 kingdom of ormuz
kingdom of ormuz
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
Kingdom of Ormuz
Kingdom of Ormuz (Portugal)
Establishment
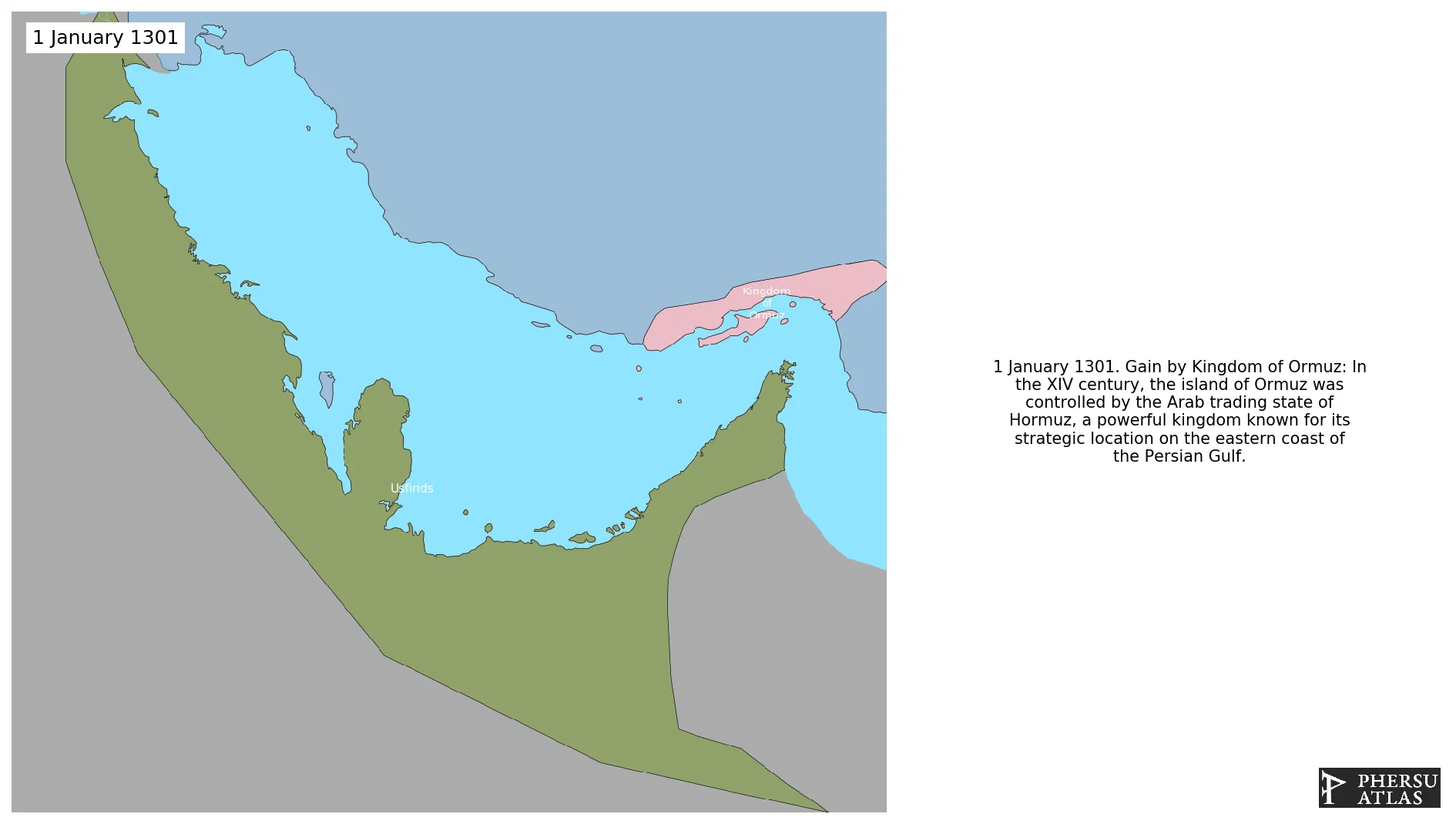
January 1301: In the XIV century, the island of Ormuz was controlled by the Arab trading state of Hormuz, a powerful kingdom known for its strategic location on the eastern coast of the Persian Gulf.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Capture of Hormuz in 1507 occurred when the Portuguese Afonso de Albuquerque attacked Hormuz Island to establish the Fortress of Hormuz.
November 1507: Portuguese conquest of Ormuz.
Conquests and wars with Ottoman involvement during the rule of Suleiman I.
January 1561: The area was occupied by Ottoman forces in the middle of the 16th century under the leadership of Suleiman the Magnificent, who expanded the empire's territory into the Lhasa eyalet region in 1560.
Was a succession crisis caused by the death of the King of Portugal without heirs. The conflict saw two main claimants to the Portuguese throne: António, Prior of Crato, proclaimed in several towns as King of Portugal, and his first cousin Philip II of Spain, who eventually succeeded in claiming the crown, reigning as Philip I of Portugal.
October 1580: Philip II of Spain succeeded in claiming the Portuguese crown, reigning as Philip I of Portugal.
Was a global conflict between the Portuguese Empire and the Dutch Empire. The conflict primarily saw the Dutch companies invading Portuguese colonies in the Americas, Africa, and the East Indies.
4.1.Operations in the Pacific and Indian Oceans
Were the military operations of the Dutch in the Pacific and Indian Oceans during the Dutch-Portuguese War.
January 1622: The Battle of Hormuz in 1621/2 against the English East India Company resulted in the loss of the fortress of Hormuz to the combined forces of Persia and England which dislodged the Portuguese from the Middle East.
January 1321: The Usfurids had an uneasy relationship with the main regional power at the time, the princes in Hormuz, who took control of Bahrain and Qatif in 1320.
January 1358: In 1357, the Khan of the Golden Horder Jani Beg of the Golden Horde conquered Chupanid-held Tabriz for a year, putting an end to the Ilkhanate remnant.
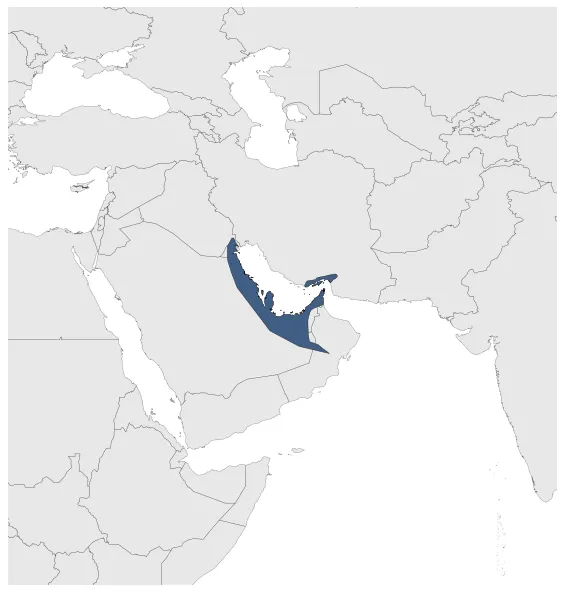
January 1418: The Kingdom of Ormuz dominated eastern Arabia until the 16th century.
January 1418: The Jabrids were a dynasty that dominated eastern Arabia in the 15th and 16th centuries. They belonged to the tribe of Bani Khalid.
January 1501: From 1500, Kuwait was under the influence of the Kingdom of Hormuz for two centuries.
January 1515: Bandar Abbas was conquered by the Portuguese in 1514.
April 1622: The Safavid ruler Abbas I of Persia expelled the Portuguese from the Persian Gulf, with the exception of Muscat.
Disestablishment
January 1622: The Battle of Hormuz in 1621/2 against the English East India Company resulted in the loss of the fortress of Hormuz to the combined forces of Persia and England which dislodged the Portuguese from the Middle East.
April 1622: The Safavid ruler Abbas I of Persia expelled the Portuguese from the Persian Gulf, with the exception of Muscat.
Selected Sources
Atwood, C. P. (2004): Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, New York (USA), p. 236
Fernández Álvarez, M. (1998): Felipe II y su tiempo, cuarta edición, p. 523

 kingdom of ormuz
kingdom of ormuz