By 24 July, the NPA had retaken Xuzhou.
September 1926: Both Jiujiang and Nanchang had come under KMT control.
June 1927: The NRA captured the vital railway junction of Xuzhou.
February 1927: Zhejiang was under complete Kuomintang control.
October 1926: By 2 September, the Republican Army had nearly surrounded Wuchang. Whilst Wu and most of his army fled north to Henan province, his remaining troops in the walled city held out for over a month.
April 1928: The Kuomintang captured Tengzhou by 16 April.
March 1927: Bai's Republican forces marched into Shanghai victorious.
April 1928: Chinese Republican forces troops entered Jinan.
August 1926: The Kuomintang captured the Yangtze port of Yuezhou. Hunan came under complete KMT control.
September 1927: Shanxi warlord Yan Xishan aligned his province with the Nanjing government.
December 1927: The combined NRA and Guominjun forces took Xuzhou.
1.1.Jinan incident
Was a dispute between the Japanese army and the Kuomintang.
May 1928: The Jinan incident began as a 3 May 1928 dispute between Chiang Kai-shek's National Revolutionary Army (NRA) and Japanese soldiers and civilians in Jinan, the capital of Shandong province in China, which then escalated into an armed conflict between the NRA and the Imperial Japanese Army.
April 1929: The Japanese army occupied Jinan until March 1929.
 Chinese Warlord Era
Chinese Warlord Era