If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the Western European theatre of World War II.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
May 1940: Hitler announced the re-integration of Eupen-Malmedy into Germany while the rest of Belgium remained under military occupation.
June 1940: German occupation of the Channel Islands, which lasted for most of World War II.
August 1942: Luxembourg was annexed by Germany into Gau Moselland.
April 1945: The Slovak Republic was abolished after the Soviet occupation in 1945.
June 1944: Following the Allied invasion of Normandy in June 1944 and the liberation of France later that year, the Free French Provisional government of the French Republic (GPRF) was installed as the new national government, led by de Gaulle.
September 1943: The Italian surrended to the Allies in September 1943 and the Germans took over the Italian occupation zones in France.
September 1944: End of the German Occupation of Monaco.
September 1943: In September 1943, following Mussolini's fall in Italy, the German Army occupied Monaco and began the deportation of the Jewish population.
November 1942: On 11 November 1942, the Italian Army invaded and occupied Monaco.
Was the French invasion of Saarland, Germany, in the first stages of World War II.
September 1939: The French held German territory along all of the Rhine-Moselle front, but after the collapse of Poland, General Maurice Gamelin on 21 September ordered French units to return to their starting positions on the Maginot Line. On 17 October the withdrawal was complete.
September 1939: The French 32nd Infantry Regiment made further gains on 12 September, seizing the German town of Brenschelbach.
September 1939: The French occupied most of the Warndt Forest.
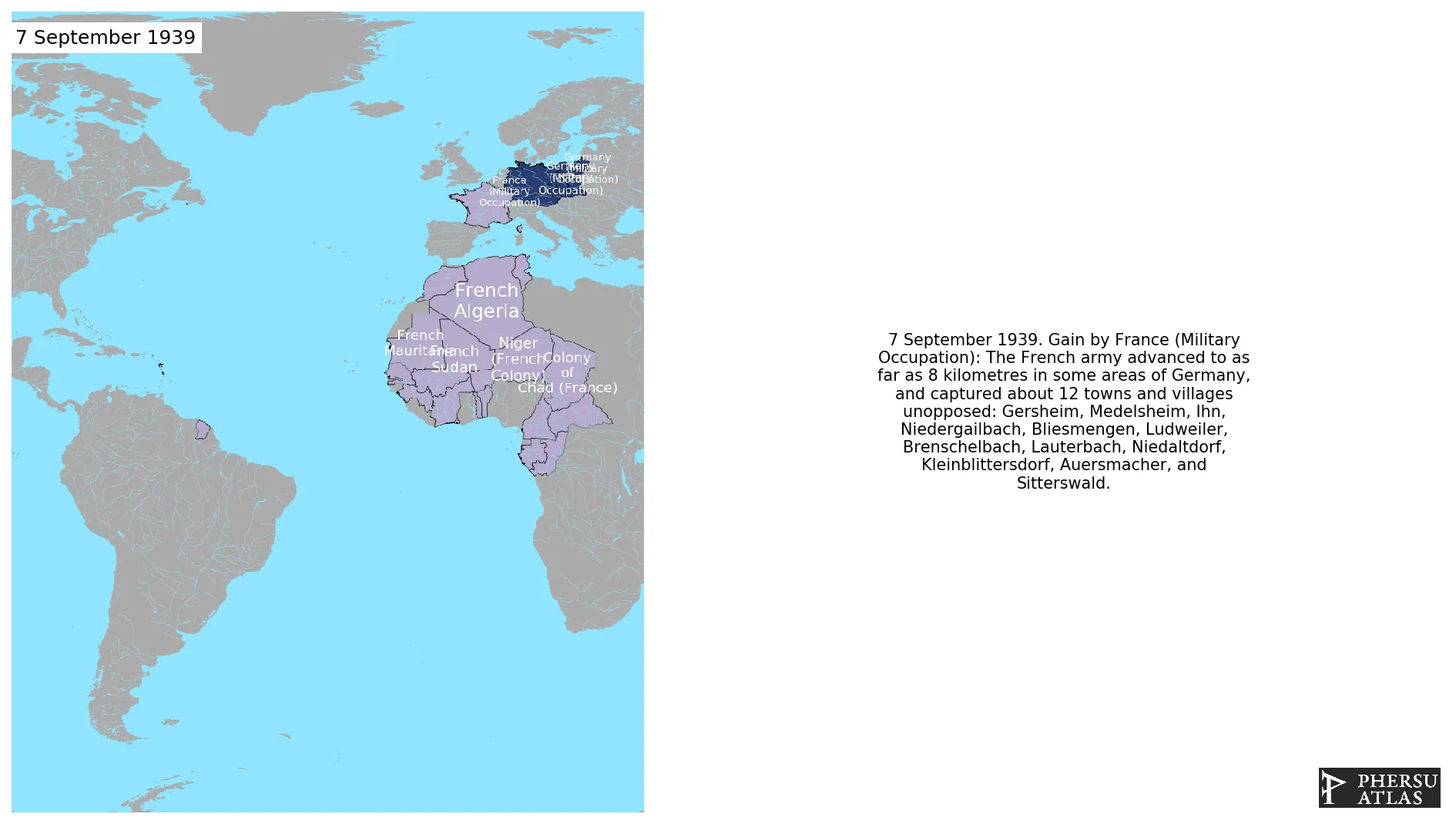
September 1939: The French army advanced to as far as 8 kilometres in some areas of Germany, and captured about 12 towns and villages unopposed: Gersheim, Medelsheim, Ihn, Niedergailbach, Bliesmengen, Ludweiler, Brenschelbach, Lauterbach, Niedaltdorf, Kleinblittersdorf, Auersmacher, and Sitterswald.
Was the struggle for the control of Norway between Germany and the Allies that ended with the German military occupation of that country.
April 1940: Bergen and Trondheim are captured by Germany.
April 1940: In Oslo, the Norwegian government has left, and Vidkun Quisling becomes the head of the new government.
April 1940: The British 146th Brigade is forced to withdraw from Steinkjer by German forces.
May 1940: Norwegian and Allied forces attack Narvik, entering the town after a short fight.
April 1940: Allied forces decide to withdraw from Namsos and Åndalsnes, abandoning the effort against German forces at Trondheim.
May 1940: Territorial change based on available maps.
April 1940: British forces land at Namsos and Harstad as Anglo-French forces prepare to launch operations against German forces at Trondheim and Narvik.
May 1940: German forces enter Åndalsnes.
May 1940: Anglo-French forces land at Mosjøen to block German advances to Narvik.
April 1940: The Narvik landing force evades British naval forces and defeats the Norwegian vessels in the fjord.
April 1940: British forces land at Åndalsnes.
April 1940: German air-landed soldiers land at and capture the airport at Oslo.
May 1940: French Foreign Legion and Polish forces land at Tromsø and Harstad.
April 1940: Kongsberg fell to German forces without a fight.
April 1940: German forces moved north from Oslo reach Lillehammer and captured the town.
April 1940: Egersund is captured without resistance by the Germans, as is Arendal.
June 1940: The surrender of Norway to the German invading force is complete and resistance is ended.
Were the administrative territorial changes of Denmark (occupied by Germany) and its overseas territories (free from German occupation) during World War II.
April 1940: Lasting approximately four hours, the German ground campaign against Denmark was one of the shortest military operations of the Second World War.
April 1941: On 9 April 1941, the Danish envoy to the United States, Henrik Kauffmann, signed a treaty with the U.S. authorizing it to defend Greenland and construct military stations there. Kauffmann was supported in this decision by the Danish diplomats in the United States and the local authorities in Greenland. Signing this treaty "in the name of the King" was a clear violation of his diplomatic powers, but Kauffmann argued that he would not receive orders from an occupied Copenhagen.
May 1940: The United Kingdom occupied Iceland to pre-empt a German occupation.
May 1945: German forces in North West Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands surrender.
May 1945: Following the liberation of Denmark and the end of World War II in Europe, the occupation of the Faroe Islands was terminated in May 1945 and the last British soldiers left in September.
August 1943: Germany occupied Denmark in Operation Weserübung. The king and government functioned as normal in a de facto protectorate over the country until 29 August 1943.
June 1944: Iceland dissolved its union with Denmark and the Danish monarchy and declared itself a republic.
May 1945: On 5 May 1945, Greenlanders celebrated the liberation of Denmark in Nuuk. The Greenland Administration under Eske Brun surrendered its emergency powers and again came under direct control from Copenhagen.
May 1940: After the occupation of Denmark, British forces from 12 April 1940 made a pre-emptive bloodless invasion of the Faroe Islands to prevent their occupation by German troops.
July 1941: The defence of Iceland was transferred from Britain to the United States.
Was the German Invasion of Luxembourg during World War II.
May 1940: The battle for Luxembourg began on 10 May 1940 and lasted just one day. Facing only light resistance, German troops quickly occupied Luxembourg.
Was the German Invasion of the Netherlands during World War II.
May 1940: Battle of Maastricht.
May 1940: Battle of Mill.
May 1940: Battle of the Grebbeberg.
May 1940: Battle of Zeeland.
May 1940: After the bombing of Rotterdam, the Dutch surrendered in the late afternoon of 14 May, signing the capitulation early the next morning.
May 1940: Battle of Rotterdam.
Was the German Invasion of Belgium during World War II.
May 1940: Battle of Fort Eben-Emael.
May 1940: The Belgian Command withdrew its forces behind the Namur-Antwerp line.
May 1940: When news of the German breakthrough at Sedan reached Prioux, the French withdrew from Gembloux.
May 1940: The Germans reached the outskirts of Bruges, and captured Ursel.
May 1940: Nevele, Vynckt, Tielt and Iseghem fall on the western and central part of the Leie front.
May 1940: The Germans captured Terneuzen and Ghent that day.
May 1940: The outnumbered Belgians abandoned Brussels and the Government fled to Ostend. The city was occupied by the German Army on 17 May.
May 1940: Battle of Boulogne.
The Battle of France was the German invasion of France during World War II that ended with the French Armistice of Compiègne on 22 June 1940.
7.1.Central Front of the German Invasion of France (World War II)
Was the front of the Meuse Line during the German invasion of France in World War II.
May 1940: The German advance forces reached the Meuse line late in the afternoon.
May 1940: German advance in Belgium.
May 1940: Stonne changed hands 17 times and fell to the Germans for the last time in the evening.
June 1940: Battle of Dunkirk.
May 1940: Battle of Montcornet.
May 1940: On 12 May, Sedan was captured without resistance and the Germans defeated the French defences around Sedan on the west bank of the Meuse.
7.2.Fall Rot
Was the operation to complete the conquest of France by the German Army during the Battle of France.
June 1940: Frontline of the Battle of Belgium in that date.
June 1940: German advance in France.
June 1940: On 14 June, Paris fell to the German forces. The Parisians unable to flee the city found that in most cases the Germans were extremely well mannered.
June 1940: German conquest of Rennes.
June 1940: German conquest of Nantes.
June 1940: German conquest of Brest.
June 1940: German advances in France by June, 25th 1940.
June 1940: The German 7th Panzer Division headed west over the Seine river through Normandy and captured the port of Cherbourg on 18 June.
June 1940: The remnants of French Army 2 Group are encircled by German forces.
7.3.French Armistice
Was the Armistice of 22 June 1940 when France surrendered to Germany during World War II.
7.3.1.Franco-German Armistice
The French Armistice of 22 June 1940 was signed at 18:36 near Compiègne, France, by officials of Nazi Germany and the French Third Republic. The armistice partitioned France: northern and central France were militarly occupied by Germany, Alsace-Lorraine was inglobated into the German State, and the remainder of France became Vichy France, a regime loyal to Germany.
June 1940: The Armistice of 22 June 1940 was signed at 18:36 near Compiègne, France, by officials of Nazi Germany and the French Third Republic. It did not come into effect until after midnight on 25 June. Northern and coastal France fell under direct German occupation, whereas a French government aligned with Germany ("Vichy France") was established in the south. Alsace-Lorraine was annexed to Nazi Germany.
7.3.2.Franco-Italian Armistice
The Franco-Italian Armistice, or Armistice of Villa Incisa, signed on 24 June 1940.
June 1940: Franco-Italian Armistice, or Armistice of Villa Incisa, signed on 24 June 1940, in effect from 25 June. Some regions of southern France remained under Italian occupation.
Refers to the battles on the northern French and Belgian front during the German invasion of the region.
May 1940: Frontline of the Battle of Belgium in that date.
May 1940: Surrender of French troops in Calais.
May 1940: Defensive Perimeter around Dunkirk established. The Germans occupy the surroundings of Dunkirk.
June 1940: Evacuation of British and Belgian forces from Dunkirk completed.
May 1940: Antwerp and Suarlee fell to Germany on 19 May.
Was the invasion of southern France by Fascist Italy during the Battle of France.
June 1940: German forces occupied Les Granges-Saint-Paul.
June 1940: That day the fort of Pont Saint-Louis engaged in its last artillery duel with the Italians. No vehicles managed to cross the bridge before the armistice. The capture of "the pearl of France", Menton, a famous tourist destination, was "an undeniable success" (despite its cost) for the Italians.
June 1940: After eliminating the French field fortifications with artillery fire, the Germans took the city of Bramans.
Was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II.
10.1.German Offensive in Yugoslavia
German offensive during the World War II Axis invasion of Yugoslavia.
April 1941: Late in the afternoon of the 10th April German Tanks entered the city of Zagreb.
April 1941: SS-Obersturmfuehrer (1st Lt.) Klingenberg of the 2d SS Motorized Infantry Division entered Belgrade with an SS patrol. The mayor of Belgrade officially handed over the city to Klingenberg
10.2.Allied Counteroffensive
Allied military operations to liberate Belgium and Luxembourg during World War II.
January 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
Was the military occupation of Vichy France carried out by Germany and Italy in November 1942. It marked the end of the Vichy regime as a nominally-independent state and the disbanding of its army, but it continued its existence as a puppet government in Occupied France.
November 1942: Military occupation of Vichy France carried out by Germany and Italy in November 1942. It marked the end of the Vichy regime as a nominally-independent state and the disbanding of its army (the severely-limited Armistice Army), but it continued its existence as a puppet government in Occupied France.
Was a phase in the Western European campaign of World War II which involved actions near the German defensive Siegfried Line.
September 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
September 1944: German garrison of Le Havre surrenders.
September 1944: Allied liberation of Antwerp.
12.1.Clearing the Channel Coast
Was a World War II operation undertaken by the First Canadian Army in August 1944 to capture the French coastline along the Strait of Dover.
May 1944: Allied forces arrive at the outskirts of Dunkirk.
September 1944: Dieppe was captured by the 2nd Canadian Infantry Division on 1 September.
September 1944: Ostend, a Belgian city and one of the German "channel forts", was liberated in 1944 by Allied forces.
September 1944: The 1st Polish Armoured Division crossed the Belgian border and captured Ypres.
September 1944: The Germans surrender to the 3rd Canadian Division in Boulogne-sur-Mer.
September 1944: Calais fell to the Allied forces on 30 September
September 1944: The attack on the Cap Gris Nez batteries in 1944 was part of the Allied invasion of Normandy during World War II. The operation was led by General Bernard Montgomery and resulted in the capture of strategic coastal positions.
September 1944: Allied troops crossed the Ghent-Bruges Canal against strong opposition.
12.2.Battle of the Scheldt
Was a series of military operations led by the First Canadian Army, with Polish and British units attached, to open up the shipping route to Antwerp so that its port could be used to supply the Allies in north-west Europe.
October 1944: Allied advances by October 16th in the Low Countries and Belgium, during the Battle of the Scheldt.
November 1944: Allied advances by November 10th in the Low Countries and Belgium, during the Battle of the Scheldt.
Was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II.
13.1.Allied Invasion of Normandy
The allied forces launched an invasion of German-occupied France with the Normandy landings of 6 June 1944 (D-Day).
June 1944: The five beachheads of the Allied invasion of Normandy were connected by 12 June.
June 1944: Allied forces invade France, landing on the coast of Normandy. Two of the beaches (Juno and Gold) were linked on the first day
13.2.Battle of Cherbourg
Was a battle fought in Cherbourg, France, immediately after the successful Allied landings on 6 June 1944.
June 1944: On 18 June the US 9th Infantry Division reached the west coast of the peninsula, isolating the Cherbourg garrison from any potential reinforcements. There was little opposition on the western side of the peninsula and on the eastern side, the exhausted defenders around Montebourg collapsed.
June 1944: Allied troops, mainly American, captured the fortified port of Cherbourg.
13.3.Battle of Saint-Lô
Was an allied military operation that liberated the region around Saint-Lô, France.
July 1944: American forces occupy Saint-Lô.
13.4.Battle of Caen
Was an Allied military operation that liberated the region around Caen, France.
July 1944: Caen, a major objective, was still in German hands at the end of D-Day and would not be completely captured until 21 July.
13.5.Operation Cobra
Was an offensive launched by the United States First Army seven weeks after the D-Day landings, during the Normandy campaign of World War II that led to the collapse of the German Normandy front.
July 1944: Allied operations to liberate St. Lo.
13.6.Conquest of Normandy
Was the Allied conquest of German-occupied Normandy during World War II.
August 1944: Allied military operation in Normandy.
13.7.Battle of Mortain
Was a German counter-attack near Mortain, in northwestern France during the Battle of Normandy.
August 1944: Frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
August 1944: Allied liberation of Le Mans.
13.8.Operation Totalize
Was an offensive launched by Allied troops in the First Canadian Army during the later stages of Operation Overlord in order to break through the German defences south of Caen.
August 1944: Based on available maps.
13.9.Battle of the Falaise Pocket
Was an Allied operation during the Battle of Normandy that led to the destruction of the German pocket in the area of the French cities of Trun, Argentan, Vimoutiers and Chambois.
August 1944: Allied forces clear the Chambois area.
August 1944: By the evening of 21 August, the Falaise pocket had been sealed, with Germans trapped inside.
13.10.Liberation of Paris
A military battle that took place during World War II from 19 August 1944 until the German garrison surrendered the French capital on 25 August 1944.
August 1944: Battle of Paris frm 19 August 1944 until the German commander in Paris, Lt. Gen. Dietrich von Choltitz, surrendered formally to Brig. Gen. Jacques Philippe Leclerc of the French 2nd Army at 15:15 of 25 August 1944.
13.11.Battle for Brest
Was fought in August and September 1944 in Brest as part of the Battle of Normandy during World War II.
September 1944: General Ramcke surrendered the city of Brest on 19 September 1944 to the Americans.
Was the landing operation of the Allied invasion of Provence (Southern France) on 15 August 1944.
August 1944: Allied operations In Southern France, 15-28 August 1944.
August 1944: Allied liberation of Grenoble.
August 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
August 1944: On 29 August, the Allies captured Montélimar.
September 1944: Allied liberation of Dijon.
September 1944: Operation Dragoon encountered Siegfried Line campaign "closing" central france
September 1944: Lyon was liberated by the French 2nd Corp.
September 1944: Allied advance in Germany in that date.
September 1944: Allied liberation of Autun.
September 1944: Allied liberation of Langres.
August 1944: Allied liberation of Marseille and Toulon.
14.1.Main invasion (operation Dragoon)
The invasion of the bulk of the armies partecipating to operation Dragoon during World War II.
August 1944: Operation Dragoon landing in France started on the morning of 15 August.
Was a three-day battle during the Liberation of Belgium that cleared part of the West Flanders from German troops.
September 1944: Allied liberation of Moerbrugge.
Was the Allied liberation of the Netherlands from the German occupying forces.
September 1944: Maastricht, Gulpen, Meerssen are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Sint-Oedenrode, Veghel, Son en Breugel are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Eindhoven is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Veldhoven is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Deurne is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Mook is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Helmond,Oss are liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Venray is liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Den Bosch, Tilburg, Bergen op Zoom are liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Tholen,Goes are liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Middelburg is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Hengelo is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Groningen is liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Veere,Koudekerke are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Nijmegen, Geldrop, Someren, Terneuzen are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Assen,Diepenveen,Olst are liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Vlissingen,Westkapelle are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Weert is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Apeldoorn is liberated by the Allies of World War II
December 1944: Blerick is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Arnhem, Zwolle are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Almelo is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Westerbork,Brummen,Deventer are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Simpelveld is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Doetinchem,Borculo,Eibergen,Enschede are liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Kerkrade is liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Wissenkerke,Zoutelande are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Zutphen, Leeuwarden, Zoutkamp are liberated by the Allies of World War II
16.1.Battle of Nijmegen
Was the liberation of the Dutch city of Nijmegen from German occupation during World War II.
September 1944: The Battle of Nijmegen or Liberation of Nijmegen occurred from 17 to 20 September 1944.
16.2.Battle of Overloon
As a battle fought during the Second World War between Allied forces and the German Army which took place in and around the village of Overloon in the south-east of the Netherlands .
October 1944: Overloon is liberated by the Allies of World War II
Was the operation of the U.S. Army to liberate German-occupied Lorraine during World War II.
September 1944: Allied advance in France up to Nancy, which is abandoned by German forces.
December 1944: Allied forces accept surrender of last of the Metz forts.
Was the invasion of the western territories of Germany mainly by the United States, United Kingdom, France and Canada at the end of World War II.
April 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
March 1945: Frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
April 1945: Allied military operations during the encirclement of the Ruhr area (March-April 1945).
April 1945: Allied advance in Germany in that date.
May 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
April 1945: Allied reduction of Ruhr Pocket.
March 1945: Allied military operations during the encirclement of the Ruhr area (March-April 1945).
March 1945: American forces clear large part of Wesel in street-to-sreet fighting.
18.1.Battle of Aachen
Was a battle of World War II, fought by American and German forces in and around Aachen, Germany, between 2-21 October 1944.
October 1944: The German commander of Aachen garrison surrenders at 12:05 of 21 October 1944 ot American forces.
18.2.Operation Clipper
Was an Allied offensive by the British XXX Corps (which included the American 84th Infantry Division) to reduce the Geilenkirchen salient in mid-November 1944.
November 1944: Allied forces arrive 2 miles Sout-West of Geilenkrichen.
18.3.German Offensive on the Western Front during the Allied invasion
Was a offensive of Germany against the Allies that were invading German-occupied Europe during World War II.
December 1944: Territorial changes caused on December 16th 1944 by the German Ardenne Offensive of 1944 ("Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein").
December 1944: Territorial changes caused on December 20th 1944 by the German Ardenne Offensive of 1944 ("Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein").
December 1944: Territorial changes caused on December 25th 1944 by the German Ardenne Offensive of 1944 ("Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein").
18.4.Operation Blackcock
Was an operation to clear German troops from the Roer Triangle, formed by the towns of Roermond and Sittard in the Netherlands and Heinsberg in Germany during the fighting on the Western Front in the Second World War.
January 1945: Allied forces complete capture of Heinsberg.
18.5.Operation Veritable
Was an Allied military operation in the Reichswald Forest, in Germany, towards the end of World War II.
February 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the Rhineland campaign.
February 1945: Allied forces complete capture of Cleve.
March 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the Rhineland campaign.
18.6.Operation Grenade
Was the crossing of the Roer river between Roermond and Düren by the U.S. Ninth Army which marked the beginning of the Allied invasion of Germany.
18.7.Operation Lumberjack
Was a military operation with the goal of capturing the west bank of the Rhine River and seizing key German cities, near the end of World War II.
March 1945: Allied conquest of Cologne.
March 1945: At Bitburg, the Soviet 5th Infantry Division cut through the German lines.
March 1945: Allied forces entered Euskirchen on 4 March.
Was a military operation, lasting from 23 October 1944 until 26 April 1945, in which Soviet and Norwegian forces wrested away control of Finnmark, the northernmost county of Norway, from Germany.
April 1945: The Norwegians declared Finnmark to be free.
November 1944: Allied forces penetrated 116 km northwest of Neiden before halting in Tana.
October 1944: With the help of local fishermen, the Soviets were able to cross the Neiden River on 27 October and capture the ridge. Fighting was fierce, and the Germans managed to burn every building in the village, save for the local church, before withdrawing.
Took place November 19, 1944 in the small town of Vianden, in northern Luxembourg. It was one of the most important battles of the Luxembourg Resistance during World War II.
November 1944: One of the most important battles of the Luxembourg Resistance during World War II took place November 19, 1944 in the small town of Vianden.
Was an Allied military operation to liberate central Alsace from German forces.
February 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
January 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
Selected Sources
Battle of the Scheldt. Canadiansoldiers.com. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://www.canadiansoldiers.com/history/campaigns/northwesteurope/scheldt.htm
Blau, G.E.(1953): PART TWO THE YUGOSLAV CAMPAIGN. U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://history.army.mil/books/wwii/balkan/20_260_2.htm
Campaign In The West, Situation 4 June 1940. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope13.jpg
Chronologisch overzicht van de bevrijding van Nederlandse plaatsen in de Tweede Wereldoorlog. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 12 september 2020 on https://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chronologisch_overzicht_van_de_bevrijding_van_Nederlandse_plaatsen_in_de_Tweede_Wereldoorlog
Crossing Of The Rhine, 22-28 March 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope79.jpg
Durand, F. B (2016): History of Timor-Leste, Chiang Mai (Thailand), p. 114
East Timor and Indonesia Action Network. Retrieved on may 11th, 2021 on https://www.etan.org/etanpdf/2006/CAVR/03-History-of-the-Conflict.pdf
Encirclement Of The Ruhr, 29 March-4 April 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope80.jpg
Final Operations, 19 April-7 May 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope82.jpg
German Ardennes Counter-Offensive, 26 December 1944 16 January 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope73.jpg
NORTHWESTERN EUROPE, 1940 - CAMPAIGN IN THE WEST, 1940 - Situation 21 May and Operations Since 16 May. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://www.westpoint.edu/sites/default/files/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe/WWIIEurope12.pdf
NORTHWESTERN EUROPE, 1940 - CAMPAIGN IN THE WEST, 1940 Situation 16 May and Operations - Since 10 May. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://westpoint.edu/sites/default/files/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe/WWIIEurope11.pdf
OPERATION COBRA, 25-29 July 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope62.jpg
Operations In Southern France, 15-28 August 1944 & The Invasion Force. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope67.jpg
Pogue, F. (1954): United States Army in World War II: The European theater of operations, Washington D.C. (USA), p. 226
Pursuit To The West Wall, 26 August-14 September 1944 United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope66.jpg
Reduction Of Ruhr Pocket And Advance To the Elbe And Middle Rivers, 5-18 April 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope81.jpg
Sullivan, G.R.: Ardennes-Alsace p.23. U.S. Army Center of Military Hisotry. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://www.history.army.mil/brochures/ardennes/aral.htm
The Breakout, 1-13 August 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope64.jpg
The Rhineland Campaign, Operations 8 February-5 March & Operations 6-10 March 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope76combined.jpg
Tomasevich, J. (1975): War and Revolution in Yugoslavia, 1941-1945, Stanford University Press, p.68
U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/brochures/ardennes/p49(map).jpg
WESTERN EUROPE, 1940 - CAMPAIGN IN THE WEST, 1940 - The Pursuit, 13-25 June. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://www.westpoint.edu/sites/default/files/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe/WWIIEurope15.pdf
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 203
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 208
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 221
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 233
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 323
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 400
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 450
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 530
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.250
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.258
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.260
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.261
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.266
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.269
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.284
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.291
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.308
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.351
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.382
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.424
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.425
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp. 213-214
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.249-250
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.250-253
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.251-256
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.272-274
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.276-282
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.279-280
 World War II (Western Front)
World War II (Western Front)