If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
The eastern theater of the American Civil War consisted of the major military and naval operations in the states of Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, and Pennsylvania, the District of Columbia, and the coastal fortifications and seaports of North Carolina.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
May 1862: Battle of Princeton Court House. Witthdrawal of Union General Jacob Dolson Cox.
October 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Buckland Mills. Union cavalry caught in ambush, defeated.
October 1863: First Battle of Auburn. Inconclusive.
November 1863: Union troop retreat after the First Battle of Auburn.
November 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Buckland Mills.
November 1864: Union troop retreat after the First Battle of Saltville.
May 1863: Battle of Salem Church. Confederate General Lee defeats Sedgwick.
October 1863: Battle of Bristoe Station. Meade defeats elements of Lee's forces, but Confederates destroy railroad during retreat.
September 1862: Battle of Charleston. Confederate troops occupy Charleston during Kanawha Valley offensive.
December 1861: Battle of Dranesville. Union defeats Confederate forces under J.E.B. Stuart.
February 1862: Battle of Elizabeth City. Union victory.
June 1862: After suffering a defeat at the Battle of Bull Run in 1862, Union forces under the command of General Irvin McDowell did not pursue the Confederate Army and instead retreated back to their fortifications in Washington.
April 1864: Battle of Plymouth. Confederate land forces, supported by naval ram, retake two Union forts near Plymouth, North Carolina.
May 1863: Second Battle of Fredericksburg. Union forces under John Sedgwick defeat Confederate forces left to guard the town by Lee.
December 1861: In 1861, during the American Civil War, General John E. Wool led 4,000 Federal troops to secure the Eastern Shore of Virginia for the Union. This strategic move helped solidify Union control over the region and prevent Confederate forces from gaining a foothold.
November 1863: Second Battle of Rappahannock Station. Union forces surge across river, forcing Lee to retreat.
June 1862: Battle of Gaines' Mill or Chickahominy River. Confederate General Robert E. Lee defeats Union General George B. McClellan.
July 1861: Battle of Hoke's Run. Robert Patterson defeats Jackson's Confederates but fails to capitalize on his victory.
February 1862: The town of Edenton in the proximity of Elizabet City (North Carolina) was taken by Union troops without bloodshed.
March 1862: Union general Nathaniel P. Banks occupied Winchester just after Confederate general Stonewall Jackson had withdrawn from the town.
April 1862: Battle of Fort Macon. Confederate fort surrenders after Union artillery bombardment.
June 1862: Although the city of Norfolk was not under attack, it was isolated and increasingly worthless to the Confederate Army. In May, the city was abandoned.
June 1862: Battle of Tranter's Creek. Confederate forces retreat after Colonel Singletary is killed.
March 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Kelly's Ford.
May 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Suffolk (Hill's Point). Inconclusive.
June 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Suffolk (Hill's Point).
July 1863: Battle of Manassas Gap. Indecisive battle by day, Confederates withdraw by night.
October 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Auburn. Confederates attack Union rearguard, indecisive.
November 1863: Union troop retreat after the Second Battle of Auburn.
December 1863: Battle of Mine Run. Meade bombards Lee's Confederates.
January 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Mine Run.
March 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Walkerton. Confederate victory.
April 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Walkerton.
August 1864: Battle of Smithfield Crossing. Confederate forces routed a small Union detachment, but a Union counterattacked stopped the Confederates; ultimately ending the last engagement in West Virginia of the Civil War.
October 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Saltville. Confederates defeat Union Black Cavalry, war crimes committed against captured blacks.
December 1864: Battle of Marion. Union victory.
October 1864: Battle of Boydton Plank Road. Union forces take control of road.
August 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Manassas Gap.
September 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Smithfield Crossing.
March 1862: Battle of New Bern. Union troops disembark from ships and capture the town.
October 1861: Battle of Cockle Creek. Union victory.
Was a military campaign of Union in the western part of Virginia. The region was conquered and later became the state of West Virginia.
September 1861: Battle of Carnifex Ferry. Union victory. Confederates withdraw by night after several hours of fighting.
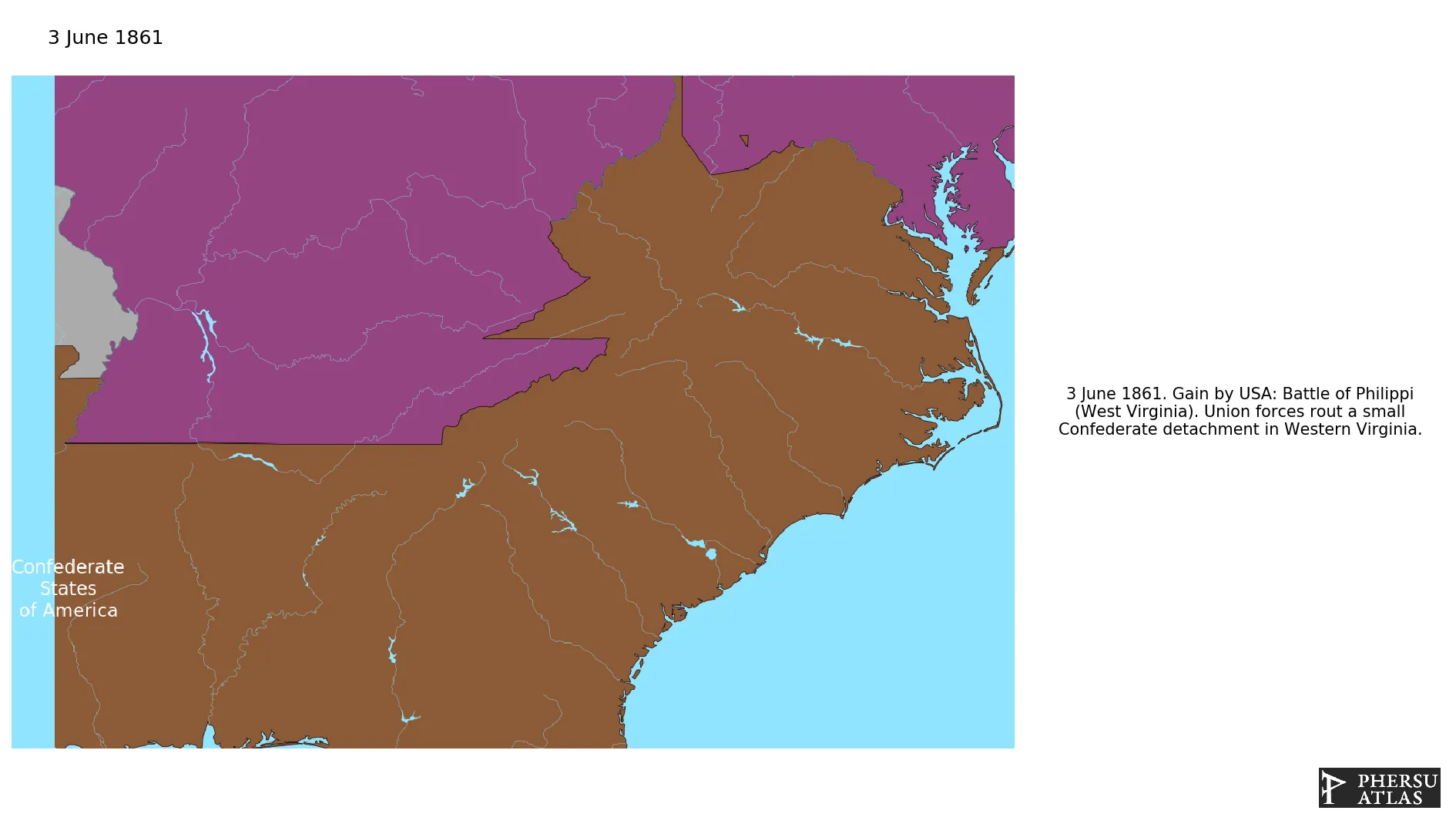
June 1861: Battle of Philippi (West Virginia). Union forces rout a small Confederate detachment in Western Virginia.
July 1861: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Rich Mountain.
August 1861: Battle of Kessler's Cross Lanes. Confederates under John B. Floyd surprise and defeat Union forces under Erastus B. Tyler.
October 1861: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Greenbrier River. Confederates withdraw after inconclusive battle.
July 1861: Battle of Corrick's Ford: Control of western Virginia was now firmly in Union hands and it stayed that way for the rest of the war.
Were a series of military operations by the Union in North Carolina during the American Civil War.
February 1862: Battle of Roanoke Island. Union forces under Ambrose E. Burnside capture island from Henry A. Wise
February 1865: Battle of Wilmington (North Carolina). Last Confederate port falls.
August 1861: Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries: Two forts on the Outer Banks (Fort Clark and Fort Hatteras) had been built by the Confederates. The Union retained both forts.
January 1865: Second Battle of Fort Fisher. Union takes fort.
Was a Confederate raid in Virginia during the American Civil War.
January 1862: Battle of Hancock. Unsuccessful Confederate attack on Maryland town.
February 1862: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Hancock.
Was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March to July 1862 during the American Civil War.
March 1862: Union General George B. McClellan landed his army at Fort Monroe.
April 1862: The IV Corps of Brig. Gen. Erasmus D. Keyes made initial contact with Confederate defensive works at Lee's Mill, an area McClellan expected to move through without resistance.
May 1862: General George B. McClellan’s Army of the Potomac occupies the Yorktown-Warwick River line recently abandoned by Confederate forces.
May 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Williamsburg.
May 1862: Battle of Seven Pines: the union army reached the outskirts of Richmond.
July 1862: After suffering heavy casualties at the Battle of Malvern Hill, General George McClellan ordered the Army of the Potomac to retreat to Harrison's Landing on the James River in Virginia in 1862 during the American Civil War. This move was seen as necessary to regroup and resupply the Union forces.
August 1862: General George B. McClellan received the order to retreat from the Virginia Peninsula in 1862 during the American Civil War.
Was a Confederate campaign through the Shenandoah Valley in Virginia during the American Civil War.
March 1862: First Battle of Kernstown. Union forces defeat Confederates under "Stonewall" Jackson.
May 1862: First Battle of Winchester: Jackson enveloped the right flank of the Union Army under Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks and pursued it as it fled across the Potomac River into Maryland.
Was a series of battles fought in Virginia during August and September 1862 in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.
August 1862: General Stonewall Jackson remained in position until August 12, 1862, when he withdrew to Gordonsville during the American Civil War. This retreat was part of his strategic movements in Virginia against the Union forces.
August 1862: In 1862, during the American Civil War, Union General John Pope withdrew his forces to the Rappahannock River, thwarting Confederate General Robert E. Lee's plans for an offensive. This strategic move led to the Second Battle of Bull Run.
Was a Confederate campaign in Maryland during the American Civil War.
September 1862: Battle of Harpers Ferry. Stonewall Jackson captures Union garrison under Dixon S. Miles
September 1862: Battle of Antietam or Sharpsburg. Union General McClellan ends Lee's first invasion of North, bloodiest single day of the war.
September 1862: On September 4 Confederate General Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia
had begun an invasion of the North. Lee hoped to cut key rail lines west and isolate Washington, with Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, as his probable objective. By September 16th Lee's army took position in Sharpsburg, Maryland.
September 1862: Battle of Shepherdstown. Confederate victory.
April 1863: The Chancellorsville Campaign began in 1863 with General Joseph Hooker leading the Union army across the Rappahannock River into Confederate territory in the border regions south to the Rapidan River.
May 1863: Battle of Chancellorsville. Confederate General Lee defeats Hooker's Army of Potomac.
September 1862: Frederick conquered by Confederate States of America.
Were a series of military operations part of the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.
December 1862: Battle of Goldsboro Bridge. General Foster defeats Confederates and destroys the bridge.
December 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of White Hall.
December 1862: Battle of Kinston. Union forces under John G. Foster defeat Confederates under Nathan Evans.
January 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of White Hall.
Was a military invasion of Pennsylvania by the main Confederate army under General Robert E. Lee in summer 1863.
July 1863: General George Meade led the Union Army of the Potomac, while General Robert E. Lee commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia during the American Civil War. Lee's successful retreat across the Potomac River after the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863 marked a turning point in the war.
June 1863: On June 26, elements of Confederate Maj. Gen. Jubal Early's division of Ewell's Corps occupied the town of Gettysburg after chasing off newly raised Pennsylvania militia in a series of minor skirmishes.
June 1863: CSA forces occupied Westminster, Maryland.
August 1863: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Williamsport.
July 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Carlisle. Inconclusive.
July 1863: Battle of Williamsport. Indecisive.
June 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Donaldsonville. Inconclusive.
June 1863: On June 28, 1863, a Civil War skirmish between Confederate and Union armies took place at Wirghtsville, Pennsylvania.
June 1863: General J.E.B. Stuart and an army of 8,000 Confederate cavalrymen occupied Rockville on June 28, 1863, while on their way to Gettysburg.
June 1863: General Jubal Early's Confederate Division occupied York, Pennsylvania. This was significant as York was the largest Northern town to fall to the Confederates during the war.
July 1863: Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart led his troops to Carlisle, Pennsylvania in June 1863 during the Gettysburg Campaign. After a brief skirmish and burning the Carlisle Barracks, Stuart retreated to Gettysburg where the decisive Battle of Gettysburg would take place.
July 1863: Battle of Fairfield.Cavalry engagement won by the Confederate army during the Gettysburg Campaign secured the important Hagerstown Road.
July 1863: Battle of Gettysburg: The defeat of his massive infantry assault, Pickett's Charge, caused Lee to order a retreat that began the evening of July 4.
July 1863: Battle of Boonsboro. Indecisive action at rearguard of Lee's retreat.
June 1863: By June 29, Confederate General Lee's army was strung out in an arc from Chambersburg (45 km northwest of Gettysburg) to Carlisle (48 km north of Gettysburg) to near Harrisburg and Wrightsville on the Susquehanna River.
June 1863: Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart's cavalry reached Fairfax Court House in 1863. They were delayed by a small battle on June 27, part of the Gettysburg Campaign during the American Civil War.
Were a series of military operations part of the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.
February 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Morton's Ford. Inconclusive.
March 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Morton's Ford.
A series of battles fought in Virginia during May and June 1864, in the American Civil War.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of North Anna. Inconclusive.
June 1864: Battle of Cold Harbor. Confederate General Lee repulses Grant.
May 1864: Battle of Spotsylvania Court House. Grant and Lee meet inconclusively, Grant writes to Halleck "I propose to fight it out on this line if it takes all summer".
May 1864: General Ulysses S. Grant's forces crossed the Rapidan River.
May 1864: Battle of Yellow Tavern. Union forces win cavalry battle, Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart is mortally wounded.
May 1864: Battle of Haw's Shop. Union advance.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of the Wilderness. Grant and Lee meet inconclusively.
Was a series of battles fought at the town of Bermuda Hundred, outside Richmond, Virginia, during May 1864 in the American Civil War.
May 1864: Battle of Ware Bottom Church. Confederate victory.
June 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Ware Bottom Church.
June 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Proctor's Creek.
June 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Swift Creek.
May 1864: Battle of Port Walthall Junction. Union forces destroy railroad.
May 1864: Battle of Swift Creek. Union forces damage railroad, but are stopped by Confederate forces.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Chester Station. Union forces under Benjamin Butler pushed back.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Proctor's Creek. Confederate Beauregard defeats Butler.
Was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War.
August 1864: Battle of Globe Tavern. Confederate forces lose control of railroads at Petersburg.
June 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Petersburg. Confederate Beauregard defeats Butler.
October 1864: Battle of Peebles' Farm. Union victory near Petersburg.
Were a series of American Civil War battles fought March 29 - April 9, 1865, in Virginia that concluded with the surrender of Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia to the forces of the Union Army.
April 1865: Battle of Appomattox Court House. Confederate General Lee's forces surrounded. He subsequently surrenders.
April 1865: Battle of Sutherland's Station. Union victory.
April 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Amelia Springs. Inconclusive.
April 1865: Battle of Rice's Station. Confederate forces are caught off guard by John Gibbon's forces.
April 1865: Third Battle of Petersburg. Union General Grant defeats Lee.
April 1865: Battle of High Bridge. Union forces thwart Lee's attempts to burn bridges and to resupply, Grant proposes that Lee surrender, but he refuses.
Selected Sources
Battle History. Gettysburg Pensylvania Historic Crossroads. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.gettysburgpa.gov/history/slideshows/battle-history
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.457
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.466
List of American Civil War battles. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 31 March 2024 on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_American_Civil_War_battles
Rockville. The Historical Marker Database. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.hmdb.org/m.asp?m=174764
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.337
Wrightsville. The Historical Marker Database. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.hmdb.org/m.asp?m=171286
 Eastern Theatre (American Civil War)
Eastern Theatre (American Civil War)