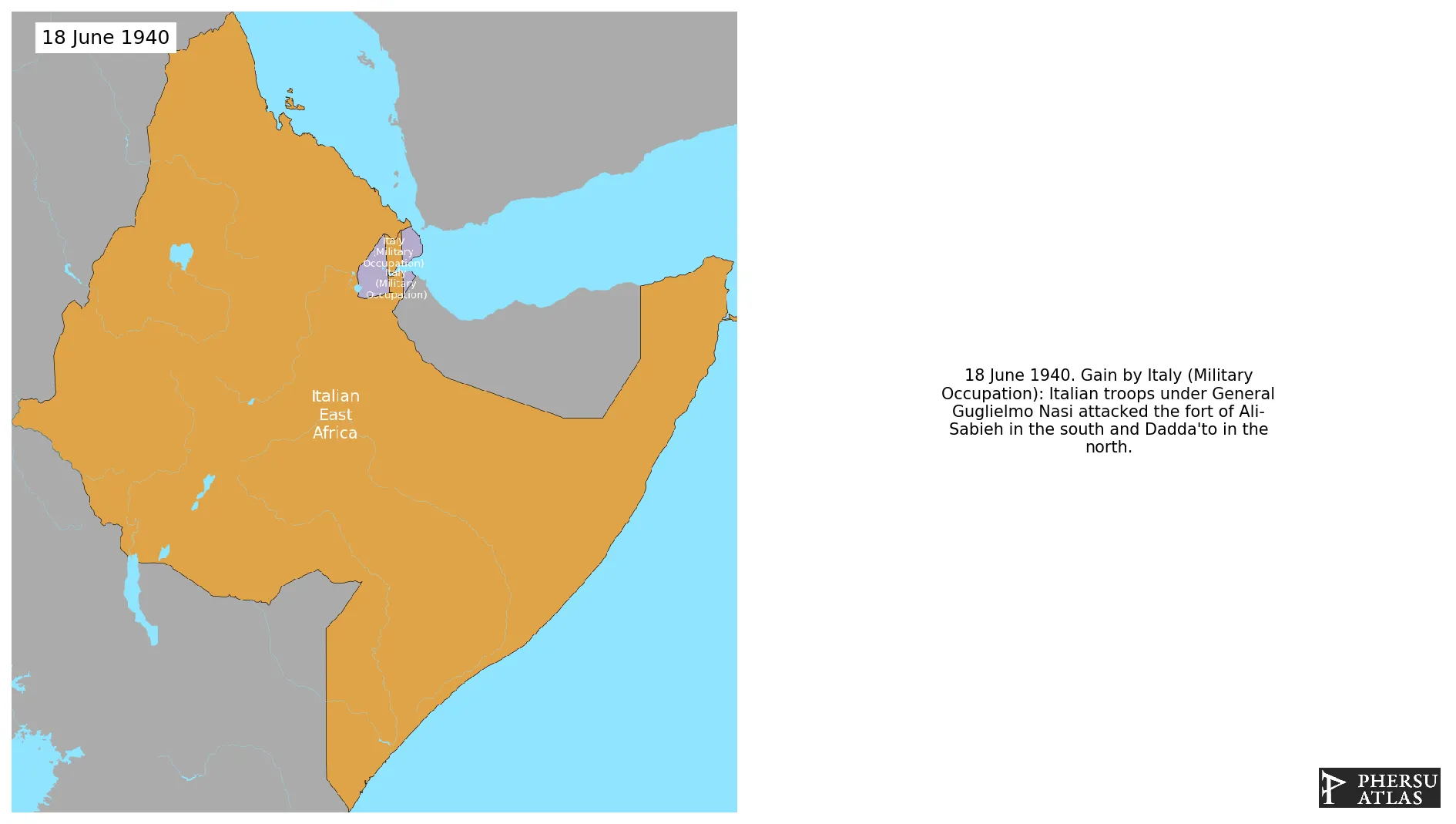
World War II (East African Theatre)
World War II (East African Theatre)
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the East African theatre of World War II.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was an Italian military campaign in French Somaliland during World War II.
June 1940: Italian troops under General Guglielmo Nasi attacked the fort of Ali-Sabieh in the south and Dadda'to in the north.
June 1940: By the end of June the Italians had also occupied the border fortifications of Magdoul, Daimoli, Balambolta, Birt Eyla, Asmailo, Tewo, Abba, Alailou, Madda and Rahale.
December 1942: Christian Raimond Dupont, Governor of French Somaliland, surrendered to British forces. French Somaliland ceased to be part of the Vichy France colonial empire.
July 1940: Germain succeeded Legentilhomme as commander-in-chief of French forces. He was loyal to Vichy France.
August 1940: When the Italian invasion of British Somaliland began on 3 August, the forces at Loyada moved on Zeila, which they had taken by 5 August.
August 1940: The Italian 17th Colonial Brigade under Colonel Agosti occupied the French fort at Loyada on the border with British Somaliland in early August.
November 1940: The border area of western French Somaliland was occupied by Italian troops. Under increasing British pressure, the Italians withdrew from Hanlé beginning in October 1940 and from Dagguirou by April 1941, when the French had returned.
May 1941: The French returned in Dagguirou.
Was an Italian military campaign in Sudan during World War II.
July 1940: The Italian army captured Kassala, then Gallabat.
July 1940: Karora and Kurmuk were taken by Italian forces.
January 1941: British General William Platt occupied the Eritrean city of Gallabat.
January 1941: On 21 January 1941, the Italian command, under British pressure, decided to evacuate Cassala and other difficult to defend locations to shorten the front.
Was the Italian invasion of British East Africa (Kenya) during World War II.
July 1940: The Italians carried out a larger attack by about four battalions on 10 July, after a considerable artillery bombardment and after three days the British withdrew unopposed. The Italians eventually advanced to water holes at Dabel and Buna, nearly 100 km inside Kenya but lack of supplies prevented a further advance.
March 1941: Dabel and Buna remained under Italian control until liberated in February 1941.
Was the Italian conquest of British Somaliland during World War II.
August 1940: The Italian invasion force occupied Hargeisa.
August 1940: The Italian northern column reached Zeila despite naval bombardments.
August 1940: The British retirement was followed up cautiously by the Italians, who attacked the defenders at Barkasan.
August 1940: By 10 August, de Simone had closed up on the British positions behind the Tug Argan and prepared the Italian attack.
August 1940: In the north, the Bertoldi column captured Zeila, about 240 km north-west of Berbera, cutting communications with French Somaliland and then began a slow advance south-east along the coast road, under intermittent air attack from Aden and bombardment from the sea, pushing back the SCC rearguards as far as the village of Bulhar by 17 August.
August 1940: The Italian eastern column, comprising mainly Eritrean Bande (colonial troops), reached Odweina.
August 1940: Italian forces entered Berbera victorious on 19 August 1940, just over 2 weeks after the start of the offensive in British Somaliland.
Was the British invasion and occupation of Italian East Africa during World War II.
January 1941: The brigade retreated on the night of 22/23 January, leaving Italian General Ugo Fongoli, his staff and 800 men behind as prisoners.
January 1941: Battle of Agordat.
February 1941: Banno was captured by British forces.
February 1941: Afmadu was captured on 11 February by British forces.
February 1941: Mega conquered by great britain.
February 1941: Jelib was attacked on both flanks and from the rear. The Italians were routed and 30,000 were killed, captured or dispersed in the bush.
February 1941: Moyale, 110 km south-east of Mega on the border with Kenya, was occupied.
February 1941: British forces occupied Italian Somaliland and militarily administered the territory.
March 1941: By early March Cunningham's forces had captured most of Italian Somaliland.
March 1941: The 5th Indian Division captured Fort Dologorodoc.
March 1941: The town of Barbera was captured by the British.
March 1941: British forces advanced westwards into eastern Ethiopia and in late March, linked with forces from the Southern Front around Harar and Diredawa.
March 1941: On 26 March, Harar was captured by the British.
March 1941: Keren was captured by British forces after a battle lasting 53 days.
April 1941: Asmara was declared an open town and the British entered unopposed.
April 1941: The British came to control Ogaden, and later Haud, in the aftermath of the East African Campaign in 1941.
April 1941: On 6 April 1941, Addis Ababa was occupied by British forces led by officer Harry Wetherall.
April 1941: Bonetti surrendered and the Allied force took 9,590 prisoners and 127 guns. Aosta ordered the governor, Agenore Frangipani, to surrender the city to forestall a massacre of Italian civilians, as had occurred in Dire Dawa. Ashamed of not being allowed by his superior to fight to the death in the old style, the Italian governor, General Agenore Frangipani, killed himself with poison the next day.
April 1941: The South Africans captured Dessie on the main road north from Addis Ababa to Asmara.
May 1941: British occupation of Eritrea.
September 1941: On 28 September 1941, after losing 950 casualties and running out of provisions, Gonella surrendered with 1,629 Italian and 1,450 Ethiopian soldiers to the 25th East African Brigade (Brigadier W. A. L. James).
November 1941: The Occupied Enemy Territory Administration in Ethiopia was a British military occupation administration in Ethiopia during East African Campaign of World War II. It expanded from early 1941 until the final Italian defeat in November.
December 1941: The Anglo-Ethiopian Agreement was a joint effort between Ethiopia and the United Kingdom at reestablishing Ethiopian independent statehood following the ousting of Italian troops by combined British and Ethiopian forces in 1941 during the Second World War.
February 1941: On 25 February 1941, the motorised 23rd Nigerian Brigade (11th African Division) advanced 378 km up the coast in three days and occupied the Somali capital of Mogadishu unopposed.
February 1941: On the night of 31 January/1 February, the Italians retreated along a track towards Tole and Arresa and on 8 February, abandoned vehicles were found by the pursuers.
March 1941: By 17 March, the 11th (African) Division completed a 17-day dash along the Italian Strada Imperiale (Imperial Road) from Mogadishu to Jijiga in the Somali region of Ethiopia.
July 1941: The Italians were cut off by the Free Belgian forces (Major-General Auguste Gilliaert) who had defeated the Italians at Asosa and Saïo.
March 1941: On 20 March, Hargeisa was captured by the British.
May 1941: The Duke of Aosta and his garrison surrendered in Amba Alagi to the British commander, Lieutenant-General Sir Alan Cunningham.
March 1941: On 29 March 1941, Dire Dawa was occupied by British forces.
February 1941: On 2 February, the British took Hobok.
February 1941: The port of Kismayu, located in present-day Somalia, was captured by British forces.
June 1941: Italian forces held out at Assab, the last Italian harbour on the Red Sea. Operation Chronometer took place from 10 to 11 June, with a surprise landing at Assab by the 3/15th Punjab Regiment from Aden, carried by a flotilla comprising HMS Dido, Indus, Clive, Chakdina and SS Tuna.
February 1941: An advance force of the South African Division captured Jumbo.
June 1941: Italian general Gazzera abandoned Jimma and about 15,000 men surrendered to the British.
November 1941: British forces captured Gondar.
Selected Sources
Playfair, I. S. O. et al. (1959): The Mediterranean and Middle East: The Early Successes Against Italy (to May 1941). History of the Second World War, United Kingdom Military Series. Vol. I (4th impr. ed.), London (UK), pp. 418-420
Thompson, Virginia McLean; Adloff, Richard (1968). Djibouti and the Horn of Africa. Stanford University Press. p. 21.
 World War II (East African Theatre)
World War II (East African Theatre)