World War I western Front
World War I western Front
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the theatre of war in western Europe during World War I.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
May 1915: Second Battle of Artois: On 9 May, five French corps had attacked two German divisions on a 25 km front and advanced 4 km on the front of the 5th Bavarian Reserve Division between the Lorette Spur and La Targette. The 77th Division and the DM of XXXIII Corps penetrated between Carency and Neuville.
May 1915: Second battle of Artois: the French army conquered Carency.
May 1915: With the Second Battle of Artois, Ablain-Saint-Nazaire is freed by French forces.
June 1915: Second Battle of Artois: Neuville is freed by French forces.
September 1915: Third Battle of Artois: French III and XII Corps proceeded slowly and with little progress southeast of Neuville-Saint-Vaast.
February 1916: Battle of Verdun: The Germans took Fort Douaumont and then French reinforcements halted the German advance by 28 February.
June 1916: With the aid of diphosgene gas, the Germans came within 1 km of the last ridge before Verdun.
July 1916: Advancement of the French up to July 14.
January 1917: By December 1916 the French had pushed the Germans back 2.1 km from Fort Douaumont.
March 1917: The French took Péronne.
March 1917: The German retirement took place between 9 February and 20 March 1917, after months of preparation. The German retreat shortened the Western front by 40 km.
April 1917: Battle of Arras: initial French advancement.
April 1917: The Nivelle Offensive was a failed military operation led by French General Robert Nivelle during World War I. It took place in 1917 in the region of Chemin des Dames in France. The offensive resulted in heavy casualties and led to widespread mutinies within the French army.
June 1917: Battle of Messines (1917).
September 1917: Battle of Passchendaele.
December 1917: Battle of Passchendaele.
June 1915: During the First World War, Neutral Moresnet was annexed by Germany.
May 1915: Second Battle of Artois: After the initial disbandment the Germans concentrated their reserves on 140m altitude and repulsed the attack.
November 1916: The final phase of the battle took place in October and early November, again producing limited gains with heavy loss of life. All told, the Somme battle had made penetrations of only 8 kilometres and failed to reach the original objectives. The advancement showed on map are up to november.
April 1917: The French Third Army in the centre advanced astride the Scarpe River and in the south, the British Fifth Army attacked the Hindenburg Line but made few gains. The British armies then conducted smaller attacks to consolidate the new positions.
June 1915: Second Battle of Artois: the French were driven back after a few days, due to the very intense reaction of the German artillery and infantry.
November 1917: Battle of Passchendaele: The Canadian Corps relieved the II ANZAC Corps and took the village of Passchendaele on 6 November.
November 1917: Battle of Cambrai:On 20 November the British launched the first massed tank attack and the first attack using predicted artillery-fire. he attack was a great success for the British, who penetrated further in six hours than at the Third Ypres in four month.
September 1915: Third Battle of Artois: Battle of Loos: The British were able to break through the weaker German defences and capture the village of Loos-en-Gohelle, mainly due to numerical superiority.
July 1916: On 1 July, after a week of heavy rain, British divisions in Picardy began the Battle of the Somme with the Battle of Albert, supported by five French divisions on their right flank. The attack had been preceded by seven days of heavy artillery bombardment. The experienced French forces were successful in advancing but the British artillery cover had neither blasted away barbed wire, nor destroyed German trenches as effectively as was planned.
September 1915: Third Battle of Artois: French XXXIII and XXI Corps had taken the town of Souchez.
May 1916: The Germans turned their focus to Le Mort Homme. After some of the most intense fighting of the campaign, the hill was taken by the Germans in late May. On 24 May, the Germans took the second summit, Côte 295.
April 1917: French advancement after the Battles of Arras and of Vimy Ridge.
July 1917: Battle of Passchendaele.
March 1917: During the Somme battle and through the winter months, the Germans created a fortification behind the Noyon Salient that would be called the Hindenburg Line. During the German withdrawal, the British Third Army and Fifth Army followed up and conducted the Capture of Bapaume, 17 March 1917.
June 1916: The Germans captured Fort Vaux on 7 June.
June 1916: The German advance was contained on 23 June.
September 1915: Third Battle of Artois: In very wet weather the French Tenth Army captured Vimy Ridge, except for the highest point, where German counter-attacks retook the ground from XXXIII Corps.
September 1916: Advancement of the French forces up to 15 september.
May 1917: The Nivelle Offensive was a failed military operation led by French General Robert Nivelle during World War I. It took place in 1917 in the region of Chemin des Dames in France. The offensive resulted in heavy casualties and led to widespread mutinies within the French army.
December 1917: Battle of Cambrai: The advance produced an awkward salient and a surprise German counter-offensive began on 30 November, which drove back the British in the south and failed in the north.
December 1916: The French recaptured Fort Vaux in November.
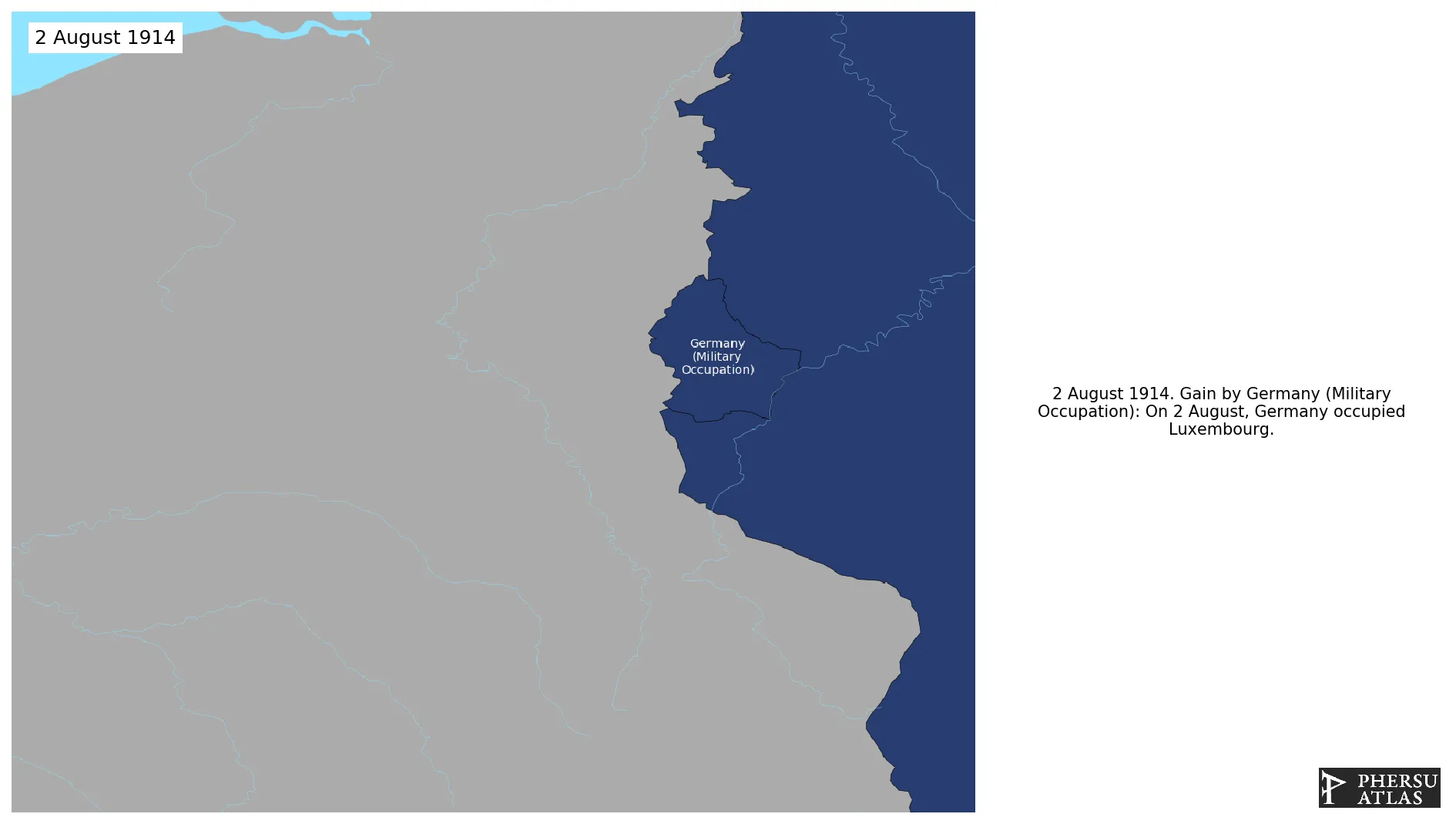
Was the German occupation of Luxembourg during World War I.
August 1914: On 2 August, Germany occupied Luxembourg.
Was the German offensive in the Flanders at the beginning of World War I.
August 1914: The First and Second Armies, led by French generals Joseph Joffre and Auguste Dubail, attacked towards Sarrebourg-Morhange in Lorraine, which was then under German control. The battle resulted in the territory being occupied by France.
August 1914: German siege at Namur that lasted from about 20-23 August.
August 1914: Battle of Mons.
August 1914: Siege of Maubeuge.
August 1914: Battle of St. Quentin.
September 1914: The German Army came within 70 km of Paris but at the First Battle of the Marne (6-12 September).
October 1914: Race for the Sea: German forces arrive in Ypres and Baielleul.
October 1914: Changes of the Western front by 8 October 1914.
August 1914: Armies under German generals Alexander von Kluck and Karl von Bülow attacked Belgium on 4 August 1914 and occupied Liege.
August 1914: The French occupied Mulhouse on 8 August.
August 1914: French forces captured Mulhouse, a city in Alsace, from the German Empire. However, they were later forced out by German counter-attacks led by General August von Mackensen and Crown Prince Wilhelm.
September 1914: Race for the Sea: German forces arrive in Ham.
May 1915: Second Battle of Ypres: by the end of the battle the Ypres salient was compressed, with Ypres closer to the line.
August 1914: Battle of Charleroi.
October 1914: Germans take Antwerp.
August 1914: The Belgian capital, Brussels, fall to the Germans.
October 1914: Race for the Sea: German forces arrive in Bapaume.
September 1914: The opposing forces in Western Europe made reciprocal outflanking manoeuvres, known as the Race for the Sea and quickly extended their trench systems from the Swiss frontier to the North Sea.
September 1914: Race for the Sea: German forces arrive in Mericourt.
August 1914: The first battle in Belgium was the Siege of Liège, which lasted from 5-16 August.
Was a series of German attacks along the Western Front during the First World War, beginning on 21 March 1918. Following American entry into the war in April 1917, the Germans decided that their only remaining chance of victory was to defeat the Allies before the United States could ship soldiers across the Atlantic and fully deploy its resources.
March 1918: Somme Offensive.
April 1918: Somme Offensive.
April 1918: The Lys Offensive was a major German attack on the Western Front during World War I in April 1918. The Germans managed to penetrate Allied lines to a depth of 9.3 mi (15 km).
June 1918: Aisne Offensive.
July 1918: Champagne-Marne Offensive.
June 1918: Noyon-Montdidier Offensive.
Was the last major German offensive on the Western Front during the First World War.
July 1918: Second Battle of the Marne.
August 1918: Second Battle of the Marne.
Was a series of massive Allied offensives that led to the collapse of the Western Front and of the German Empire.
August 1918: Allied advancement up to 30 August.
September 1918: Avancement up to 25 September.
October 1918: Battle of Cambrai.
October 1918: Courtrai is liberated by the British Second Army.
October 1918: The British arrived in Roubaix.
November 1918: Entente advance in central Europe by 11 November 1918.
August 1918: Battle of Amiens (1918).
September 1918: Allied advancement up to 25 September.
August 1918: Second Battle of the Somme: Bapaume fell to the French on 29 August.
August 1918: Second Battle of the Somme: Albert was captured by the French on 22 August.
September 1918: Havrincourt and St Mihiel conquered by French Third Republic.
September 1918: The Germans had been forced back to the Hindenburg Line.
Selected Sources
Cook, C. / Stevenson, J. (2006): The Routledge Companion to World History since 1914, Routledge, p.3
Cook, C. / Stevenson, J. (2006): The Routledge Companion to World History since 1914, Routledge, p.4
 World War I western Front
World War I western Front