Spanish-American War
Spanish-American War
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a war between Spain and the United States of America. The immediate cause of the war was the American support to Cuban independence.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the Pacific theatre of the Spanish-American War.
June 1898: A small U.S. task force under Captain Henry Glass captures Guam.
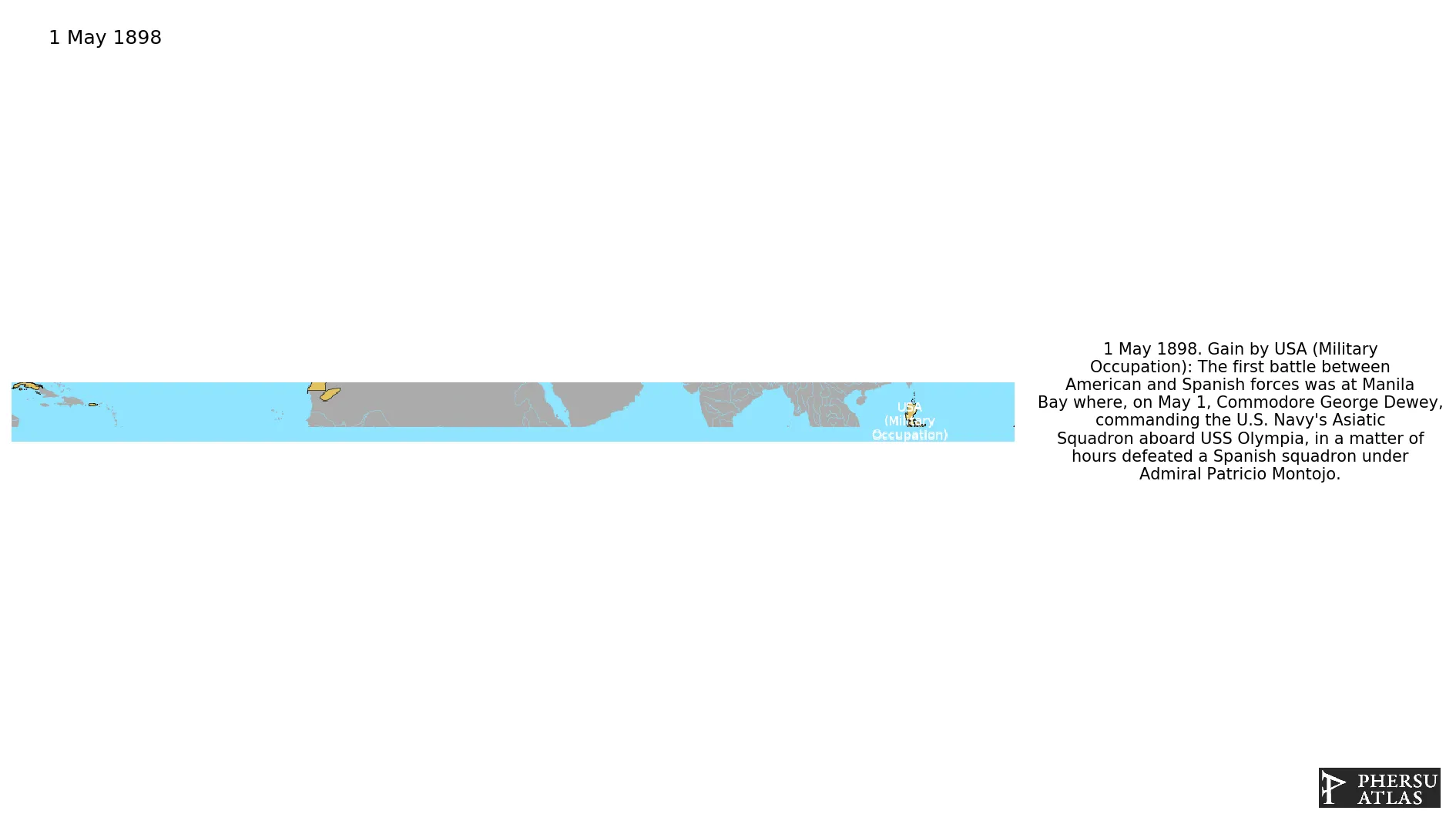
May 1898: The first battle between American and Spanish forces was at Manila Bay where, on May 1, Commodore George Dewey, commanding the U.S. Navy's Asiatic Squadron aboard USS Olympia, in a matter of hours defeated a Spanish squadron under Admiral Patricio Montojo.
Was the Caribbean theatre of the Spanish-American War. The United States of America eventually occupied Cuba.
July 1898: The Battle of Santiago de Cuba was a naval battle that occurred on July 3, 1898, in which the United States Navy decisively defeated Spanish forces.
June 1898: From June 22 to 24, the Fifth Army Corps under General William R. Shafter landed at Daiquirí and Siboney, east of Santiago, and established an American base of operations.
July 1898: Battle of El Caney. American victory. Santiago (Cuba) is now on the verge of being captured.
July 1898: Battle of San Juan Hill.
June 1898: Battle of Guantánamo Bay during the Spanish-American War: American and Cuban forces seized the strategically and commercially important harbor of Guantánamo Bay.
2.1.Puerto Rico Campaign
Was a U.S. military campaign to occupy the island of Puerto Rico during the Spanish-American War.
August 1898: On the evening of August 6, Captain Charles J. Barclay of Amphitrite ordered 28 sailors and 7 officers commanded by Lt. Charles N. Atwater and Assistant Engineer David J. Jenkins ashore to relight and occupy the Fajardo Light.
July 1898: The troops of Lt. Col. Francisco Puig leave the towns of Adjuntas and Utuado to advancing American forces.
August 1898: Arroyo (Puerto Rico) was taken by American forces.
August 1898: When the 4th August U.S. troops entered the town of Guayama, they discovered that the Spaniards had fled north and abandoned the city, ending the Battle of Guayama.
July 1898: U.S. general Garretson troops entered Yauco in the afternoon.
August 1898: All military actions in Puerto Rico were suspended August 13, after President William McKinley and French Ambassador Jules Cambon, acting on behalf of the Spanish government, signed an armistice whereby Spain relinquished its sovereignty over the territory of Puerto Rico.
July 1898: American forces of Major General Miles capture Guánica.
August 1898: American forces set up camp on Silva Heights for the night and the following day they continued their drive to Mayagüez. They arrived the following morning to find that the Spanish forces had abandoned the city to retreat to the east towards Lares.
August 1898: General James H. Wilson defeats Spanish forces in a smart action at Coamo, Puerto Rico.
July 1898: U.S. forces arrived at the town of Arecibo on the northern coast of the island.
August 1898: The 4th Ohio requested reinforcements and on August 9, attacked the Spaniards and a short firefight erupted. The numerical superiority of the Americans forced the Spanish to retreat from Guamaní Heights.
Was the U.S. conquest of Manila, nominally under Spanish control but factually under the control of the First Philippine Republic. The battle was part of the Spanish-American War.
August 1898: U.S. forces captured Manila.
Was the treaty that ended the Spanish-American War. Spain ceded most of its colonies (the Philippines, Puerto Rico, Cuba, Guam) to the United States.
April 1899: Cuba became a U.S. protectorate at the end of the Spanish-American War.
December 1898: The United States and Spain conclude the Treaty of Paris, whereby the Philippines are ceded to the Americans for a sum of $20 million, along with Puerto Rico and Guam. Cuba is also declared free and the Spanish pledge to pay $400 million for all Cuban debts. This concludes nearly four centuries of Spanish rule in the Western Hemisphere.
Selected Sources
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1492
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1496
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1497
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1499
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1501
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1502
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1503
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1505
 Spanish-American War
Spanish-American War