Italian Front (Second Punic War)
Italian Front (Second Punic War)
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the Carthaginian military campaign in the Italian Peninsula led by General Hannibal during the Second Punic War.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
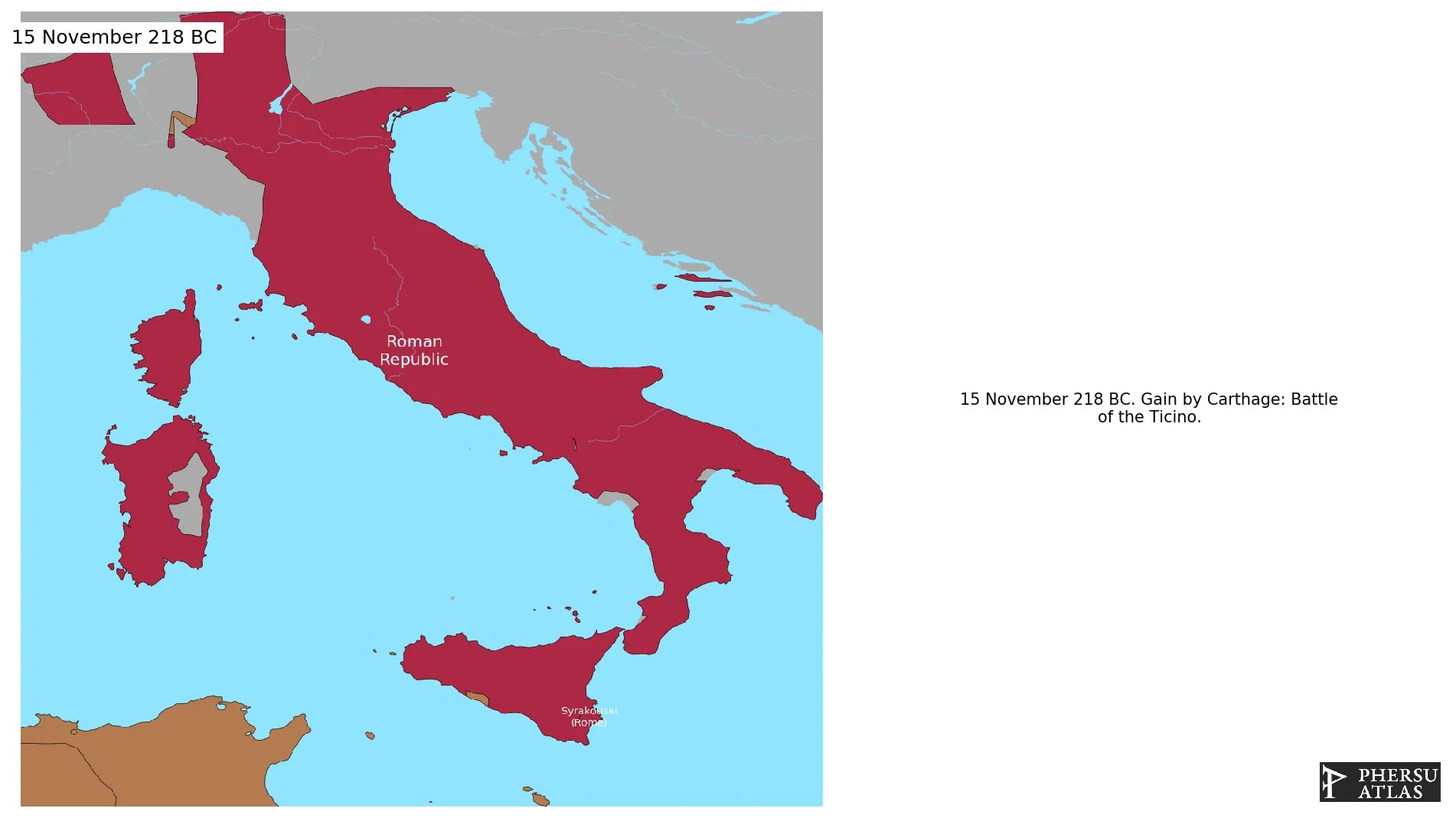
November 218 BC: Battle of the Ticino.
January 217 BC: The first military action consisted in conquering the Punic stronghold of Melita, which immediately surrendered without a fight.
January 217 BC: The Romans dedicated themselves to the fortification of the cities of Cisalpine Gaul and ordered the colonists, 6,000 for each new city to be founded, to be in the established place within thirty days. The first of the colonies was founded on the Po river and was called Placentia, the other was located north of the river and called Cremona.
January 217 BC: Battle of Trebbia.
June 217 BC: Battle of Lake Trasimeno. Victory of Carthage.
June 217 BC: In -217, Hannibal, a Carthaginian military commander, continued his march through Italy and reached the territories of Luceria and Argos Hippium. These areas were plundered by his soldiers as part of his campaign during the Second Punic War against Rome.
July 217 BC: Battle of Lake Trasimeno.
July 217 BC: In -217, Hannibal, a Carthaginian military commander, led his troops to plunder the territories of Luceria and Argos Hippium in Apulia. This marked a significant advance in his campaign against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
January 216 BC: Returning to Italy, Servilius contented himself with reoccupying Pantelleria which had fallen into Carthaginian hands.
August 216 BC: In the Battle of Cannae on August 2, 216 BCE, Hannibal Barca’s Carthaginians destroyed two Roman armies in perhaps the most famous double envelopment in history.
September 216 BC: Hannibal lost between 3,000 and 6,000 men at Canne but achieved, after the crushing victory, the first important political-strategic results. Some centers began to abandon the Romans. Hannibal sent his brother Magone south to Bruttium with part of his forces, while he and the bulk of the army headed to Campania where he managed to obtain the defection of Capua after a series of negotiations.
September 216 BC: In -216, after the Battle of Cannae, Hannibal sent his lieutenant Annone to Bruzio in Calabria to secure the territory for Carthage. The Bruttians, a local tribe, supported the Carthaginians in their uprising against Roman control.
September 216 BC: The Carthaginian army left the area of Cannae after the battle.
November 216 BC: Siege of Nuceria Alfaterna.
January 215 BC: Battle of the Selva Litana.
April 215 BC: During the Second Punic War, the Carthaginian general Hannibal besieged and captured the important center of Casilinum in -215. This victory was part of Hannibal's campaign to conquer Roman territory in Italy.
April 212 BC: Battle of Tarentum. Carthaginian General Hannibal conquers Tarentum.
December 212 BC: The support of Syracuse for Carthage provokes the Roman siege of the city. Rome conquers Syracuse and its territories.
January 211 BC: The first battle of Herdonia was fought in 212 BC, during the Second Punic War, between the Carthaginian army of Hannibal and the Roman army. The Carthaginians defeated the Romans and occupid Apulia.
January 209 BC: Siege of Agrigento.
January 208 BC: The siege of Taranto in 209 BC led to the reconquest of the city, and its port, by the Romans.
June 207 BC: The battle of the Metauro ended with the complete victory of Rome; the Carthaginian army was destroyed and Hasdrubal fell fighting in the field. Hannibal learned of his brother's tragic fate only when Hasdrubal's head was thrown into his camp by the Romans. He decided to abandon Apulia and Lucania again and return to Bruzio. The battle confirmed Roman supremacy over Italy. Without Hasdrubal's army to support him, Hannibal was forced to evacuate pro-Carthaginian cities across much of southern Italy and retreat to Bruttium.
January 204 BC: Scipio Africanus, a Roman general, successfully recaptured the port of Locri from Hannibal, the Carthaginian military commander, in -205. This victory was a significant blow to Hannibal's forces during the Second Punic War.
January 202 BC: After the Roman victories at the Campi Magni, the Carthaginian Senate, seeing that the city was practically defenseless, ordered the remnants of the two armies operating outside Africa, that of Hannibal and that of Mago, to return to defend their homeland. The two generals thus left the territories occupied in Liguria and Calabria.
January 201 BC: During the Second Punic War, Ankon sided with the Romans against the Carthaginians, sending numerous soldiers.
September 216 BC: The Piganiol in fact writes that Hannibal, after having obtained the alliance of Daunia, excluding Lucera, and of the Samnites of the most impervious regions, also secured that of Capua, to which the Carthaginian promised the autonomy of the city and to place it at the head of the Italian confederation, replacing it in Rome.
December 217 BC: The Carthaginians eventually settled in the territory of Geronio where an entrenched camp was built.
December 218 BC: Battle of Trebbia.
January 217 BC: In the year 217 BC the new consuls, Gneo Servilio Gemino and Gaio Flaminio with the four consular legions and allies, around 50,000 men in all, marched towards Rome. The remains of the two legions of Sempronio Longo, strengthened by new elements and by allies of Syracuse, stopped to garrison Etruria under the leadership of Flaminio and two other legions under the command of Servilius Gemino stood at Rimini, the northern border of the peninsula. Rome was abandoning Cisalpine Gaul where it had just begun to enter.
January 209 BC: Magone landed and conquered Genoa.
January 217 BC: Hannibal's diplomacy in Cisalpine Gaul pushed the Gauls Boi and Insubri to revolt. These drove the settlers from Piacenza.
January 217 BC: Siege of Modena.
December 218 BC: Battle of the Ticino.
March 217 BC: Battle of Piacenza.
February 217 BC: Battle of Piacenza.
May 215 BC: During the Second Punic War, the Carthaginian general Hannibal besieged Casilinum, a strategic center in Italy. The Roman Republic eventually lost control of the territory to Hannibal after a prolonged siege lasting from late 216 to early 215 BC.
Selected Sources
Eutropio, Breviarium ab Urbe condita, III, 8-9
Eutropio, Breviarium ab Urbe condita, III, 13-14
Eutropio, Breviarium ab Urbe condita, III, 14
Eutropio, Breviarium ab Urbe condita, III, 14, 16
Eutropio, Breviarium ab Urbe condita, III, 18
Livio, Ab Urbe condita libri, XXVI, 47
Polibio, III, 74, 79
Strabone, Geografia, V, 2,9
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.49
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.52
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.55
 Italian Front (Second Punic War)
Italian Front (Second Punic War)