If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the theatre of war west of the Mississippi River during the American Civil War.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
May 1865: After the end of the Civil War in 1865, the Battle of Palmito Ranch took place in Texas, where Confederate forces under Colonel John Salmon Ford clashed with Union troops. Despite the Confederates winning the battle, Palmito Ranch was reintegrated into the United States.
July 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Camden Point. Union victory.
July 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Fort Smith. Union victory. Federal troops maintain control of western Arkansas
June 1865: At Fort Towson in Choctaw lands, General Stand Watie officially became the last Confederate general to surrender on June 25, 1865.
May 1865: Battle of Palmito Ranch. Confederate victory. Last battle in Texas during final phases of the Civil War. Southernmost battle on land in Civil War.
August 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Camden Point.
May 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Palmito Ranch.
August 1864: Confederate retreat after the Battle of Fort Smith.
Were a series of battles between the Missouri State Guard and the Union during the American Civil War.
September 1861: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Wilson's Creek or Oak Hills.
October 1861: A splinter government in Neosho, Missouri, declared the secession of the state from the United States.
September 1861: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Lexington. Union forces badly defeated by Missouri State Guard.
October 1861: Battle of Fredericktown: Union victory.
October 1861: First Battle of Springfield. Union forces capture town.
December 1861: Skirmish at Blackwater Creek. Union forces under General Pope capture a newly recruited Missouri State Guard regiment.
December 1861: Battle of Mount Zion Church: The resulting Union victory here and elsewhere in central Missouri ended Confederate recruiting activities in the region and pushed conventional Confederate forces out of the area.
October 1861: Union troop retreat after the First Battle of Lexington.
August 1861: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Carthage.
August 1861: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Wilson's Creek or Oak Hills.
July 1861: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Carthage.
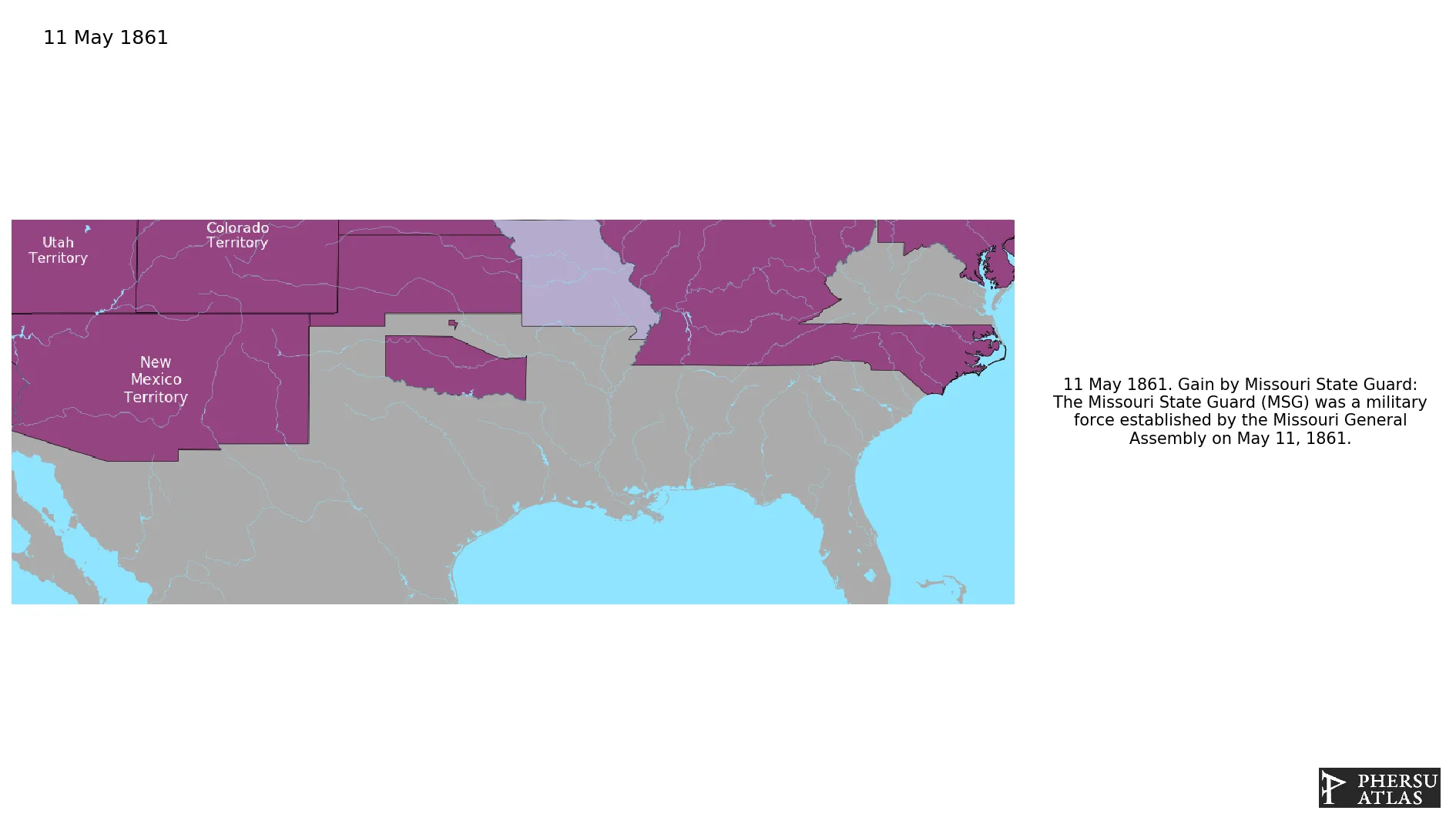
May 1861: The Missouri State Guard (MSG) was a military force established by the Missouri General Assembly on May 11, 1861.
Was the conquest of Arizona by the Confederate Army during the American Civil War.
August 1861: Arizona was officially proclaimed a territory on August 1, 1861, following the Confederate victory at the Battle of Mesilla.
July 1861: First Battle of Mesilla. Confederate victory secures the southern part of the New Mexico Territory for the CSA.
July 1861: Confederate forces from Texas advance into New Mexico. Federal forces abandon Fort Fillmore.
Was a December 1861 campaign in the American Civil War in which pro-Union Native Americans, led by Upper Creek Chief Opothleyahola, fought their way north from Indian Territory.
December 1861: Battle of Chusto-Talasah. Opothleyahola's Unionist Creeks and Seminoles defeated near present-day Tulsa.
November 1861: Battle of Round Mountain. Opothleyahola's Unionist Creeks and Seminoles defeated near present-day Stillwater.
Was the military invasion of New Mexico by Confederate Brigadier General Henry Hopkins Sibley during the American Civil War.
March 1862: The Confederate forces reached Albuquerque.
March 1862: Confederate forces captured Santa Fe on March 13, 1862.
March 1862: Battle of Glorieta Pass. Tactical retreat of Union forces.
April 1862: Battle of Peralta. Union forces defeat the 5th Texas Mounted Volunteers.
Was a battle near Leetown, northeast of Fayetteville, Arkansas during the American Civil War. By defeating the Confederates, the Union forces established Federal control of most of Missouri and northern Arkansas.
March 1862: Battle of Pea Ridge or Elkhorn Tavern: By defeating the Confederates, the Union forces established Federal control of most of Missouri and northern Arkansas.
Was a military campaign of Union forces started from California to fight against the Confederates in Arizona.
March 1862: The California Column arrives at Stanwix Station.
May 1862: The California Column captures Tucson (1862).
August 1862: The California Column captures Franklin (modern-day El Paso, Texas).
Were a series of military operation part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
July 1862: Battle of Cotton Plant. Union victory.
Were a series of military operations part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
January 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Galveston. Confederate victory.
September 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Sabine Pass. Confederate victory.
September 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Sabine Pass.
October 1863: Union troop retreat after being defeated in the Second Battle of Sabine Pass.
Were a series of military operations part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
November 1862: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Old Fort Wayne.
October 1862: Battle of Old Fort Wayne. Confederate forces go into Full retreat under Douglas H. Cooper, with the Union gaining control of the Indian territory.
November 1862: Battle of Clark's Mill. Union force surrenders to larger Confederate force.
Was a military campaign by the Union to conquer Vicksburg, Mississippi, during the American Civil War.
May 1863: Battle of Snyder's Bluff. Union feint during Vicksburg Campaign.
May 1863: Battle of Port Gibson. General Grant defeats the Confederates.
May 1863: Battle of Raymond. Failed Confederate attempt to protect Vicksburg from approaching Federals.
June 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Snyder's Bluff.
December 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Chickasaw Bayou. Confederate General John C. Pemberton defeats William Tecumseh Sherman.
June 1863: Battle of Milliken's Bend. In the largest battle fought between Confederate and Black troops, after nearly two days of close combat, the Confederates were defeated in their attempt to raise the siege of Vicksburg.
May 1863: Battle of Jackson, Mississippi. Union victory.
May 1863: Battle of Champion Hill. Union General Grant defeats Pemberton.
July 1863: Siege of Vicksburg: the entire Mississippi area controlled by the union. It cut off the Trans-Mississippi Department (containing the states of Arkansas, Texas and part of Louisiana) from the rest of the Confederate States, effectively splitting the Confederacy in two.
January 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Chickasaw Bayou.
June 1863: Battle of Lake Providence. Confederates withdraw to Floyd, Louisiana.
Was a Confederate military campaign in Missouri during the American Civil War.
January 1863: Second Battle of Springfield. Confederates enter town, but are unable to take nearby fort.
February 1863: The Confederates retreated after the Second Battle of Springfield.
Was a Confederate military campaign in Missouri during the American Civil War.
May 1863: Battle of Chalk Bluff. Confederate victory.
May 1863: Marmaduke suffered considerable casualties and his momentum had been checked, forcing him to abandon his second expedition into Missouri.
Was a Confederate military campaign in western Louisiana during the American Civil War.
June 1863: Battle of LaFourche Crossing. Confederates disengage, and fled to Thibodaux.
June 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Donaldsonville. Confederate forces failed to take Fort Butler.
July 1863: Battle of Kock's Plantation. Union troops retreat to Fort Butler in Donaldsonville, seized during the Second Battle of Donaldsonville.
July 1863: Confederate troop retreat after the Second Battle of Donaldsonville.
June 1863: The Confederate States of America captured Brashear City.
Were a series of military operations part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
February 1864: Battle of Middle Boggy Depot. Union troops massacred Confederate forces as the Confederates burned their encampments.
February 1864: The Confederates retreated 72 km southwest down the Dragoon Trail. The Union advance continued south toward Ft. Washita the next day, but when the expected reinforcements did not arrive Philips' Expedition into Indian Territory stalled on February 15, near old Stonewall.
July 1863: Battle of Honey Springs. In Indian Territory, two largely Black and American Indian forces meet. Union victory.
Was a Confederate raid in Kansas during the American Civil War.
August 1863: Lawrence Massacre.
August 1863: On August 25th, four days after the raid on the city, General Ewing issued his General Order No. 11, in which he ordered the forced evacuation of four Missouri counties along the Kansas border.
Was a military campaign by the Union to conquer Little Rock, Arkansas, during the American Civil War.
August 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Bayou Meto (Battle of Reed's Bridge). Confederate forces delay the Union advance on Little Rock.
September 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Bayou Meto (Battle of Reed's Bridge).
Was a major Union offensive campaign in the Trans-Mississippi theater of the American Civil War.
April 1864: Battle of Monett's Ferry. Confederate forces driven back.
April 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Mansfield or Sabine Cross Roads. Banks Union Red River Campaign halted by the Confederates.
April 1864: Battle of Pleasant Hill. Confederate attack fails.
May 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Mansfield or Sabine Cross Roads.
May 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Pleasant Hill.
March 1864: Battle of Fort De Russy. Fort DeRussy fell to the Union and the Red River to Alexandria was open.
Was the final campaign conducted by the Union Army in Arkansas during the Civil War.
April 1864: Battle of Elkin's Ferry. Confederates unable to prevent Union river crossing.
April 1864: Battle of Prairie D'Ane. Union Major General Frederick Steele defeats Sterling Price.
Was a Confederate raid in Arkansas, Missouri, and Kansas during the American Civil War.
October 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Independence.
October 1864: Battle of Little Blue River. Confederate victory.
October 1864: Second Battle of Newtonia. Union Major General James G. Blunt defeats Joseph O. Shelby.
October 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Byram's Ford.
October 1864: Battle of Glasgow. Union forces surrender.
September 1864: Battle of Fort Davidson (Battle of Pilot Knob). Union forces detonate their own fort after losing to Confederates.
October 1864: Second Battle of Lexington. Union forces driven out of town.
October 1864: Battle of Westport. Union forces win decisive battle to take control of Missouri.
Selected Sources
Beers, Henry Putney (1986). The Confederacy: A Guide to the Archives of the Government of the Confederate States of America. Washington, DC: NARA. p. 329
Colton, Ray Charles (1985). The Civil War in the Western Territories. University of Oklahoma Press. pp. 122–123.
Flaherty, M.: California and the Civil War - The California Column and the March to Tucson, 1862. Military Museum. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.militarymuseum.org/CaliforniaColumn.html
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.429
Jones, T.L. (2011): Historical Dictionary of the Civil War, Volume 1, Scarecrow Press, p. 546
List of American Civil War battles. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 31 March 2024 on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_American_Civil_War_battles
SANTA FE NATIONAL CEMETERY. U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.cem.va.gov/pdf/InterpretiveSigns/SantaFeNationalCemetery.pdf
Secession Ordinances of 13 Confederate States. University of Houston. Retrieved on 4 April 2024 on https://www.digitalhistory.uh.edu/disp_textbook.cfm?smtID=3&psid=3953
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.347
 Trans-Mississippi Theatre
Trans-Mississippi Theatre