Gallic Wars
Gallic Wars
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Roman military campaign under general Julius Caesar that resulted in the conquest of transalpine Gaul (modern-day France, Switzerland and Belgium).
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
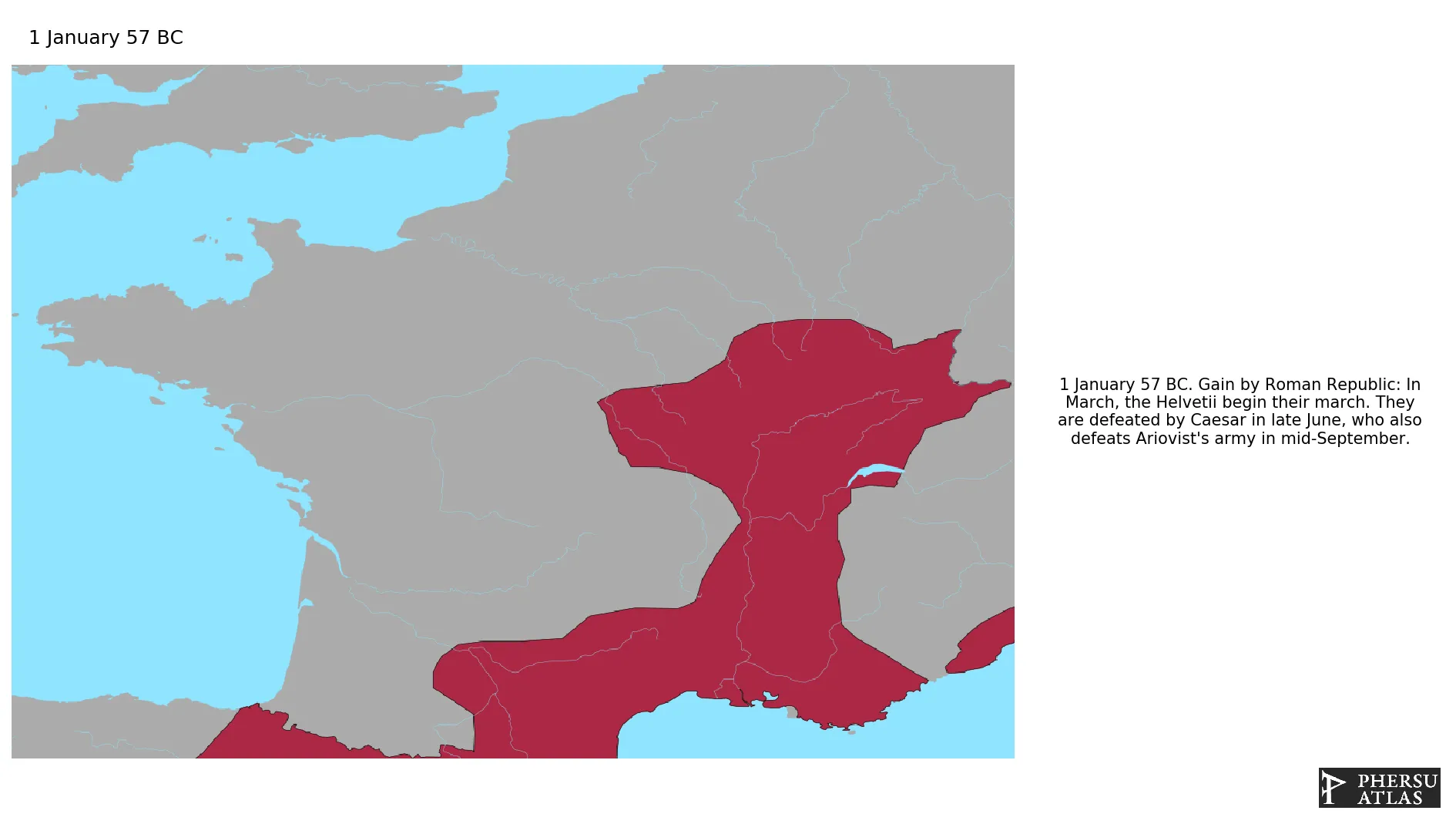
January 57 BC: In March, the Helvetii begin their march. They are defeated by Caesar in late June, who also defeats Ariovist's army in mid-September.
January 56 BC: Campaigns against the Belgae.
January 56 BC: Although there is no evidence of a Roman occupation of Jersey, historians consider that it is entirely feasible it was occupied by the Romans. Various Roman archeological artefacts have been found on the island, such as coins discovered on the north coast at Ile Agois. There are several sites attributed to the Romans on the island, such as Caesar's fort at Mont Orgeuil. By 57 BC, Caesar had resolved to conquer all of Gaul.
January 52 BC: Roman punitive expedition to the Belgica. Devastation of the tribal area of the Eburones.
January 50 BC: Successful Roman military operations, organized Gallic resistance largely collapses.
January 55 BC: The tribes of the Menapi and Morini in north-eastern Gaul resisted the Romans, who undertook successful campaigns in Aquitaine and the area of modern-day Normandy. Caesar's command is extended by five years.
January 53 BC: Second Britain Expedition. In November: Uprising of the Eburones under Ambiorix and crushing defeat of Roman units at Aduatuca.
January 51 BC: At the beginning of the year, the Gallic uprising breaks out. In spring/summer, Avaricum falls to the Romans, who are also successful against the Parisii. Gallic victory at Gergovia, but this is followed by the successful Roman siege of Alesia: Vercingetorix capitulates at the end of September.
 Gallic Wars
Gallic Wars