If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
July 1941: On July 7, Germany occupied Žytomyr and Berdičev.
July 1941: German advances in USSR during Operation Barbarossa by July 9th.
November 1941: The Lokot Republic was established in central Russia by Bronislav Kaminski, a Russian collaborator with the Nazis.
August 1941: The Transnistria Governorate was established, which was not formally annexed to Romania unlike Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina.
December 1941: German advances in USSR during Operation Barbarossa by December 5th.
September 1941: German advances in USSR during Operation Barbarossa during September 1941.
Refers to German operations that lead to the occupation of the Baltic states during the invasion of Russia of World War II.
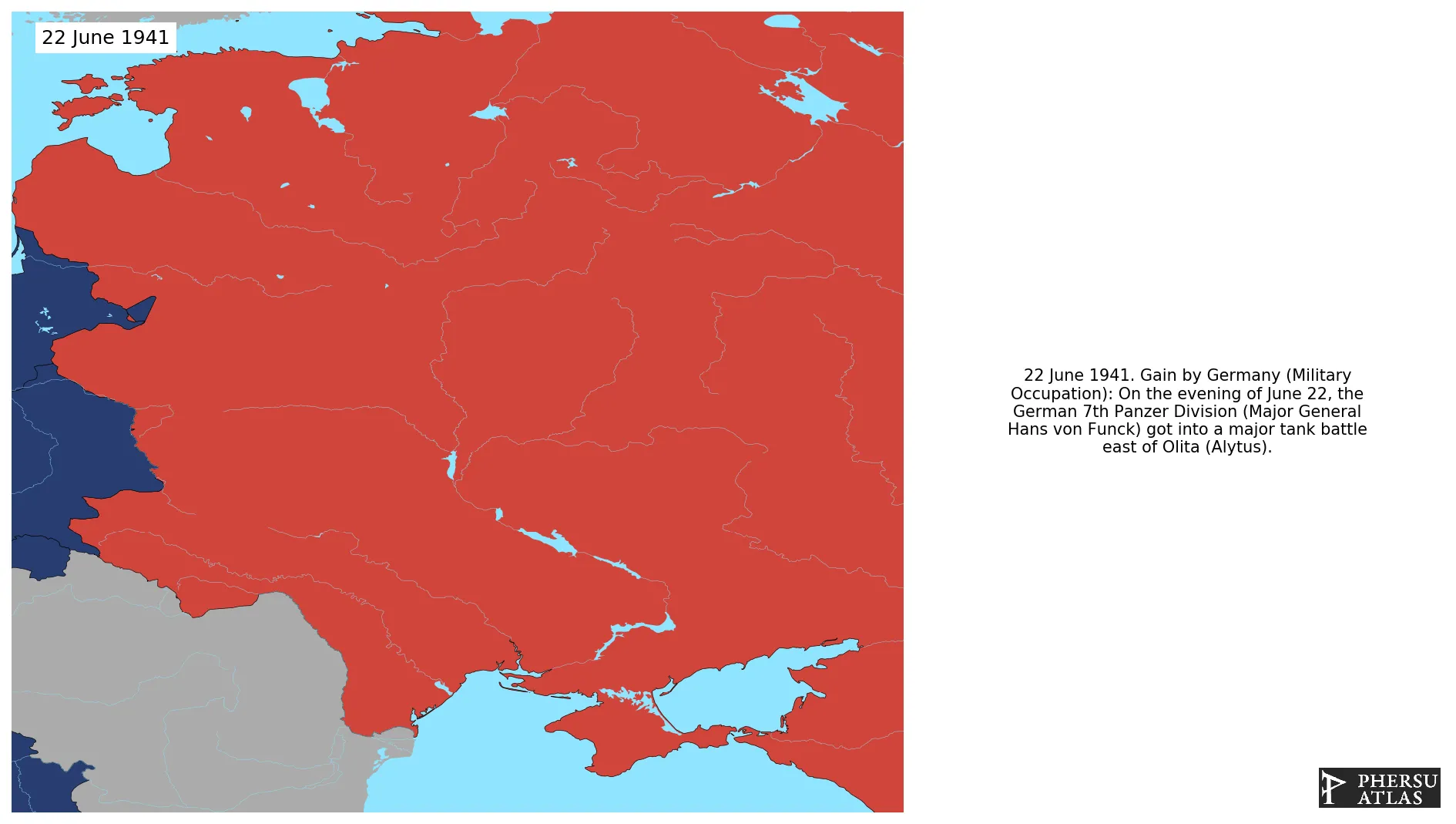
June 1941: On the evening of June 22, the German 7th Panzer Division (Major General Hans von Funck) got into a major tank battle east of Olita (Alytus).
June 1941: Tauroggen is occupied by German forces.
June 1941: Fighting was fought around Polangen, the Soviet 10th Rifle Division's defenses were breached and it was forced to retreat north.
June 1941: The 8th Panzer Division (General Brandenberger), covered on the left by the 290th Infantry Division, took Georgenburg.
June 1941: The German LVI. Army Corps reached the Ukmerge area on 24 June.
June 1941: The German XXVIII. Army Corps attacked with the 122nd and 123rd Infantry Divisions near Neustadt and northwest of Sintautai.
June 1941: The breakthrough between Mariampol and Kalvarja was forced by the German Army.
June 1941: Heavy losses of Soviet troops during the counterattacks and lack of fuel and ammunition led to the fall of Kaunas and Vilna on June 24.
June 1941: The front parts of the Soviet 28th Panzer Division (Raseiniai) were wedged and lost 14 tanks and 20 guns, leaving the battlefield on the night of June 24th.
June 1941: German military occupation of Schaulen (today Šiauliai), Lithuania.
June 1941: On the morning of June 26, the 8th Panzer Division (General Brandenberger) and the 3rd Motorized Division (General Jahn) reached the Düna, taking Dünaburg and securing a bridgehead on the right bank of the river.
June 1941: German motorized corps reached the river at Krustpils on June 26.
June 1941: As late as June 28, Libau was occupied by the Germans without any particular resistance.
June 1941: At the end of June, the German 1st Army Corps with the 1st, 11th and 21st Infantry Divisions concentrated on the Düna in the Friedrichstadt area.
July 1941: Ventspils (Windau) was taken by the Germans on July 1st.
July 1941: East of Dünaburg near Kraslava the Düna crossing by the Germans took place on July 3rd.
July 1941: The pushed-off Soviet 42nd Panzer Division held out in the Dagda District until the evening of July 3.
July 1941: Units of the German LVI. motorized corps occupied Rezekne on July 4th.
July 1941: The Germans retook Ostrow.
July 1941: The German 217th Infantry Division, supported by the Navy, took Pernau on 9 July.
July 1941: German forces reached the Dorpat-Pernau line on July 10.
August 1941: On August 5, the German units reached Tallinn.
August 1941: On August 7th, 1941, German forces under the command of Field Marshal Wilhelm Ritter von Leeb reached the coast of the Gulf of Finland at Kunda.
July 1941: On the evening of July 3, German troops occupied Gulbene.
July 1941: On July 6 the city of Ostrow fell back into German hands.
June 1941: On June 29, Jelgava (Mitau) was occupied by the German 18th Army.
June 1941: The German 121st Infantry Division attacked in the Wirballen area and was soon engaged in house-to-house fighting in Kibarten.
July 1941: German troops threw back the remnants of the Soviet 41st Rifle Corps across this river and occupied the western part of Pskov.
June 1941: The 3rd Infantry Division (motorized) of Germany advanced to Dubissa, where a bridgehead was established at Ariogala in the afternoon.
August 1941: On August 27, Admiral W. F. Tributz issued the order to evacuate his naval troops, on this day German troops entered Tallinn.
June 1941: Motorized corps of General Reinhardt reached the western Düna near Jakobstadt and Lievenhof.
July 1941: On July 1, the Soviet 8th Army was further withdrawn to the Gulbene - Lake Lubana line.
Was a German strategic operation conducted by the Wehrmacht's Army Group Centre during the penetration of the Soviet border region. The operation loed to the occupation of Belarus.
June 1941: Minsk, the capital of Belarus, fell to the Wehrmacht.
2.1.German Invasion of Belarus
Was a German strategic operation conducted by the Wehrmacht's Army Group Centre during the penetration of the Soviet border region. The operation led to the occupation of Belarus.
June 1941: By the night of 25 June, the Soviet counterattack was defeated, and the commander of the 6th Cavalry Corps was captured yb the Germans in Grodno.
Was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) on the Eastern Front of World War II.
August 1941: The Germans Captured Tallinn by August 28.
September 1941: Finns captured the Beloostrov and Kirjasalo salients and conducted defensive preparations.
June 1941: Riga conquered by germany.
August 1941: The German XXVI. Army Corps reached the Luga sector near Kingisepp on August 17.
October 1941: Until mid-October the large Baltic islands were occupied by German forces.
September 1941: On September 8, the Wehrmacht captured Schlisselburg on the shore of Lake Ladoga.
A joint German-Romanian offensive during the German invasion of the Soviet Union in World War II, with the primary objective of recapturing Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina and the Hertsa region, ceded by Romania to the Soviet Union a year before.
July 1941: On July 5, Chernivtsi, the capital of northern Bukovina, was captured by the Romanian 3rd and 23rd Vânători Battalions.
July 1941: On July 16, after heavy fighting, Kishinev, the capital of Bessarabia, was taken by the Romanian 1st Armored Division (Divizia 1 Blindată).
July 1941: By July 26, Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina were under Romanian-German control.
August 1941: On August 17, Bessarabia and northern Bukovina were officially reintegrated into the Romanian state.
July 1941: By the evening of July 4, parts of the German XI. and XXX. Army corps broke through on the Stolnichena, Zaikany, Shuchulia, Kulugar-Sosh and Busila lines and broke through to Balti.
Was the struggle between Germany and the USSR for the area of Kiev during World War II.
July 1941: The German forces managed to break through the fortified Stalin Line in the southeast portion of Zhytomyr Oblast.
July 1941: The Axis ground forces reached the Dnieper tributary Irpin River.
November 1943: Continuing to advance West of Kiev, Soviet forces take Zhitomir, important rail center.
September 1941: German occupation of Kiev.
Was the struggle between Germany and the USSR for the area of Smolenks during World War II.
September 1943: Bryansk is liberated by the Red Army during Smolensk operation.
September 1943: Soviet forces take Smolensk and Roslavl on central front.
September 1943: After four days of battle, Soviet rifle divisions captured Dukhovshchina.
September 1943: Yartsevo, an important railroad hub near Smolensk, was liberated by Soviet troops.
July 1941: German troops, commanded by Field Marshal Fedor von Bock, conquered the city of Smolensk on July 15, while the battle could be considered concluded on the 26th with the liquidation of the last pockets of Soviet resistance, laying the foundations for the attack towards the capital.
Was the World War II German offensive in Uman, Ukraine, against the 6th and 12th Soviet Armies.
July 1941: Panzergruppe 1 occupied the important strategic point of Bila Tserkva.
August 1941: Battle of Uman.
Was an Axis military campaign fought between 26 September 1941 and 11 October 1941 on the northern shores of the Sea of Azov during Operation Barbarossa.
October 1941: The Germans captured Melitopol and Berdiansk.
October 1941: Germans captured Kharkiv on 24 October.
Was the attempt of German troops to conquer Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Soviet Union.
October 1941: By 13 October 1941, the Wehrmacht had reached the Mozhaisk defense line.
October 1941: German forces captured the city of Kalinin and south Kaluga and Tula.
October 1941: Mozhaisk and Maloyaroslavets conquered by germany.
October 1941: Naro-Fominsk fell to the Germans on 21 October.
October 1941: Battle of Bryansk.
October 1941: Volokolamsk conquered by germany.
November 1941: The Germans took Stalinogorsk on 22 November 1941.
November 1941: Just northwest of Moscow, the Wehrmacht reached Krasnaya Polyana, little more than 29 km from the Kremlin in central Moscow.
October 1941: The Germans reached the outskirts of Tula until 26 October.
November 1941: Istra conquered by germany.
October 1941: Spearheads of the German 3rd and 4th Panzer Groups met at Vyazma.
November 1941: Solnechnogorsk conquered by germany.
November 1941: The German Third Panzer Army captured Klin after heavy fighting on 23 November.
Was the siege of the city of Odessa, in the Soviet Union, during the early phase of Operation Barbarossa.
October 1941: Siege of Odessa.
Was a battle of the Eastern Front of World War II, fought around Rostov-on-Don between the Army Group South of Nazi Germany and the Southern Front of the Soviet Union.
October 1941: By 17 October 1941 the Mius River was crossed by the 14th Panzer Division and Taganrog was captured by German troops.
November 1941: On 21 November the Germans took Rostov.
November 1941: On 27 November the Soviet 37th Army, commanded by Lieutenant-General Anton Ivanovich Lopatin, as part of the Rostov Strategic Offensive Operation, counter-attacked the 1st Panzer Army's spearhead from the north, forcing them to pull out of the city of Rostov.
Was the counteroffensive of the Soviet troops against the Germans, that had put Moscow under siege.
December 1941: Soviet troops liberated Naro-Fominsk.
December 1941: Soviet armies retook Solnechnogorsk.
December 1941: The Red Army approaches Kaluga, south-west of Moscow (full liberation on 31 December).
January 1942: Maloyaroslavets conquered by USSR.
December 1941: A Soviet offensive liberated Kalinin and the Red Army reached Klin.
December 1941: The Red army takes Klin.
Was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) on the Eastern Front of World War II.
December 1941: Germans retreated from Tikhvin back to the Volkhov River.
January 1944: Red Army units gain ground in Leningrad area. Germans forces pushed 60-100 km away from the city. Enemy is cleared from area between Tosno and Lyuban.
Was a Soviet military operation in January 1943 during World War II, that succesfully broke the Wehrmacht's siege of Leningrad.
January 1943: Schlüsselburg conquered by USSR.
January 1943: Soviet Reconquests from the Germans up to January 22.
Was an operation conducted by the Soviet forces that succeeded in recapturing the Demyansk salient.
February 1943: A Soviet operation succeeded in retaking the Demyansk salient.
Selected Sources
German Invasion Of Russia, 22 June-25 August 1941. United States Military Academy of West Point. Retrieved on 6 April 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope19.jpg
German Invasion Of Russia, Advance On Moscow, 26 August-5 December. United States Military Academy of West Point. Retrieved on 6 April 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope20.jpg
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 10
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.137
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.146
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.165
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.6
 Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa