If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Were a series of wars between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow (later the Tsardom of Russia).
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military invasions of the the Grand Duchy of Moscow by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
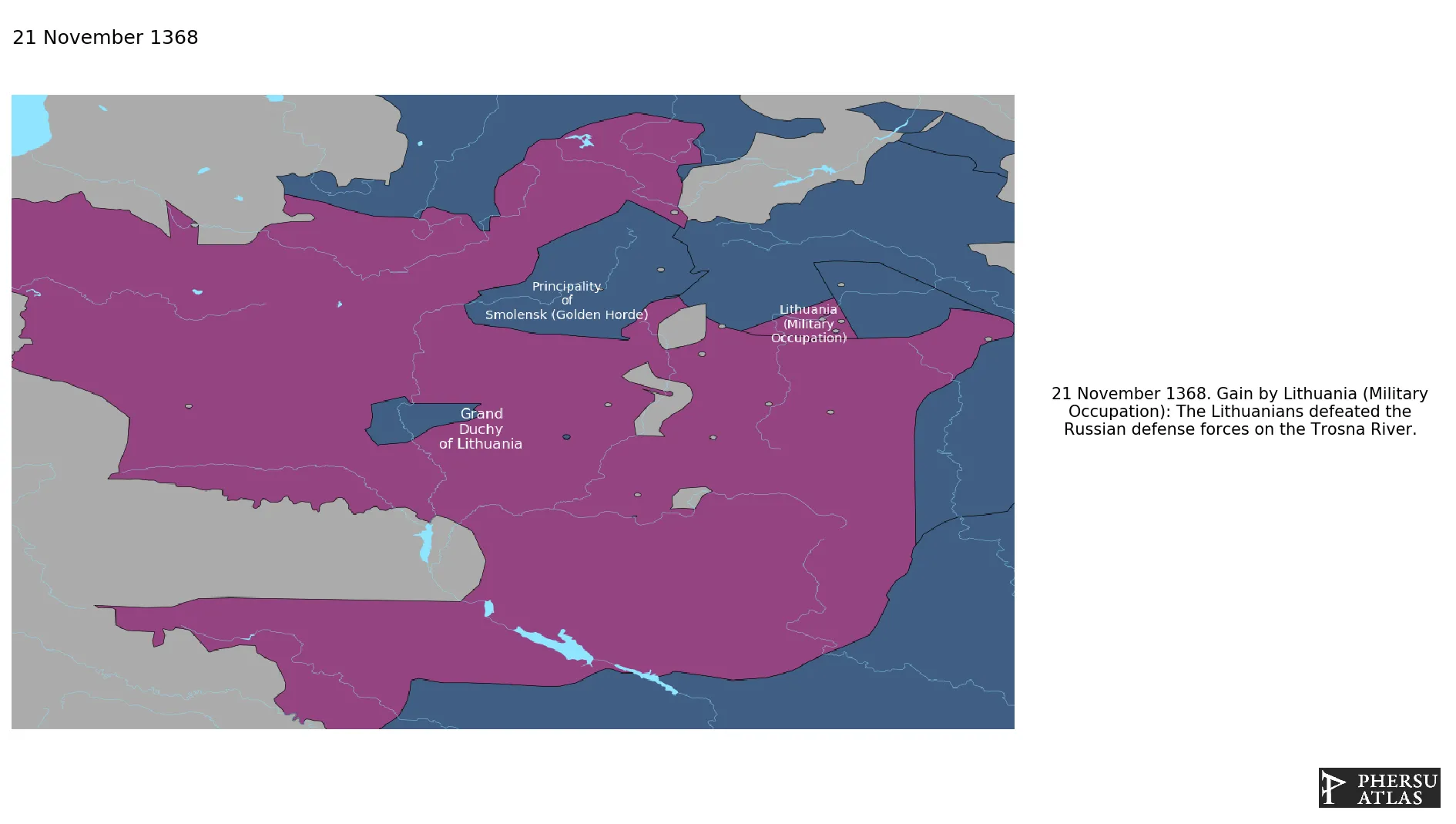
1.1.Invasion of Russia by Algirdas
Was a military campaign launched by Lithuanian Grand Duke Algirdas in Russia.
November 1368: The Lithuanians defeated the Russian defense forces on the Trosna River.
January 1369: In 1368, Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania gathered a large army, which included his brother Kęstutis and forces from Tver and Smolensk. The army was assembled in secret and marched quietly so that not to give an advance warning to the Russians. After crossing the Lithuania-Russia border, Lithuanians began pillaging and burning various villages.
June 1372: Prince of Moscow Dmitry Donskoy marched with his army to meet the invading Lithuanian army, which was stopped near Lyubutsk.
December 1368: The Lithuanians surrounded the Kremlin of Moscow, burned and looted it.
1.2.Russian counterattack against Algirdas
Was the Russian counterattack to the Lithuanian invasion started in 1368.
December 1368: The Lithuanian army retreated from all Russian territories without a serious attempt at taking the Moscow Kremlin.
April 1370: In early 1370, Moscow attacked Tver and Bryansk which belonged to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
November 1370: On November 26, the Lithuanian army besieged Volokolamsk. The battle continued for two days. Lithuanians killed Prince Vasily Ivanovich Berezuysky, commander of the city's defenses, but did not succeed in capturing the city.
December 1370: The Lithuanian army led by Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, besieged Moscow on December 6. Algirdas' forces burned and pillaged, but did not succeed in taking the city's Kremlin where the Prince of Moscow, Dmitry Donskoy, had retreated.
December 1370: A truce between Russia and Lithuania was concluded. Lithuanian Grand Duke Algirdas retreated from the occupied territories.
1.3.Kęstutis' raid
Was a military campaign launched by Kęstutis, the brother of Lithuanian Grand Duke Algirdas, in Russia.
June 1372: In spring 1372, Lithuanians raided Russian lands again. This time Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, did not participate. The Lithuanian Army was commanded by Kęstutis (Algirdas' brother) and his son Vytautas and Algirdas' son Andrei of Polotsk. They attacked Pereslavl-Zalessky, burned the posad and churches, looted and extracted a ransom.
June 1372: Mikhail II prince of Tver (allied with Lirhuania) attacked the city of Dmitrov.
June 1372: The armies of Lithuania and Tver attacked Kashin and its duke acknowledged Tver's suzerainty.
1.4.Truce - Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-1372)
Was a treaty that ended the Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-72).
September 1372: The Treaty of Lyubutsk was a peace treaty signed in summer of 1372 between Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, and Dmitri Donskoi, Prince of Moscow. The treaty ended the Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1368-72) and resulted in a seven-year peace period. Lithuanian forces left the occupied territories.
Was a war between Moscow and Lithuania that included figths on the Ugra river and the Lithuanian annexion of Smolensk.
January 1403: Vasily hesitated until Vytautas advanced on Pskov. Alarmed by Lithuania's continuing expansion, Vasily sent an army to aid the Pskovians against his father-in-law. The Russian and Lithuanian armies met near the Ugra River.
February 1403: The commander didn't ventured to commit his troops to battle. A peace ensued, whereby Vytautas kept Smolensk.
January 1405: The Principality of Smolensk was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1404.
Was a war of the Grand Duchy of Moscow, in alliance with the Crimean Khanate, against the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Ruthenia in alliance with the Golden Horde Khan Akhmat.
September 1492: In August 1492, without declaring war, Ivan III of Moscow began large military actions: he captured and burned Mtsensk, Lyubutsk, Serpeysk, and Meshchovsk; raided Mosalsk; and attacked territory of the Dukes of Vyazma.
February 1494: Grand Duke of Lithuania Alexander Jagiellon sent a delegation to Moscow to negotiate a peace treaty. An "eternal" peace treaty was concluded on February 5, 1494. The agreement marked the first Lithuanian territorial losses to Moscow: the Principality of Vyazma and a sizable region in the upper reaches of the Oka River.
Was a war between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
4.1.Muscovite invasion
Was a Muscovite invasion of Lithuania.
June 1500: In May 1500, hostilities resumed between the Duchy of Moscow and Lithuania. The Muscovites, led by Grand Prince Ivan III, quickly captured Lithuanian fortresses in Bryansk, Vyazma, Dorogobuzh, Toropets, and Putyvl.
July 1500: Moscovite attack into the Kiev Voivodeship, Volhynia, and Podolia.
4.2.Livonian Intervention alongside Lithuania
The Livonian Order joined the Second Muscovite Border War as an ally of Lithuania.
August 1501: In 1501, the Livonian Order, led by Wolter von Plettenberg, allied with Lithuania and emerged victorious in the Battle of the Siritsa River (57°35′09″N 27°52′54″E).
September 1501: The Livonian Knights evacuate the area of the Siritsa River.
October 1501: Siege of Pskov by the Livonian Knights.
April 1502: In 1502, Ivan III of Moscow led a campaign to capture Smolensk, but the city successfully defended itself due to the poor strategy of the Muscovites and their lack of artillery. The military occupation of Smolensk by the Duchy of Moscow followed this failed siege.
November 1502: The Livonian knights left the are of Lake Smolino.
October 1502: The Livonian Knights defeated thejoint armies of Pskov and Moscow in the Battle of Lake Smolino.
4.3.Truce (Second Lithuanian-Muscovite border war)
A six-year truce was concluded on the Feast of the Annunciation, ending the Second Muscovite Border War. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania lost approximately 210,000 square kilometres (81,000 sq mi), or a third of its territory.
March 1503: A six-year truce was concluded between Moscow and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania on the Feast of the Annunciation in 1503. As a result of this agreement, the Grand Duchy lost about a third of its territory to Moscow, including significant regions such as Chernihiv, Novhorod-Siverskyi, Starodub, and lands around the upper Oka River. The other territories Moscow had occupied, were evacuated.
Was a war between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
5.1.Glinski rebellion
Was a revolt in 1508 in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania by a group of aristocrats led by Prince Mikhail Glinski in 1508.
March 1508: The Glinski rebellion was a revolt in 1508 in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania by a group of aristocrats led by Prince Mikhail Glinski in 1508.
Was a war between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1514: In December 1512, Tsar Vasili III of Muscovy Rus' led the invasion of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, aiming to capture the strategic trading center of Smolensk. The city fell to Moscow's forces in 1513, marking a significant territorial gain for the Duchy of Moscow.
August 1514: The city of Smolensk fell to the Duchy of Moscow in July 1514.
January 1515: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1515.
January 1520: In 1519, the Russians, led by Grand Prince Vasili III of Moscow, invaded Lithuania, raiding cities such as Orsha, Mogilev, Minsk, Vitebsk, and Polotsk. This military occupation marked a period of conflict between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Duchy of Moscow.
6.1.Truce (Fourth Lithuanian-Muscovite border war)
Was a treaty that ended the Lithuanian-Muscovite War (1512-1522). The Grand Duchy of Moscow retained Smolensk.
January 1523: In 1522, a treaty was signed by Lithuania and Russia that called for a five-year truce, no prisoner exchange, and for Russia to retain control of Smolensk.
Was a war between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
November 1534: In October 1534, a Muscovite army under the command of Prince Ovchina-Telepnev-Obolensky, Prince Nikita Obolensky, and Prince Vasily Shuisky invaded Lithuania, advancing as far as Vilnius and Navahrudak.
January 1537: In 1536, the fortress Sebezh, located in present-day Russia, successfully defended against the Lithuanian forces led by Ivan Nemirovich-Danchenko. The victory resulted in the territory falling under the military occupation of the Duchy of Moscow.
January 1538: Lithuania and Russia negotiated a five-year truce, without prisoner exchange, in which Homel stayed under the Lithuanian king's control, while the Moscovites kept Sebezh and Zavoloche.
January 1536: The Lithuanian army under Hetman Radziwill, Andrei Nemirovich, Polish Hetman Jan Tarnowski, and Semen Belsky launched a powerful counterattack and took Homel and Starodub.
Selected Sources
Baronas, D. (2011): Ekspansijos Rusioje potvyniai ir atoslūgiai in Dubonis, Arūnas (ed.). Lietuvos istorija. XIII a. - 1385 m. valstybės iškilimas tarp rytų ir vakarų Vol. III, Vilnius (Lithuania), pp. 468-471
Batūra, R. (2013): Algirdo žygiai į Maskvą 1368 1370, 1372in Zikaras, K.: Žymiausi Lietuvos mūšiai ir karinės operacijos (2nd ed.). Vilnius (Lithuania), pp. 46-49
Robert, A. / Obolensky, D. (1981): A Companion to Russian Studies: An Introduction to Russian History, Cambridge (UK), p. 86
Атлас 7 класс История России 16 - конец 17 века (Atlas, 7th grade, History of Russia, 16th - end of the 17th century.) , Дрофа Publisher (2015), Moscow (Russia), p. 2
 Muscovite-Lithuanian Wars
Muscovite-Lithuanian Wars