This article is about the specific polity Republic of Gran Colombia and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Panama, and Venezuela, along with parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil and Guyana. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiographically to distinguish it from the current Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state. Gran Colombia was dissolved in 1831 due to the political differences that existed between supporters of federalism and centralism. It broke into the successor states of Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela.
Establishment
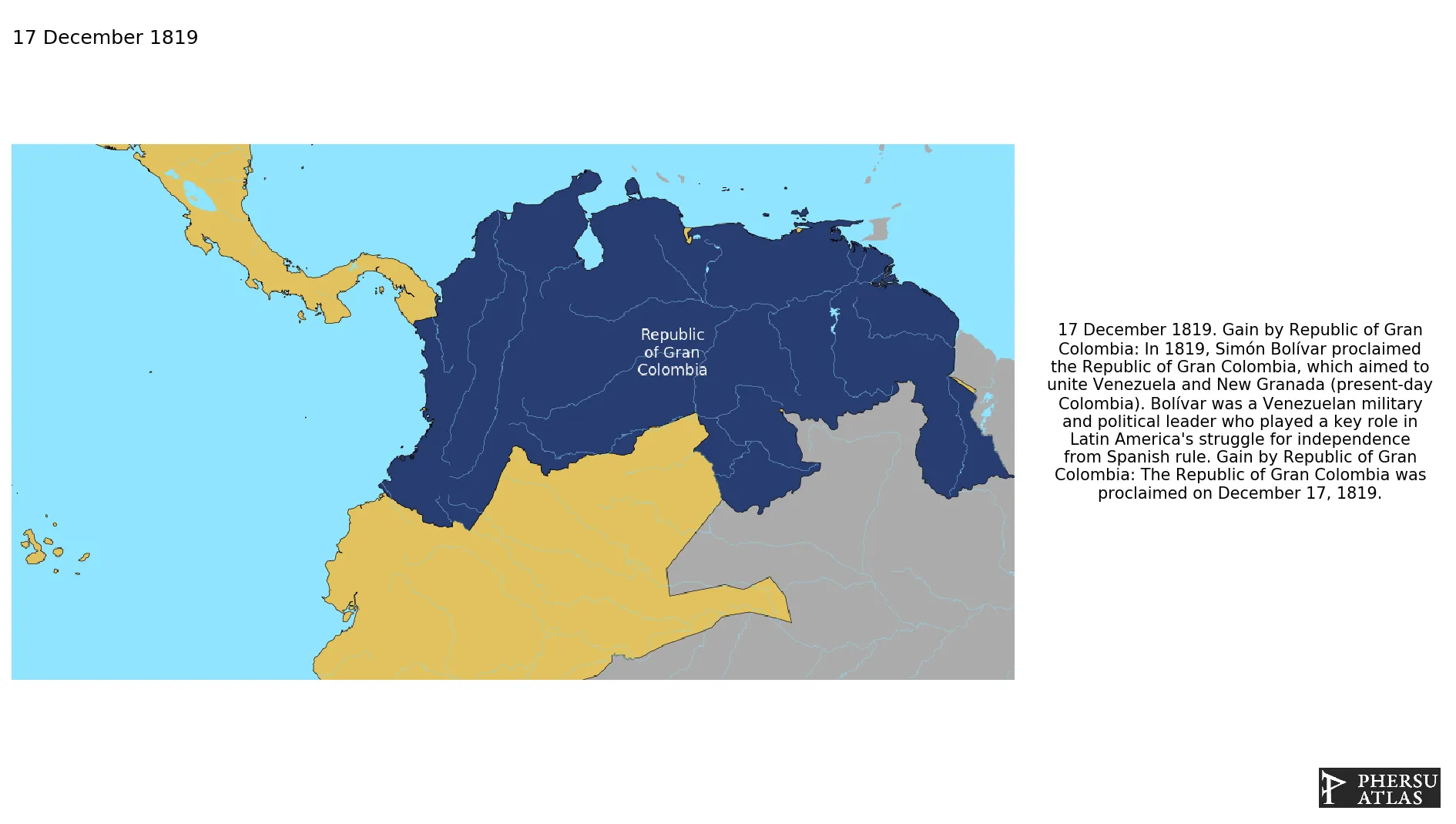
December 1819: In 1819, Simón Bolívar proclaimed the Republic of Gran Colombia, which aimed to unite Venezuela and New Granada (present-day Colombia). Bolívar was a Venezuelan military and political leader who played a key role in Latin America's struggle for independence from Spanish rule.
December 1819: The Republic of Gran Colombia was proclaimed on December 17, 1819.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of independence wars by the Spanish colonies in America that started after the French occupation of mainland Spain during the Napoleonic Wars.
1.1.Bolivian War of Independence
Was the War for indipendence from Spain by Bolivia.
August 1825: In 1825, the territory of Upper Peru declared its independence from Spain and became the Republic of Bolivia under the leadership of Simón Bolívar and Antonio José de Sucre.
1.2.Venezuelan War of Independence
Was the independence war of the Captaincy General of Venezuela against Spanish rule.
1.2.1.Proclamation of Gran Colombia
In 1819 Bolívar proclaimed the Republic Gran Colombia, which he planned to include Venezuela and New Granada.
1.2.1.1.Bolívar's campaign to liberate New Granada
Was a military campaign led by Simon Bolívar, part of the Colombian and Venezuelan wars of independence.
June 1821: Battle of Carabobo.
January 1822: Cumaná conquered by Republic of Gran Colombia.
November 1823: Puerto Cabello managed to resist a siege before finally capitulating to Colombian forces. The city was the last Spanish stronghold in the region.
1.3.Ecuadorian War of Independence
Was fought from 1820 to 1822 between Spain and several South American armies over control of the Royal Audience of Quito, a Spanish colonial jurisdiction which later became the modern Republic of Ecuador.
June 1822: He entered Quito on June 16, 1822. Amid the general enthusiasm of the population, the former Province of Quito was officially incorporated into the Republic of Colombia.
Was a conflict between the Republic of Peru and Gran Colombia caused by the unclear border betwee the two countries.
January 1829: The city of Guayaquil surrendered to Peruvian forces on 19 January 1829.
February 1829: The Peruvian Navy was led by Admiral Martin George Guise, while the Peruvian Army was commanded by General Agustin Gamarra. The Battle of Saraguro was a decisive victory for the Peruvian forces, leading to the military occupation of Loja by the Republic of Peru in 1829.
February 1829: In 1829, during the Gran Colombia-Peru War, forces led by José de La Mar and General Agustín Gamarra occupied Cuenca, a city in present-day Ecuador. This military occupation was part of the Republic of Peru's campaign against Gran Colombia.
February 1829: The Peruvians pushed north into Guayas, the district surrounding the city of Guayaquil.
February 1829: The peruvian invasion was halted with the Battle of Tarqui.
July 1829: Guayaquil was under Peruvian occupation led by General José de La Mar until it was liberated by Simón Bolívar on July 21, 1829, during the Gran Colombia era.
September 1829: The Larrea-Gual Treaty ended the Gran Colombia-Peru War. The treaty restored the status quo ante bellum.
Were a series of armed conflicts between Colombia and Ecuador in the years 1862-1863.
3.1.Ecuadorian acquisition of Colombian territory
Ecuadorian Colonels Garcia and Zamora signed the "Act of Iscuandé" through which they incorporated the canton of Buenaventura into Ecuador.
August 1830: The 23 of August of 1830 Colonels Garcia and Zamora signed the "Act of Iscuandé" through which incorporated the canton of Buenaventura to Ecuador.
January 1831: President Juan José Flores, after sending garrisons to Pasto, visited these cities and issued a decree declaring the former Department of Cauca incorporated into Ecuador.
November 1821: The Isthmus of Panama declared its independence from Spain and decided to voluntarily join Gran Colombia.
January 1822: The area of Panama joined the Republic of Gran Colombia in November 1821.
July 1823: The Federal Republic of Central America declares its independence from the Mexican Empire.
July 1823: The Federal Republic of Central America was established in 1823, consisting of the former territories of the Captaincy General of Guatemala.
May 1830: The Republic of Ecuador was formed in 1830 from the breakup of Greater Colombia.
July 1831: The union of Demerara-Essequibo and Berbice as British Guiana was a result of the British taking control of the Dutch colonies in the region. Demerara was named after the Demerara River, while Essequibo and Berbice were named after the rivers that flowed through them.
November 1831: On November 19, 1831, the federation of Gran Colombia was dissolved in the city of Santa Marta, located in present-day Colombia. The territory that belonged to Gran Colombia was divided into three separate countries: Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela.
Disestablishment
January 1831: President Juan José Flores, after sending garrisons to Pasto, visited these cities and issued a decree declaring the former Department of Cauca incorporated into Ecuador.
July 1831: The union of Demerara-Essequibo and Berbice as British Guiana was a result of the British taking control of the Dutch colonies in the region. Demerara was named after the Demerara River, while Essequibo and Berbice were named after the rivers that flowed through them.
November 1831: On November 19, 1831, the federation of Gran Colombia was dissolved in the city of Santa Marta, located in present-day Colombia. The territory that belonged to Gran Colombia was divided into three separate countries: Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela.


 Republic of Gran Colombia
Republic of Gran Colombia