Italo-Ethiopian Wars
Italo-Ethiopian Wars
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Were two invasion of Ethiopia by the Kingdom of Italy whose goal was to make Ethiopia a colony. The first invasion was not succesful, but after the second invasion Ethiopia became part of of Italian East Africa.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was an ultimately unsuccesful Italian invasion of Ethiopia.
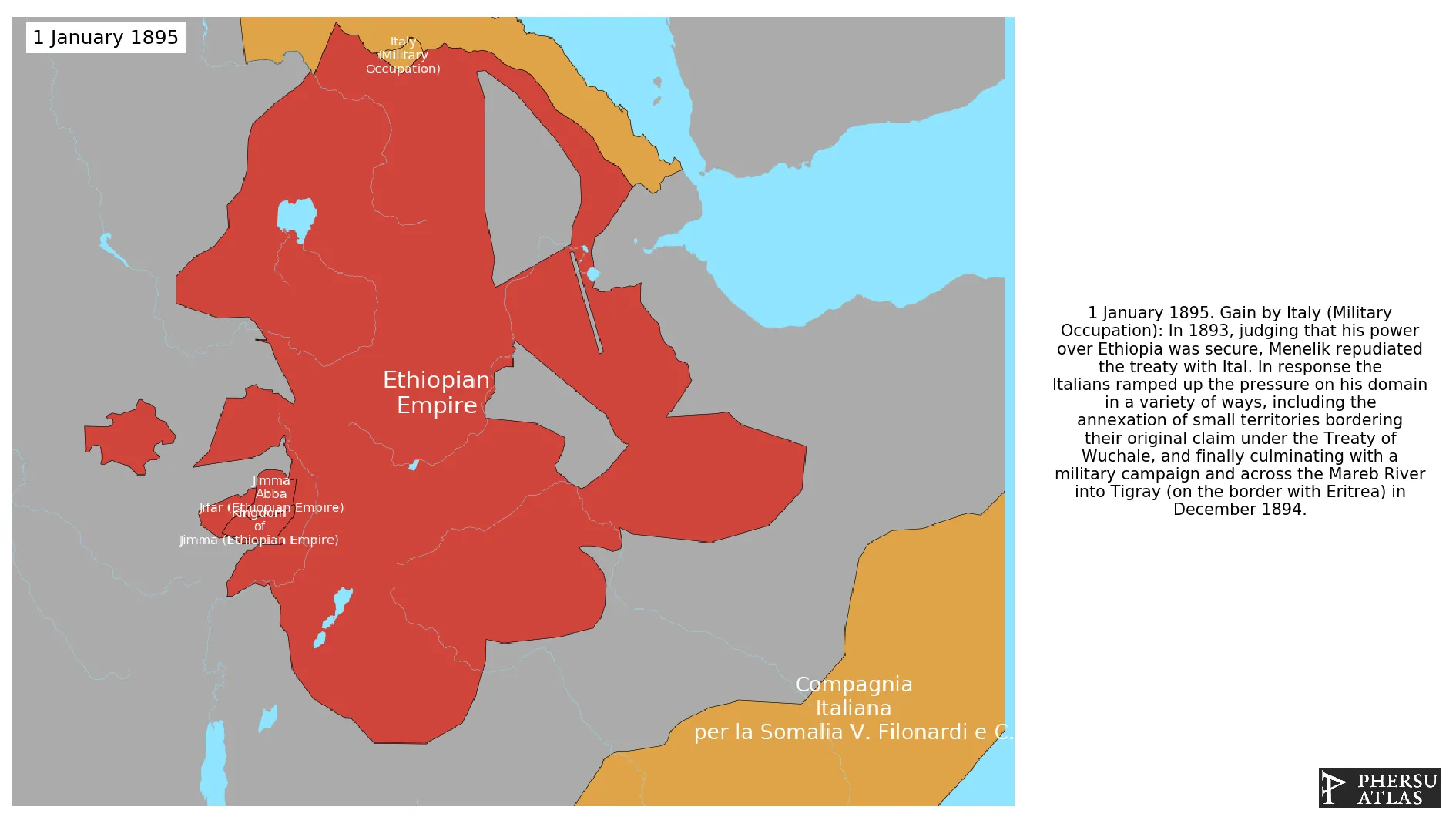
January 1895: In 1893, judging that his power over Ethiopia was secure, Menelik repudiated the treaty with Ital. In response the Italians ramped up the pressure on his domain in a variety of ways, including the annexation of small territories bordering their original claim under the Treaty of Wuchale, and finally culminating with a military campaign and across the Mareb River into Tigray (on the border with Eritrea) in December 1894.
January 1895: Battle of Coatit.
January 1895: In 1895, the Italians achieved a significant victory in Quatit, Italian Eritrea, by successfully repelling an invasion force led by Ethiopian Emperor Menelik II. This victory solidified Italian control over the territory and marked a turning point in the First Italo-Ethiopian War.
December 1895: In 1895, during the First Italo-Ethiopian War, Italian General Giuseppe Arimondi led his troops to the unfinished Italian fort in Mekele, Ethiopia. This marked Italy's military occupation of the territory.
January 1896: Battle of Mekelle.
March 1896: Battle of Adwa.
December 1895: Battle of Amba Alagi.
October 1895: Amba Alagi is temporarily occupied, as part of the Italian invasion of Tigray, on 13 October 1895 by a contingent of troops under the command of General Giuseppe Arimondi.
January 1894: In December 1894, Bahta Hagos led a rebellion against the Italians in Akkele Guzay, claiming support of Mengesha. Units of General Oreste Baratieri's army under Major Pietro Toselli crushed the rebellion and killed Bahta at the Battle of Halai.
Was the second Italian military invasion of Ethiopia. At the end of the war the country became part of Italian East Africa.
2.1.Northern Front (Second Italo-Ethiopian War)
Was the northern front of the Second Italo-Ethiopian war.
2.1.1.De Bono Offensive
Was a military offensive by Italian general Emilio De Bono during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
November 1935: The Italian avant-gardes entered Macallè.
October 1935: The Italian I Corps took the city of Adigrat.
October 1935: Dejazmach Haile Selassie Gugsa and 1,200 of his men surrendered to the Italian command near Adagmos.
October 1935: From October 15, the forces under the command of De Bono moved from Adua towards Axum to occupy the city.
October 1935: Adua was captured by the Italian II Corps.
2.1.2.Ethiopian Christmas Offensive
Was an Italian military offensive during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
December 1935: Italian military occupation of Abbi Addi.
January 1936: The Ethiopians reoccupied all of southern Tembien.
2.1.3.Badoglio Offensive
Was a military offensive by Italian general Pietro Badoglio during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
April 1936: Italian march on Gondar resulting in the occupation of Gondar and the Lake Tana area.
February 1936: Battle of Amba Aradam.
March 1936: Battle of the Scirè.
April 1936: Battle of Lake Ascianghi.
April 1936: The Italian army corps entered Dessié on April 15, 1936.
May 1936: Occupation of Addis Ababa by Italian forces.
February 1936: Second Battle of Tembien.
2.2.Southern Front (Second Italo-Ethiopian War)
Was the southern front of the Second Italo-Ethiopian war.
2.2.1.Graziani Offensive
Was an Italian military offensive commanded by General Rodolfo Graziani during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
May 1936: Italian general Graziani entered Dire Daua, a few hours before the arrival by train from Addis Ababa of the men of Badoglio. With this last formal act, the war on the southern front also ended.
October 1935: Italian general Graziani authorized the execution of the "Milan Plan": a series of small offensive attacks along the entire front to eliminate the annoying enemy garrisons and to test their resistance. In about twenty days Graziani occupied the villages of Dolo, Oddo, Ualaddaie, Bur Dodi, Dagnerei, Callafo, Scivallè and Gherlogubi, after they had been cleared following the preventive aerial bombardments ordered by the general.
January 1936: Battle of Ganale Doria.
April 1936: Battle of the Ogaden.
May 1936: The Italian columns, led by General Rodolfo Graziani, began their advance towards Harar in 1936 during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War. The city was occupied by Italian forces in the early afternoon of 6 May.
November 1935: First attack with chemical agents of the Second Italo-Ethiopian War against the village of Gorrahei, which was subsequently the main objective of the "Plan Gorizia" which began on October 28. However, it fell into Italian hands only on 6 November.
April 1936: El Fud conquered by italy.
April 1936: Segàg conquered by italy.
Selected Sources
Matteotti, F. (1938): La Formazione de l'impero coloniale italiano, Volume Terzo - L'impero (dall'occupazione di Dessiè all'assetto definitivo dell'impero), Milan (Italy), pp. 9-10
 Italo-Ethiopian Wars
Italo-Ethiopian Wars