If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the theatre of war in eastern Europe during World War I.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
February 1918: The Soviet Republic of Naissaar was occupied by German forces.
February 1918: The Council of Lithuania declared Lithuania's independence on February 16, 1918. The country was de facto occupied by German troops all the time.
January 1916: During the first year of the war, German and Austrian troops quickly conquered the Russian Vistula Land, the former Congress Poland, and in 1915, divided its administration between a German Governor General in Warsaw and an Austrian counterpart in Lublin.
December 1917: With the fall of Nicholas II, many parts of the Russian Empire took the opportunity to declare their independence, one of which was Finland, which did so in December 1917.
January 1918: Following the Russian Revolution in 1917, Estonia declared independence. However, German forces occupied the territory shortly after, with General Rüdiger von der Goltz leading the military administration.
February 1915: Russian advancement on the Eastern front by 7th February.
November 1918: On 4 June 1918, the Lithuanian parlament voted to offer the Lithuanian throne to the German noble Wilhelm Karl, Duke of Urach. He accepted the offer in July 1918 and took the regnal name Mindaugas II. However, the Kingdom of Lithuania was officially dissolved in November 1918.
September 1917: The Germans attacked and captured Riga.
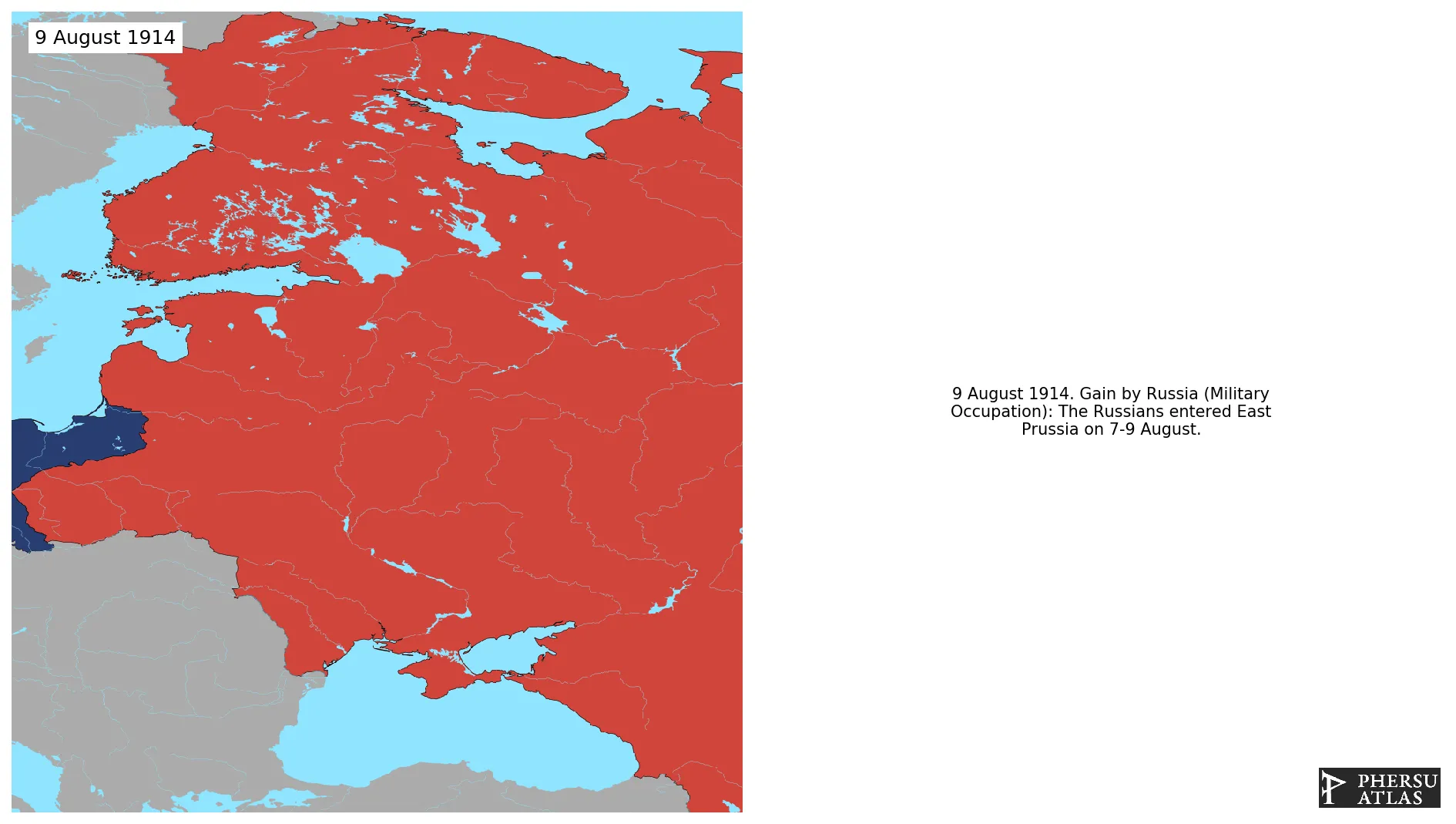
Was the Russian invasion of East Prussia in the early phases of World War I.
August 1914: The Russians entered East Prussia on 7-9 August.
August 1914: The Battle of Gumbinnen, started by the Germans, was the first major offensive on the Eastern Front during the First World War.
August 1914: Battle of Stallupönen, fought between Russian and German armies on 17 August 1914, was the opening battle of World War I on the Eastern Front.
August 1914: Movement of Russian troops during the Battle of Tannenberg.
September 1914: The First Battle of the Masurian Lakes in 1914 was a significant military engagement during World War I. It was led by German generals Paul von Hindenburg and Erich Ludendorff, resulting in a decisive victory over the Russian forces and pushing them out of East Prussia.
September 1914: Part of Russia on the border with East Prussia invaded by German forces.
Was a major battle between Russia and Austria-Hungary during the early stages of World War I. The Austro-Hungarian armies were severely defeated and forced out of Galicia.
November 1914: Front at the Battle of Lodz.
August 1914: Battle of Komarow.
August 1914: Battle of Gnila Lipa won by Russia.
September 1914: Avancement into Galica by Russia.
December 1914: After the battle of Lodz in 1914, the Eastern Front of World War I stabilized between the cities of Lodz and Warsaw.
August 1914: The Austro-Hungarian 1st Army under Viktor Dankl moved in the north towards Lublin. Battle of Kraśnik.
September 1914: Battle of Rawa won by Russia.
Was the northern part of the Central Powers' offensive on the Eastern Front in the winter of 1915.
February 1915: German advance in Prussia with the Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes.
The Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive during World War I was initially conceived as a minor German offensive to relieve Russian pressure on the Austro-Hungarians to their south on the Eastern Front, but resulted in the Central Powers' chief offensive effort of 1915, causing the total collapse of the Russian lines and their retreat far into Russia.
May 1915: The Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive during World War I was initially conceived as a minor German offensive to relieve Russian pressure on the Austro-Hungarians to their south on the Eastern Front, but resulted in the Central Powers' chief offensive effort of 1915, causing the total collapse of the Russian lines and their retreat far into Russia.
September 1915: Border changes during the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive.
August 1915: Border changes during the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive.
June 1915: Border changes during the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive.
June 1915: The Russians abandoned Galicia.
July 1915: Border changes during the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive.
Was a major Russian offensive against the Central Powers during World War I.
September 1916: Russian conquests of the Brusilov Offensive.
June 1916: Russian conquests of the Brusilov Offensive.
July 1916: Russian conquests of the Brusilov Offensive.
Romanian theatre of World War I.
May 1918: Romania signed a formal peace treaty with the Central Powers, the Treaty of Bucharest of 1918. Romania ceded the Carpathian mountain passes to Austria-Hungary. The central powers evacuated the remnant territories of Romania.
February 1917: With the Romanian Army in full control, on 24 January/6 February, the Moldavian Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence.
May 1918: Dobruja falls under the administration of the Central Powers.
May 1918: Everything below Constanța was annexed by Bulgaria.
November 1918: On November 10 Romania declared war once again to the Central Powers.
6.1.Battle of Transylvania
Was the first major operation of Romania against Austria-Hungary during World War I.
6.2.Counteroffensive of the Central Powers in Romania
Was a counteroffensive of the Central Powers in Romania.
6.3.Romanian military intervention in Bessarabia
Was a Romanian intervention in Bessarabia during the Russian Civl War.
April 1918: Bessarabia, which had declared itself as the Moldavian Democratic Republic in 15 December, united with Romania on 9 April 1918.
January 1918: The Front Section of the Rumcherod Bolsheviks entered Chișinău. The Moldavian legislative council Sfatul Țării requested military assistance from Romania. On 26 January, the Romanian Army captured Chișinău.
February 1918: With the help of Moldavia's improvised combat units, the Romanians pacified Hotin, Ismail, Tighina and Cetatea Albă. The last detachments of Communist revolutionaries were driven over the Dniester and out of the country on 20 February.
Was the last Russian offensive of World War I. Starting on July 1, 1917 the Russian troops attacked the Austro-Germans in Galicia, pushing toward Lviv.
July 1917: The Russian line collapsed altogether by July 16. On the 18th the Austro-Germans counterattacked, meeting little resistance and advancing through Galicia and Ukraine until the Zbruch River.
July 1917: The Russians retreated about 240 kilometers in the territory of modern-day Ukraine.
July 1917: In the last Russian offensive of World War I, the Russian troops attacked the Austro-Germans in Galicia, pushing toward Lviv.
Was a Central Powers offensive in World War I. It was the last major action on the Eastern Front. The northern force, consisting of 16 divisions, captured the key Daugavpils junction on the first day.
February 1918: Minsk was captured by the Central Powers together with the headquarters of the Western Army Group.
February 1918: The Southern forces broke through the remains of the Russian Southwestern Army Group, capturing Zhitomir on 24 February.
February 1918: The northern force, consisting of 16 divisions, captured the key Daugavpils junction.
February 1918: Daugavpils conquered by Austrian and German forces.
February 1918: The Central Powers captured Pskov and secured Narva.
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Brest Peace in Russia) was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918, between the new Bolshevik government of Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's participation in World War I.
March 1918: The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918, between the new Bolshevik government of Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's participation in World War I.
March 1918: Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia declared independence as the Transcaucasian Commissariat.
March 1918: On March 3, the Ottoman Grand vizier Talat Pasha signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with the Russian SFSR. Bolshevik Russia ceded Batum, Kars, and Ardahan to the Ottomans, which the Russians had captured during the Russo-Turkish War (1877-1878).
March 1918: Ukraine signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk to obtain military help from the German and Austro-Hungarian Empires. Germany helped the Ukrainian Army force the Bolsheviks out of Ukraine. By April the German-Austrian Operation Faustschlag offensive had completely removed the Bolsheviks from Ukraine. Thus Germany was able to made entire Ukraine a protectorate.
9.1.Consequences of Brest-Litovsk Treaty in Latvia
Was the reorganization of Latvia after the Brest-Litovsk Treaty.
Where the administrative changes of Belarus during World War I and the Russian Civil War.
March 1918: The Belarusian People's Republic was declared on March 9, 1918, in Minsk, by the members of the Executive Committee of the First All-Belarusian Congress, and two weeks later, on March 25, 1918, it proclaimed independence.
January 1919: With the founding of the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR) on January 1, 1919, the Belarusian People's Republic lost importance and the government went into exile.
July 1920: The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed on July 31st, 1920 in the parts of Belarus controlled by the Soviets.
Selected Sources
The Brusilov Offensive, 1 May - 20 September 1916. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://www.westpoint.edu/sites/default/files/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWI/WWOne35.jpg
Treaty of Bucharest (1918), https://web.archive.org/web/20130223024635/http://www.mtholyoke.edu/acad/intrel/routreat.html
 World War I eastern Front
World War I eastern Front