Conquest of California
Conquest of California
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a revolt against Mexican authority in California, followed shortly after by an invasion by the United States.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
January 1847: Brigadier General Stephen Watts Kearny occupies Los Angeles, ending active resistance to American rule.
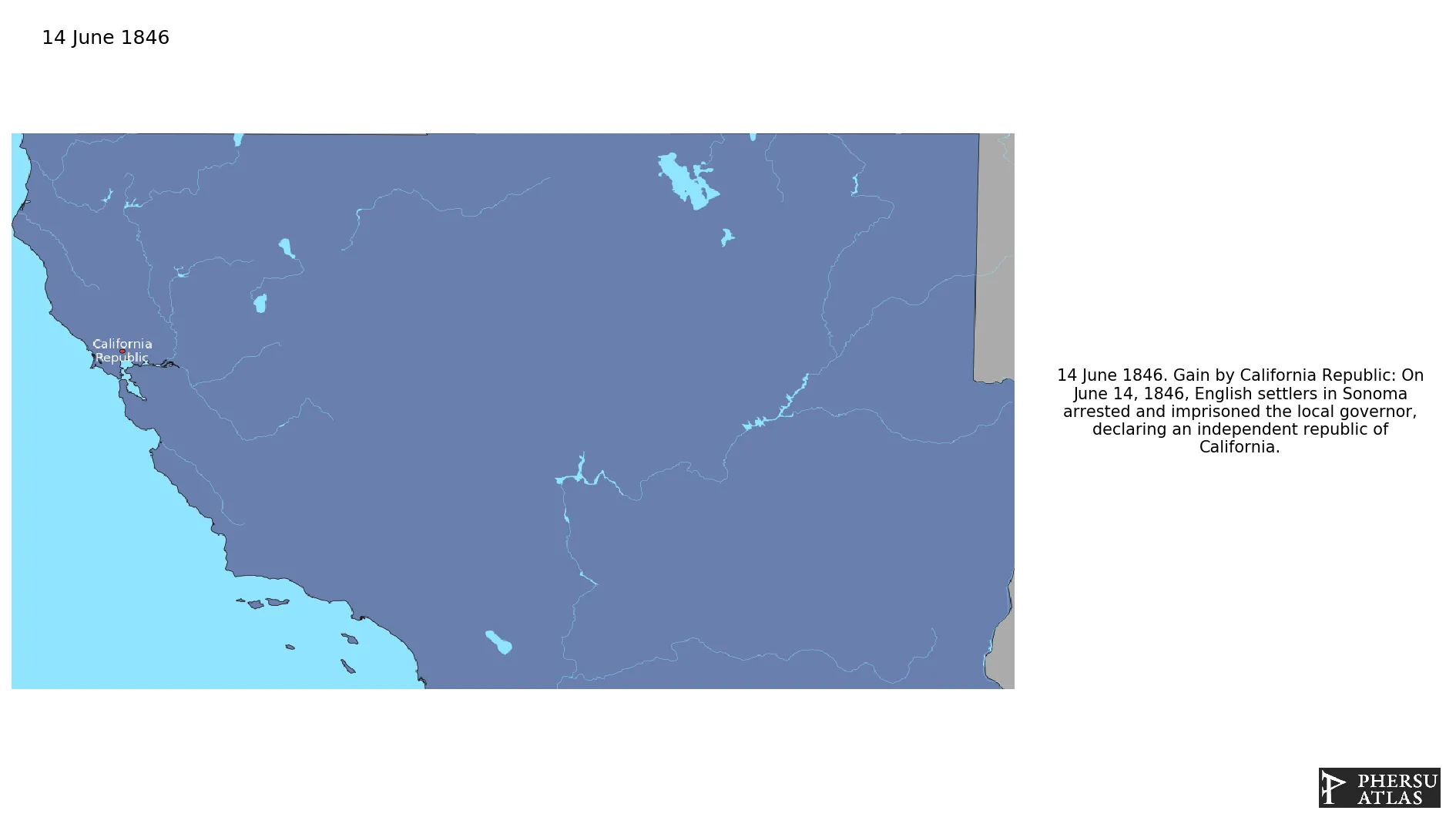
June 1846: On June 14, 1846, English settlers in Sonoma arrested and imprisoned the local governor, declaring an independent republic of California.
July 1846: A garrison of Stockton's men raised the U.S. flag at Santa Barbara.
July 1846: U.S. major John C. Frémont raised the U.S. flag over San Juan Bautista.
July 1846: In 1846, a group of American settlers known as the Osos, led by William B. Ide, peacefully took control of Yerba Buena (now San Francisco) from Mexican authorities during the Bear Flag Revolt in California. This event marked the beginning of the California Republic.
July 1846: U.S. Landing at Monterey where the Americans claim California.
July 1846: The American flag flew above Sutter's Fort and Bodega Bay.
July 1846: Battalion landed and raised the U.S. flag in San Diego.
August 1846: Commodore Robert F. Stockton entered Los Angeles.
December 1846: In 1846, a group of Californians led by William B. Ide seized Lt. Washington Bartlett, who was the acting alcalde of Yerba Buena (now San Francisco). This event was part of the Bear Flag Revolt, a movement to establish an independent California Republic during the Mexican-American War.
December 1846: In 1846, American explorer and military officer John C. Frémont reached Santa Barbara during the Mexican-American War. He raised the American flag after the territory was taken over by the United States.
January 1847: U.S. major John C. Frémont arrived at San Fernando.
December 1846: American General Stephen Watts Kearny's army approached San Pascual.
October 1846: Fifty of Flores' men took San Diego when the small American garrison of less than 20 men retreated. At Santa Barbara, the 10-man U.S. garrison also surrendered the town and escaped under pressure.
January 1847: At a deserted rancho at the north end of Cahuenga Pass, the Treaty of Cahuenga was signed. This unofficial truce, which did not have the backing of the American government and had nothing to do with the Mexican government, was honored by both the Americans and Californios. Fighting ceased, and the United States acquired "Alta California".
January 1847: At Yerba Buena, the Mexican surrendered to American forces.
November 1846: In 1846, General Stephen W. Kearny led a 100-man force during the Mexican-American War. Los Angeles had been taken by Californios led by General José María Flores, a Mexican military officer. Kearny's force learned this information from Mexican herders in the area.
July 1846: Three weeks later, on July 5, 1846, the Republic's military of 100 to 200 men was subsumed into the California Battalion commanded by Brevet Captain John C. Frémont. The Bear Flag Revolt and whatever remained of the "California Republic" ceased to exist on July 9 when U.S. Navy Lieutenant Joseph Revere raised the United States flag in front of the Sonoma Barracks and sent a second flag to be raised at Sutter's Fort.
Selected Sources
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.358
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.359
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.363
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.365
 Conquest of California
Conquest of California