Voyages of Christopher Columbus
Voyages of Christopher Columbus
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Between 1492 and 1504, Italian explorer Christopher Columbus led four Spanish transatlantic maritime expeditions in the Americas. The first voyage marked the European discovery of the American Continent and is also widely considered the end of the Middle Ages.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
November 1493: In 1493, Christopher Columbus sighted the island of Saba during his second voyage to the Americas. Saba is a small Caribbean island that was eventually claimed by the Spanish as part of their territories in the Americas.
January 1494: In 1493, Christopher Columbus arrived at St. Christoph (now St. Kitts) and claimed the island for Spain during his second voyage to the Americas.
January 1494: Vieques, a small island off the coast of Puerto Rico, was reportedly discovered by Christopher Columbus during his second voyage to the Americas in 1493. The territory was then claimed by Spanish America as part of their colonial holdings.
January 1499: In 1498, Christopher Columbus discovered and claimed Saint Barthélemy for Spain during his third voyage to the Americas. The island later became part of the Spanish America territory.
November 1493: Marie-Galante was the second island encountered by Christopher Columbus during his second voyage in 1493, after Dominica. The territory was eventually claimed by Spanish America.
November 1493: During his second expedition for America, Christopher Columbus discovered the small archipelago Îles des Saintes in 1493. The territory went to Spanish America.
November 1493: Christopher Columbus discovers the Island of Saint Martin.
November 1493: In 1493, Christopher Columbus landed on Saint-Croix (Santa Cruz) during his second voyage to the Americas. He claimed the territory for Spanish America, marking the beginning of European colonization in the Caribbean.
December 1493: Christopher Columbus, an Italian explorer sponsored by the Spanish monarchy, was the first European to see Guadeloupe in November 1493 during his second voyage to the Americas. He named the island after a Spanish monastery.
January 1494: Christopher Columbus arrives in Antigua (1493) and names the island in honour of the "Virgin of the Old Cathedral" found in Seville Cathedral in southern Spain.
January 1495: The island of Jamaica came under Spanish rule in 1494 following the arrival of the famous explorer Christopher Columbus. Columbus claimed the territory for the Spanish crown during his second voyage to the Americas.
May 1503: The Cayman Islands were discovered by Christopher Columbus during his final voyage to the Americas in 1503. The territory was later claimed by Spanish America.
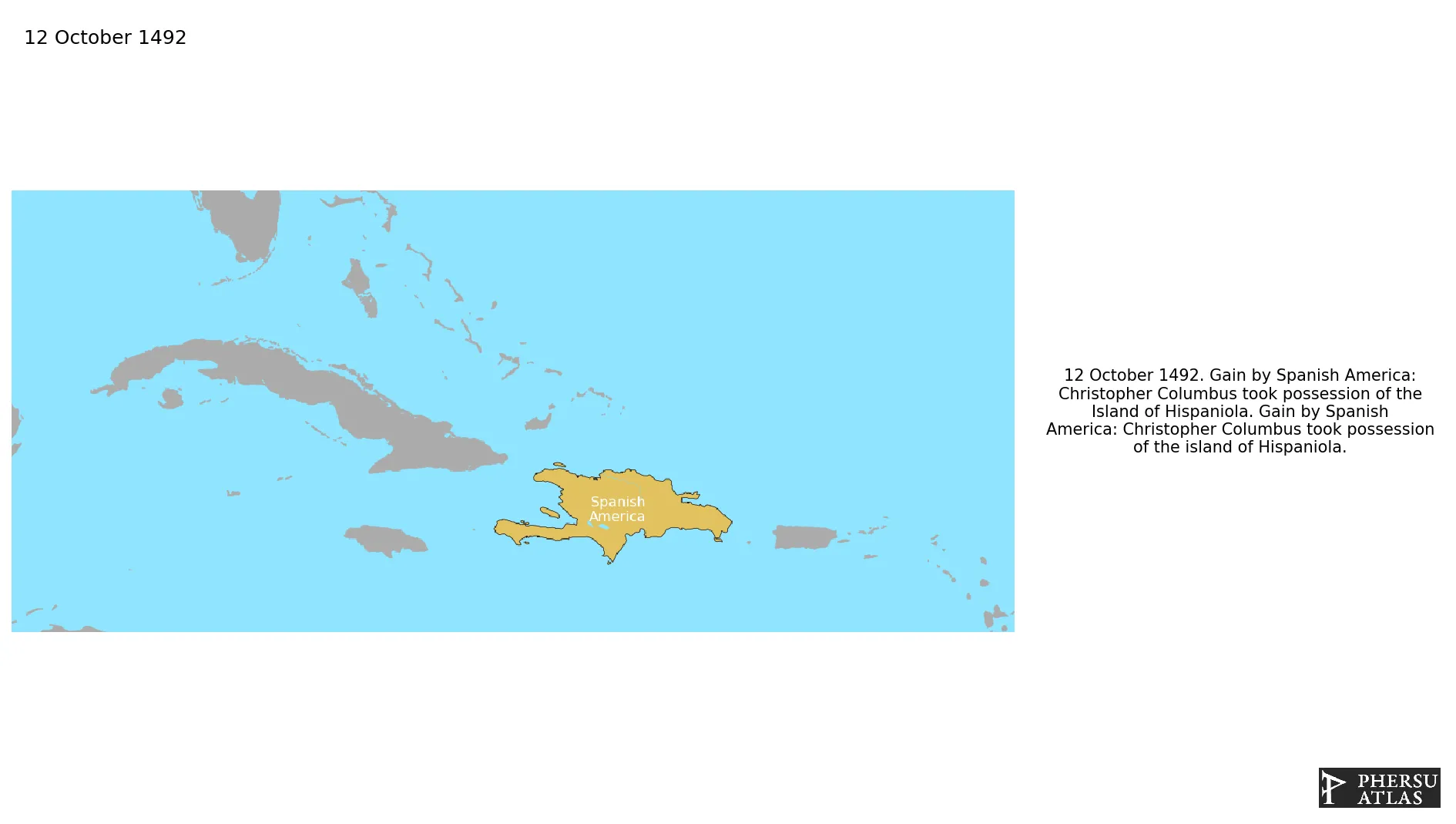
October 1492: Christopher Columbus took possession of the Island of Hispaniola.
October 1492: Christopher Columbus took possession of the island of Hispaniola.
January 1493: Christopher Columbus, an Italian explorer, was the first European to see the islands of the Bahamas, making his first landfall in the 'New World' in 1492. Columbus's arrival marked the beginning of Spanish colonization in the Americas.
January 1494: Christopher Columbus sailed past St. John on his second voyage in 1493.
July 1502: Christopher Columbu discovered Las Guanajas Islands (Bay Islands, modern-day Honduras) on July 30, 1502. The Admiral named it 'Isle of Pines', and claimed it for Spain.
November 1493: In 1493, Christopher Columbus likely saw the island of Sint Estatius, which later became part of Spanish America. Columbus was an Italian explorer who completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean, opening the way for widespread European exploration and the eventual colonization of the Americas.
 Voyages of Christopher Columbus
Voyages of Christopher Columbus