If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Were a series of wars between the Habsburg Domains and Prussia for the control of Silesia. The war started during the War of the Austrian Succession, when Frederick the Great of Prussia invaded Habsburg-held Silesia.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the first of three wars between Austria and Prussia for the control of Silesia. It was part of the War of the Austrian Succession. The war started when Prussia invaded Silesia. The possession of the region by Prussia was aknowledged by Austria at the end of the war.
1.1.Silesian Theatre (First War)
Was the Silesian theatre of the First Silesian War.
November 1741: On 9 October Austria and Prussia agreed to a secret armistice known as the Convention of Klein Schnellendorf, under which both belligerents would cease hostilities in Silesia, and Austria would eventually concede Lower Silesia in return for a final peace to be negotiated before the end of the year. Neipperg's Austrian forces were then recalled from Silesia to defend Austria against the western invaders, abandoning Neisse after a sham siege in early November and leaving the whole of Silesia under Prussian control.
June 1742: The Treaty of Breslau was a preliminary peace agreement signed in 1742 between Prussian King Frederick the Great and Austrian Empress Maria Theresa, ending the First Silesian War. The treaty ceded most of Silesia to Prussia, marking a significant territorial gain for the Kingdom of Prussia.
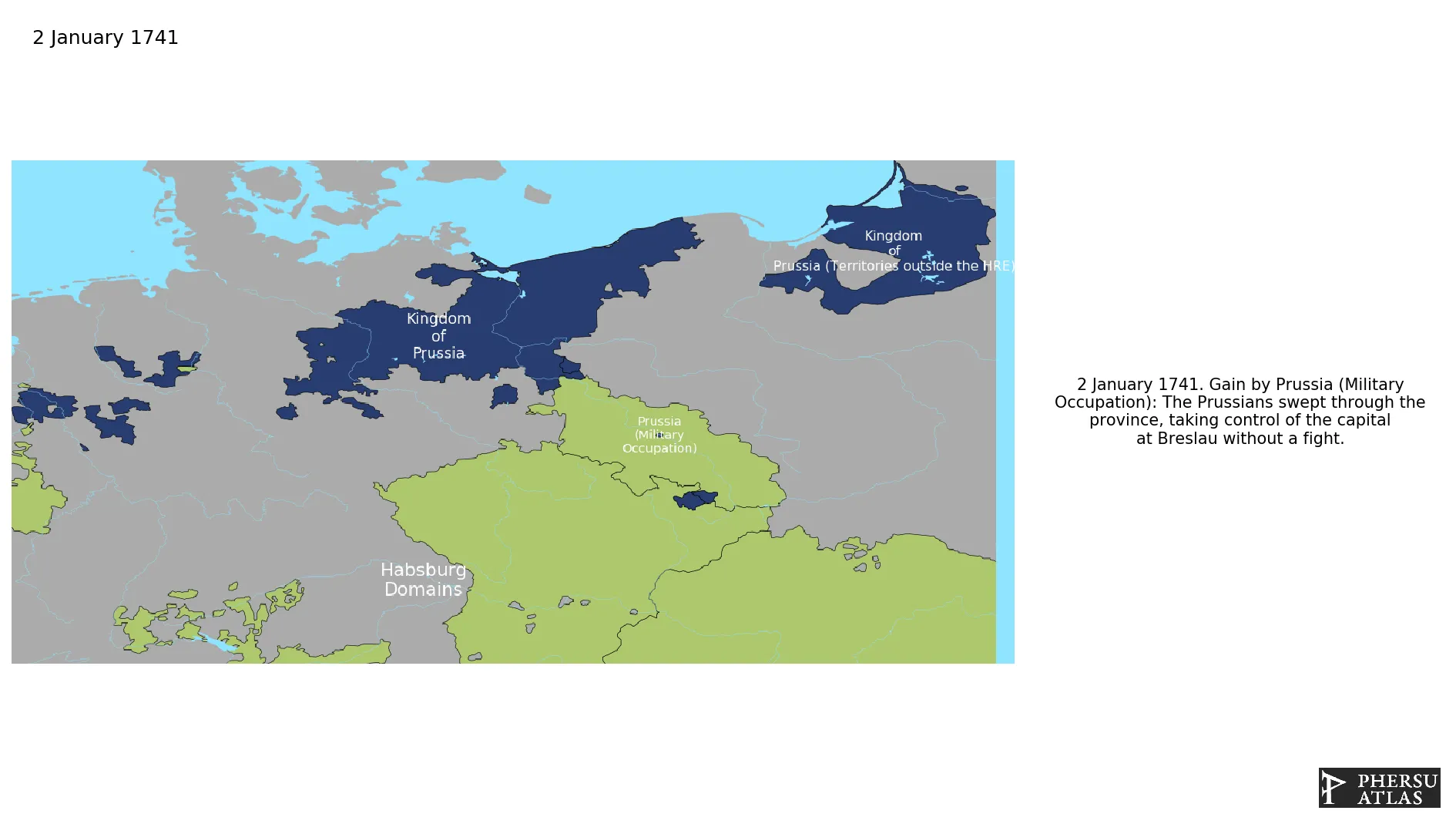
January 1741: The fortress at Ohlau was taken without resistance by Prussian forces.
March 1741: Prince Leopold II of Anhalt-Dessau took Glogau by storm.
January 1741: The Prussians swept through the province, taking control of the capital at Breslau without a fight.
January 1741: By the end of January 1741, almost the entirety of Silesia had come under Prussian control, and the remaining Austrian strongholds of Glogau, Brieg and Neisse were besieged.
June 1742: The Treaty of Breslau was a preliminary peace agreement signed in 1742 between Maria Theresa of Austria and Frederick II of Prussia, ending the First Silesian War. The treaty ceded the territory of Silesia to the Kingdom of Prussia.
May 1741: Brieg (today Brzeg) surrendered to the Prussians on 4 May.
1.2.Austrian Theatre
Was the Austrian theatre of the First Silesian War.
October 1741: The French deprecated a decisive move on Vienna, wishing to see Austria reduced rather than destroyed. So, on 24 October their forces turned north to march instead on Prague.
January 1742: Surrender of 10,000 French soldiers at Linz Habsburg forces led by Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine.
October 1741: In mid-October 1741, Charles Albert of Bavaria, supported by French forces, was preparing to besiege Vienna during the War of the Austrian Succession. The military occupation of the territory by France and Bavaria posed a significant threat to the Austrian capital.
September 1741: On 5 June, Frederick signed an alliance against Austria with France, who crossed the Rhine on 15 August. A combined Franco-Bavarian force now advanced along the Danube, towards Vienna, capturing Linz on 14 September.
1.3.Bohemian Theatre (First Silesian WarWar)
Was the Bohemian theatre of the First Silesian War.
November 1741: The Bavarian, French and Saxon armies converged around Prague in November, besieging it and ultimately storming it.
December 1741: Charles Albert was the Elector of Bavaria, who was supported by France in his claim to the Bohemian throne during the War of the Austrian Succession. He proclaimed himself King of Bohemia on 7 December 1741 after his forces occupied the territory.
January 1742: Prince Leopold's army besieged the fortress at Glatz on the edge of Bohemia.
April 1742: Frederick took Kłodzko.
January 1743: Siege of Prague.
1.4.Moravian Theatre
Was the Moravian theatre of the First Silesian War.
May 1742: The Moravian campaign in 1742 was part of the War of the Austrian Succession. The Prussians, led by King Frederick the Great, retreated from Moravia after failing to make significant gains against the Habsburg Empire. The territory was then occupied by the Habsburg military.
April 1742: Prussian forces moved onto Židlochovice in March 1742.
December 1741: In December Schwerin's army advanced through the Sudetes into Moravia, occupying the capital at Olmütz on 27 December.
1.5.Bavarian Theatre
Was the Bavarian theatre of the First Silesian War.
April 1745: With Prussia's forces driven out of Bohemia, Austria renewed its offensive against Bavaria in March 1745, swiftly over-running the defences that had been reestablished there during the winter. On 15 April the Austrians under Count Batthyány decisively defeated the Franco-Bavarian army at the Battle of Pfaffenhofen and drove the allied forces entirely out of Bavaria.
June 1743: In mid-June, the Pragmatic army arrived at Aschaffenburg, on the north bank of the River Main.
May 1743: The Battle of Simbach in 1743 saw the Bavarians defeated by Charles of Lorraine, who was a general in the Habsburg Empire. This military occupation resulted in the territory of Simbach falling under Habsburg control.
February 1742: On January 24, 1742, during the War of the Austrian Succession, Bavarian Field Marshal Bärenklau captured the capital city of Munich, which was under the control of the Habsburg Empire at the time.
January 1742: Von Khevenhüller defeated a Bavarian army at Schärding.
October 1744: Prince Charles's army was able to return to Bohemia quickly, in good order and at full strength, though it was forced to abandon control of Alsace and Bavaria. Austrian diplomats also persuaded Saxony to re-enter the conflict on Austria's side, though in a strictly defensive role. By early October the Austrians were advancing through southwestern Bohemia toward Prague.
April 1745: After this defeat, Maximilian III of Bavaria (the son of the late Emperor Charles Albert) made peace with Maria Theresa by the Treaty of Füssen on 22 April.
Was the second of three wars between Austria and Prussia for the control of Silesia. It was part of the War of the Austrian Succession.
2.1.Bohemian Theatre (Second Silesian War)
Was the Bohemian theatre of the Second Silesian War.
September 1744: Frederick the Great left a modest garrison in Prague and quickly marched on to the south, occupying Tabor, Budweis and Frauenberg.
June 1745: The Prussians followed the retreating Austrian-Saxon army into Bohemia, harassing its rear as far as Königgrätz.
September 1744: The Second Silesian War began in 1744. Frederick of Prussia was disquieted by the universal success of the Austrians and their alliance with Sardinia.
The invading army of around 70,000 men entered Bohemia in three columns: the eastern column, led by Count Kurt von Schwerin, advanced from Silesia through Glatz and across the Giant Mountains; the central column, led by Prince Leopold II of Anhalt-Dessau, marched through Saxony (with an order from the Emperor guaranteeing safe conduct), passing through Lusatia and advancing to Leitmeritz; the western column, led by Frederick himself, advanced up the Elbe through Dresden and across the Ore Mountains to Leitmeritz. After entering Bohemia, all three forces converged on Prague by the beginning of September, surrounding and besieging the Bohemian capital.
September 1744: Prague underwent a week of heavy artillery bombardment, eventually surrendering to the Prussians on 16 September.
November 1744: After some weeks of manoeuvre an Austrian-Saxon force crossed the Elbe on 19 November. At this point the Prussians abandoned Prague and gave up Bohemia, retreating in poor morale into Upper Silesia.
November 1745: The Prussian's supplies were exhausted and they withdrew again into Upper Silesia for the winter.
November 1744: By early November the Prussians were forced to retreat to Prague and the Elbe.
2.2.Silesian Theatre (Second War)
Was the Silesian theatre of the Second Silesian War.
December 1745: This Treaty of Dresden ended the Second Silesian War between Austria, Saxony, and Prussia.
November 1745: Frederick the Great won the actions of Katholisch-Hennersdorf on 24 November and Görlitz on 25 November.
May 1745: At the end of May, the Austrian-Saxon force crossed through the Giant Mountains and camped around the Silesian village of Hohenfriedberg.
April 1745: Frederick abandoned the mountainous southern tip of Upper Silesia to the Austrian vanguard of pandurs, concentrating his defences around the town of Frankenstein in the valley of the Eastern Neisse.
June 1745: The ensuing Battle of Hohenfriedberg ended in a decisive Prussian victory, sending Prince Charles's army retreating in disarray back into the mountains.
November 1745: Leopold I was the Duke of Anhalt-Dessau and a Prussian general during the War of the Austrian Succession. His army's advance into Leipzig in 1745 marked a significant military occupation by Prussia in the region.
December 1745: The armies of King Charles VII of Bavaria and King Frederick II of Prussia converged toward Dresden in early December 1745.
December 1745: The Prussians occupied Dresden on 18 December.
December 1745: Leopold's force attacked and destroyed Rutowsky's army in the Battle of Kesselsdorf.
Was the last of three wars between Austria and Prussia for the control of Silesia. It was also part of the Seven Years' War.
3.1.Saxon Theatre (Polish-Soviet War)
Was the theatre of War in the Electorate of Saxony, which was invaded by Prussia, during the Third Silesian War.
3.2.Bohemian Theatre (Third War)
Was the Bohemian theatre of the Third Silesian War.
3.3.Russian invasion of East Prussia (Third Silesian War)
Was the Russian invasion of East Prussia during the Third Silesian War.
3.4.Russian invasion of Brandenburg (Third Silesian War)
Was the Russian invasion of Brandenburg during the Third Silesian War.
3.5.Silesian Theatre (Third War)
Was the Silesian theatre of the Third Silesian War.
3.6.Russia switches sided
On 5 January 1762 the ailing Russian Empress Elizabeth died. Her nephew and successor, Tsar Peter III, was an ardent admirer of Frederick the Great of Prussia, and he reversed Russia's foreign policy and ordered a ceasefire with Prussia. Peter agreed to an armistice with Prussia in March and lifted the Russian occupation of East Prussia and Pomerania.
3.7.Treaty of Hubertusburg
Was the treaty that ended the Third Silesian War, and, together with the Treaty of Paris (1763) it ended also the Seven Years' War.
Selected Sources
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.230
 Silesian Wars
Silesian Wars