
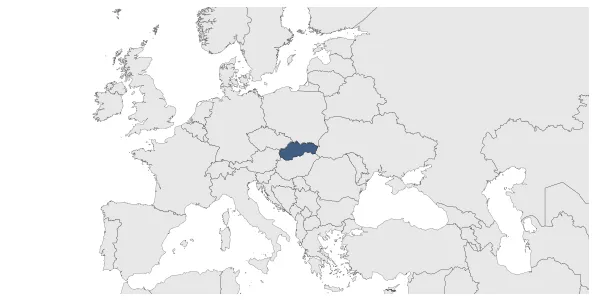
Data
Name: slovakia
Type: Cluster
Start: 1919 AD
End: 2022 AD
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 slovakia
slovakia
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. World War I
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
Were a series of treaties and military events that can be considered a direct consequence of World War I.
1.1.1.Hungarian-Czechoslovak War
Was a war between Hungary and Czechoslovakia after the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire at the end of World War I.
1.1.1.1.Hungarian Counterattack (Hungarian-Czechoslovak War)
Was Hungarian counterattack against Czech invading forces during the Hungarian-Czechoslovak War.
2. Dismemberement of Czechoslovakia
On 29 September, the Munich Agreement was signed by Germany, Italy, France, and Britain. The Munich Agreement stipulated that Czechoslovakia must cede Sudeten territory to Germany. Germany dismembered Czechoslovakia.
3. World War II
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
3.1.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
Was the Soviet offensive against German-occupied Belarus during World War II.
Was an operation of the Soviet forces of the 1st Baltic Front, commanded by General Hovhannes Bagramyan, conducted from 5 July to 29 August 1944. It drove German troops from much of Lithuania, with the main tactical objective being the city of Šiauliai.
3.1.2.Soviet Invasion of Slovakia
Was the Soviet invasion of Slovakia near the end of World War II.
3.2.World War II (Western Front)
Was the Western European theatre of World War II.
4. Dissolution of Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia peacefully split into Slovakia and the Czech Republic.



























