If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters. It was a global war, with fighting taking place in Europe, Asia, and America. At the end of the war, Philip II, who was the successor chosen by Charles II as a descendant of Charles' paternal half-sister Maria Theresa, became King of Spain and of its overseas empire. The Spanish possessions in Europe were partitioned between various European Monarchies.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
March 1705: As a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession, the governor of Buenos Aires, Valdes Incian, initiated the Siege of Colonia del Sacramento. The forces of the Spanish governor were commanded by Baltazar García Ros from 18 October 1704 until 14 March 1705, when the colonists were evacuated by Portuguese ships.
Were a seris of French military actions to occupy Spanish possession in order to support the Spanish king (who was a grandchild of the French King Louis XIV).
January 1702: Helped by the Viceroy, Max Emanuel of Bavaria, French troops replaced Dutch garrisons in the 'Barrier' fortresses in the Spanish Netherlands, granted at Ryswick.
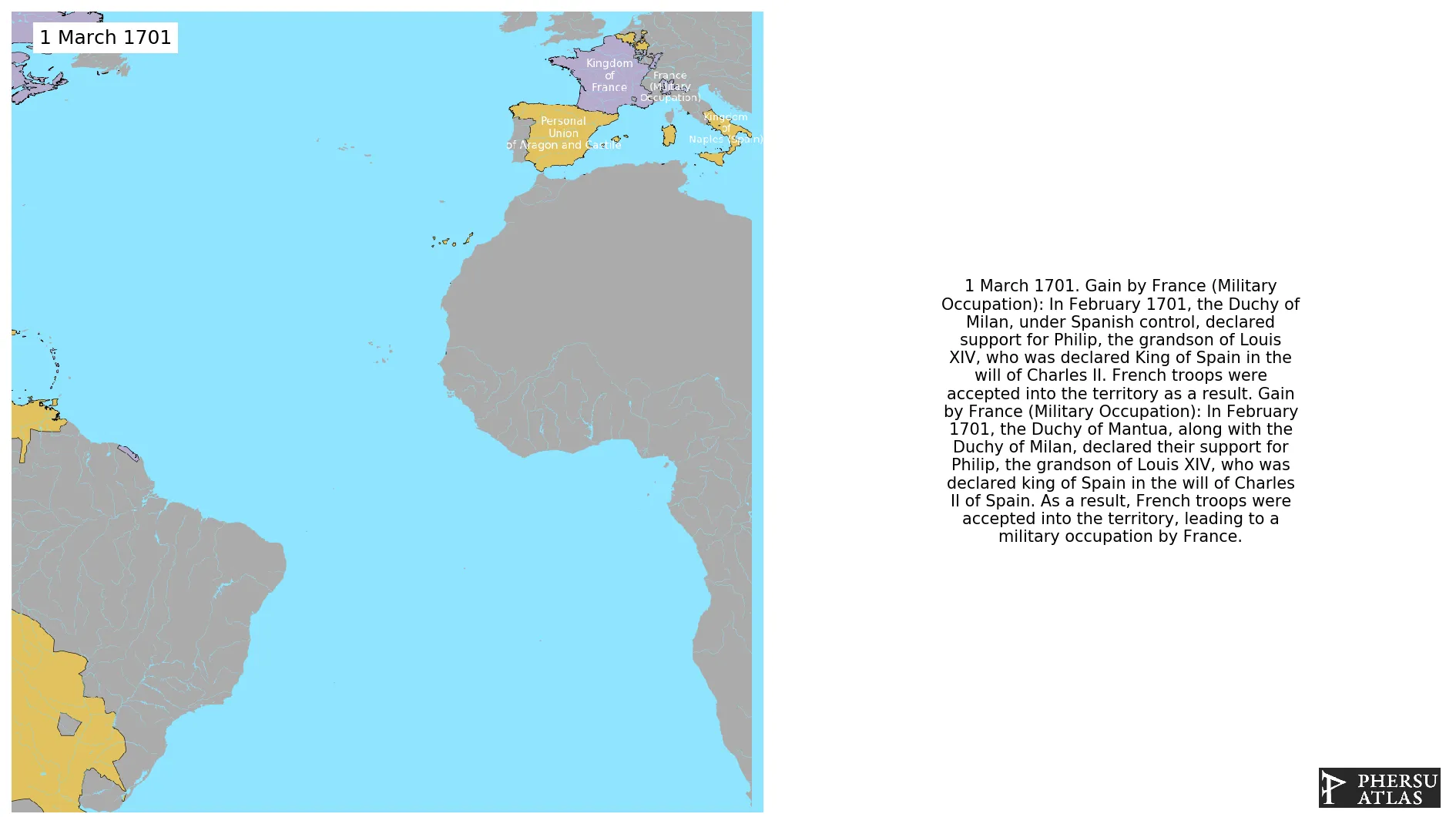
March 1701: In February 1701, the Duchy of Mantua, along with the Duchy of Milan, declared their support for Philip, the grandson of Louis XIV, who was declared king of Spain in the will of Charles II of Spain. As a result, French troops were accepted into the territory, leading to a military occupation by France.
March 1701: In February 1701, the Duchy of Milan, under Spanish control, declared support for Philip, the grandson of Louis XIV, who was declared King of Spain in the will of Charles II. French troops were accepted into the territory as a result.
Was the theatre of war of the War of the Spanish Succession in Italy.
September 1701: Victory on 1 September against Catinat's successor, Marshal François de Neufville de Villeroy, in the battle of Chiari.
November 1701: Austrian troops besiege Mantua.
September 1702: End of the siege of Mantua (1701-1702).
April 1704: From the beginning of 1704, French Marshal René de Froulay de Tessé had taken Savoy (with the exception of Montmélian).
July 1704: French military commander Louis d'Aubusson de la Feuillade occupied Susa in June.
August 1704: The Duke of Vendôme, Louis Joseph de Bourbon, was a French military commander who led the capture of Vercelli in July 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. This military occupation by France was part of their campaign in northern Italy against the Habsburg forces.
May 1705: Fall of Verrua in April 1705.
May 1705: In April 1705 French officer La Feuillade occupied the County of Nice, including Nice itself (although the citadel was not captured until January 1706).
September 1706: Prince Eugene of Savoy's victories gave the imperials effective control of the entire Po valley.
March 1707: The Convention of Milan of March 13, 1707, ensured the uncontested Austrian possession of the Duchies of Milan and of Mantua.
September 1707: Gaeta fell to the imperials after a siege.
October 1704: Ivrea conquered by france.
April 1706: The French defeated Count Christian Detlev Reventlow in the battle of Calcinato, and drove the Austrians back towards the mountains near Lake Garda.
January 1708: Imperial troops seized the Spanish Bourbon Kingdom of Naples.
Was the theatre of war of the War of the Spanish Succession in Germany and the Low Countries.
November 1702: Venlo, Stevensweert, Roermond, and Liege conquered by joint Dutch and British forces.
January 1703: In mid-January 1704 the Elector of Bavaria took Passau on the Danube.
May 1703: Siege of Bonn.
July 1703: Rheinberg and Bonn fell early to the Allied forces led by France.
September 1703: In 1703, during the War of the Spanish Succession, Margrave Louis William of Baden-Baden, a German military commander, led the imperial forces to capture the city of Landau on September 9th. This victory was a significant strategic gain for the Allied forces in the conflict.
October 1703: Marshal Tallard, a French military leader, captured Breisach am Rhein in September 1703.
November 1703: Huy, Limburg, and Geldern conquered by joint Durch and British forces.
November 1703: In 1703, Landau was conquered back by the French military under the command of Marshal Villars during the War of the Spanish Succession. The city had previously been captured by the Holy Roman Empire in 1702.
November 1704: By the Treaty of Ilbersheim, signed 7 November 1704, Bavaria was placed under Austrian military rule, allowing the Habsburgs to use its resources for the rest of the War of the Spanish Succession.
November 1704: While Ludwig von Baden besieged the Landau Fortress, which capitulated on November 26th.
January 1705: Trarbach conquered by austria.
August 1708: The cities of Ghent and Bruges in the Spanish Netherlands were occupied by France after popular discontent with the Allied administration.
December 1708: In 1708, during the War of the Spanish Succession, Ghent and Bruges were retaken by the Anglo-Dutch forces led by the Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy. This restored the authority of the Anglo-Dutch condominium over the territory, which had been under military occupation by the Dutch Republic and Great Britain.
November 1709: Mons, a city in modern-day Belgium, fell in October 1709 during the War of the Spanish Succession. The territory was then occupied by the Dutch Republic and Great Britain, led by military commanders such as the Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy.
June 1710: During the War of the Spanish Succession, the Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene led the Allied forces to victory in Douai in 1710. The Cambrin Lines were breached, and the strategic fortress of Douai fell under Dutch Republic and British military occupation.
November 1710: From the end of 1710 the campaign of the duke and prince Eugene of Savoy achieved new successes with the capture of Béthune, Saint-Venant and, at the beginning of November, Aire-sur-la-Lys.
September 1711: The Duke of Marlborough continued to hold command of the Anglo-Dutch forces in northern France, and in August he managed to bypass Villars and pass through the formidable Ne Plus Ultra defense lines, before capturing Bouchain on September 12th.
July 1712: Landrecies conquered the last fortress of the pré carré which divided it from Paris.
August 1712: In 1712, during the War of the Spanish Succession, the Duke of Marlborough led the reconquest of Douai and Le Quesnoy from French military occupation. This victory was a significant turning point in the conflict between France and the Grand Alliance.
December 1713: Freiburg conquered by france.
September 1704: Ulm and Ingolstadt conquered by austria.
September 1709: The allies invested Tournai in July. The citadel was only taken on 3 September.
September 1713: Landau, a fortified town in the Holy Roman Empire, was captured by the French under Marshal Villars in August 1713.
January 1705: Trier conquered by austria.
October 1708: Lille is besieged by the Allied (Spanish Succession).
July 1702: In June 1702, Kaiserswerth was captured by Prince Eugene of Savoy during the War of the Spanish Succession. The territory was then occupied by the Dutch Republic and Great Britain.
November 1704: The Treaty of Ilbersheim between Austria and Bavaria was signed on November 7, 1704, three months after the Battle of Blenheim. It had the effect of removing Bavaria from the War of the Spanish Succession. By the terms of the treaty, Bavaria was essentially placed under military occupation by Austria and the Palatinate.
3.1.Ramillies Campaign
Was a military campaign by England-Scotland and the Dutch Republic against French occupation in the Low Countries, during the War of the Spanish Succession.
May 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Louvain.
May 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Brussels.
June 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Oudenarde.
June 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Bruges.
July 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Ostend.
August 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Menin.
October 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Ath.
May 1706: Anglo-Dutch conquest of Ghent.
Was the theatre of war in Spain during the War of the Spanish Succession.
August 1704: British forces captured Gibraltar.
December 1705: Valencia conquered by austria.
June 1706: Portuguese, Dutch and English elements entered Madrid.
June 1706: During the War of the Spanish Succession, the city of Zaragoza was captured by the Allied forces on June 29, 1706. This victory was led by the Duke of Berwick, a prominent military leader in the Spanish army who fought for the Bourbon dynasty.
July 1706: Alicante is taken by the Allies in 1706 in the wake of their landing at Barcelona.
October 1706: Philip V returned to Madrid at the beginning of October.
December 1707: Lleida conquered by Personal Union of Aragon and Castile.
September 1708: In 1708, an English expedition led by Admiral John Norris and General John Campbell landed in Sardinia as part of the War of the Spanish Succession. The island was occupied by Great Britain for strategic purposes, aiming to secure naval dominance in the Mediterranean.
August 1710: With the battle of Zaragoza the allies regained control of Aragon.
December 1710: During the War of the Spanish Succession, French forces led by the Duke of Vendôme captured British General James Stanhope in Brihuega on December 9, 1710. This event was a significant setback for the Grand Alliance forces.
December 1710: Even if the Count of Starhemberg was able to stand up to his enemies, the allies were subsequently forced into a hasty retreat towards Catalonia, reduced only to the regions of Tarragona, Igualada and Barcelona where they remained until the end of the war.
October 1705: Barcelona, surrounded by allied troops, capitulated on 9 October also due to a popular revolt that began in the La Ribera district.
October 1706: The islands of Ibiza and Maiorca conquered by austria.
August 1713: In March 1713, Count Sinzendorf, the emperor's delegate to the congress, signed an agreement for the evacuation of the imperial troops from Catalonia: the Empress departed from Barcelona on 19 March, followed the following July by Count Starhemberg.
September 1710: Charles III, the Habsburg pretender to the Spanish throne, entered Madrid in 1710, facing resistance from the city's residents who were loyal to the Bourbon dynasty.
October 1707: The Bourbons recovered the city of Ciudad Rodrigo through the Marquis of Bay.
January 1707: Ciudad Rodrigo is conquere by the Allied of the War of the Spanish Succession.
December 1707: Much of Aragon and Valencia returned to obedience to Philip V, and the allies were driven back into Catalonia, beyond the line of the Segre and Ebro rivers.
September 1708: British forces captured Minorca.
July 1708: The duke of Orléans took Tortosa in mid-July.
September 1705: The castle of Montjuïc fell into the hands of the allies.
July 1707: Claude François Bidal d'Asfeld retook Xátiva for Spain in June.
June 1707: With the allies in full retreat, the duke of Orléans arrived from Italy and joined the duke of Berwick to retake much of what had been lost in previous military campaigns: the city of Valencia and Zaragoza fell in May.
Was a war between the American territories of Great Britain against the the American territories of Spain and France. In Europe, it is generally viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession; in the Americas, it is more commonly viewed as a standalone conflict.
5.1.Newfoundland (Queen Anne’s War)
Was the theatre of War in Newfoundland during Queen Anne’s War.
January 1709: Newfoundland's coast was dotted with small French and English communities, with some fishing stations occupied seasonally by fishermen from Europe. Both sides had fortified their principal towns, the French at Plaisance on the western side of the Avalon Peninsula, the English at St. John's on Conception Bay. In December 1708, a combined force of French, Canadian, and Mi'kmaq volunteers captured St. John's.
January 1710: In 1709, the French under the command of Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville abandoned St. John's due to lack of resources. The English then reoccupied and refortified the territory, solidifying their control over the region.
5.2.Acadia and New England (Queen Anne’s War)
Was the theatre of War in Acadia and New England during Queen Anne’s War.
October 1710: In October 1710, 3,600 British and colonial forces led by Francis Nicholson finally captured Port Royal after a siege of one week. This ended official French control of the peninsular portion of Acadia.
Were a series of treaties to end the War of the Spanish Succession.
April 1713: In the Treaty of Utrecht Duke Vittorio Amedeo II of Savoy was assigned Sicily with the relative royal title, as well as Casale and all of Monferrato, part of Lomellina and Valsesia.
April 1713: In 1713, as part of the Treaty of Utrecht, Spain ceded the rock of Gibraltar and the island of Menorca in the Balearic Islands to England. This agreement was signed by the Spanish King Philip V and the British diplomat John Methuen.
April 1713: As a result of the Treaty of Utrecht that ended the War of Spanish Succession, the Spanish part of Guelders was partitioned. The Austrians received the areas of Roermond, Niederkrüchten and Weert.
April 1713: In 1713, as part of the Treaty of Utrecht, Spain ceded the rock of Gibraltar and the island of Menorca in the Balearic Islands to England. This decision was made by the Spanish King Philip V and the British Queen Anne as a result of the War of Spanish Succession.
April 1713: In 1713, the region of Upper Gelderland, known as Overkwartier, was divided between Prussia. This included Gelderland, Viersen, Horst, and Venray. The transfer of territory was part of the Treaty of Utrecht, which ended the War of the Spanish Succession.
April 1713: In 1713, the territories of Venlo, Montfort, and Echt were ceded to the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands, also known as the Dutch Republic. This was part of the Treaty of Utrecht, which ended the War of the Spanish Succession. The Dutch Republic was a confederation of provinces in the Low Countries, led by the Stadtholder William IV of Orange.
April 1713: The viguerie of Barcelonnette (also comprising Saint-Martin and Entraunes) was reattached to France in 1713 as part of a territorial exchange with the Duchy of Savoy during the Treaties of Utrecht.
Was a peace treaty between France and Austria that was concluded on 7 March 1714 in the Baden city of Rastatt to end the War of the Spanish Succession between both countries.
March 1714: At the end of the War of the Spanish Succession, Austria was awarded the Spanish territories in Italy, including Naples, Milan, Sardinia, as well as the Southern Netherlands.
August 1714: The Electorate of Hanover was in personal union with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland since 1714.
Was a treaty between France and the Holy Roman Empire, to end the War of the Spanish Succession.
September 1714: The treaty of Rastatt in 1714 allowed France, under the rule of King Louis XIV, to retain control of Alsace and Landau, solidifying French territorial gains in the region following the War of the Spanish Succession.
September 1714: In the Treaty of Baden the French and their allies returned the east bank of the Rhine River (the Breisgau) to Austria.
September 1714: Treaty of Baden in 1714.
Selected Sources
Ramillies campaign 1706 - Allied gains. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 1 April 2024 on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ramillies_campaign_1706_-_Allied_gains.png
Saunders Webb, S. (2013): Marlborough's America, New Haven (USA), p. 144
 War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession