Data
Name: Republic of Estonia
Type: Polity
Start: 1918 AD
End: 2022 AD
Nation: estonia
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Republic of Estonia
Republic of Estonia
This article is about the specific polity Republic of Estonia and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Is a country located in the Baltic Region of Europe. It borders Russia and Latvia. It emerged from the German-occupied territories of the Russian Empire after World War I. In the early phases of World War II it was invaded by the USSR. It gained again independence with the dissolution of the USSR in 1991.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. World War I
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
Were a series of treaties and military events that can be considered a direct consequence of World War I.
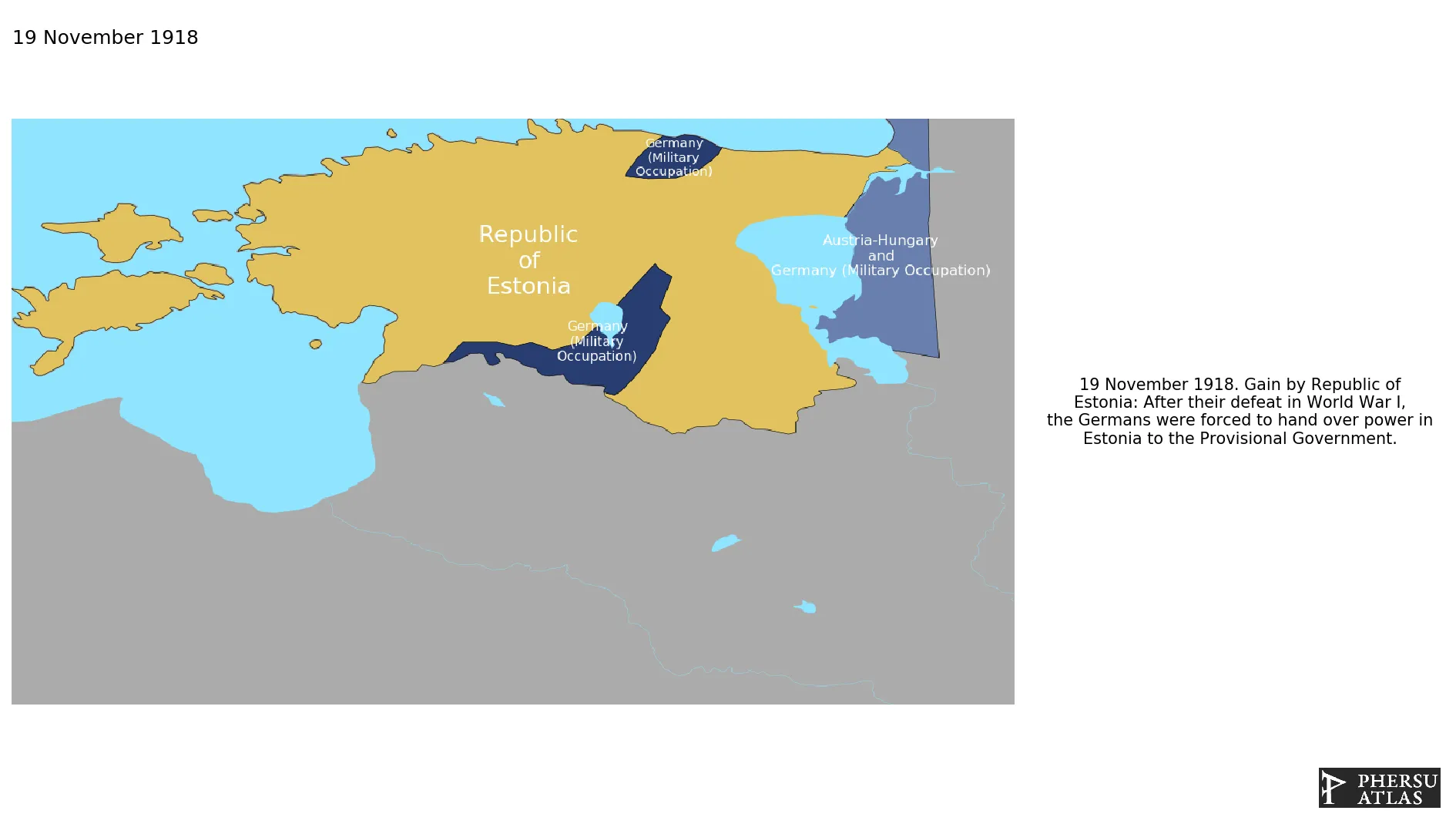
1.1.1.Creation of Estonia after the retreat of the German Army
After their defeat in World War I, the Germans handed over the power in Estonia to a Provisional Government.
1.1.2.Estonian War of Independence
Was the Estonian War of independence from Bolshevik Russia and German troops.
1.1.2.1.Soviet Offensive (Estonian War of Independence)
Was the Bolshevik invasion of Estonia, a former region of the Russian Empire that had declared independence.
1.1.2.2.Liberation of Estonian territories (Estonian War of Independence)
Estonian counteroffensive against the Bolshevik invasion.
1.1.2.3.Estonian offensives into Russia and Latvia
Offensive of the Estonian army in Russian and Latvian territories.
1.1.2.4.Battles between Estonia and Latvia
Were battles between Latvia and Estonia during the Independence wars of these two countries.
The Battle of Cēsis (alos Battle of Wenden) was a decisive battle in the Estonian War of Independence and the Latvian War of Independence were the Estonian and Latvian forces defeated the Baltic German forces.
1.1.2.4.2.Return of latvian government
Withdraw of remaining German troops from Latvia.
1.1.2.5.Final battles and peace (Estonian War of Independence)
Were the final phases of the Estonian War of Independence.
1.1.3.Latvian War of Independence
Was a series of military conflicts in Latvia between 5 December 1918, after the newly proclaimed Republic of Latvia was invaded by Soviet Russia.
1.1.3.1.Soviet offensive (Latvian War of Independence)
Soviet offensive in Latvia, a territory of the Russian Empire that had been occupied by Germany and had then declared independency.
1.1.3.2.Latvian and German counteroffensive
German and Latvian counterattack against Bolshevik forces during the Latvian War of Independence.
2. World War II
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
2.1.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
2.1.1.Soviet occupation of the Baltic states
Was the Soviet invasion of the Baltic states in the early phase of World War II as agreed by Germany and the USSR in the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact.
3. Dissolution of the Soviet Union
Was the process of internal disintegration within the Soviet Union (USSR) which resulted in the end of the country as a sovereign state, thereby resulting in its constituent republics gaining full independence.