If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Territories militarly occupied by Australia.
Establishment
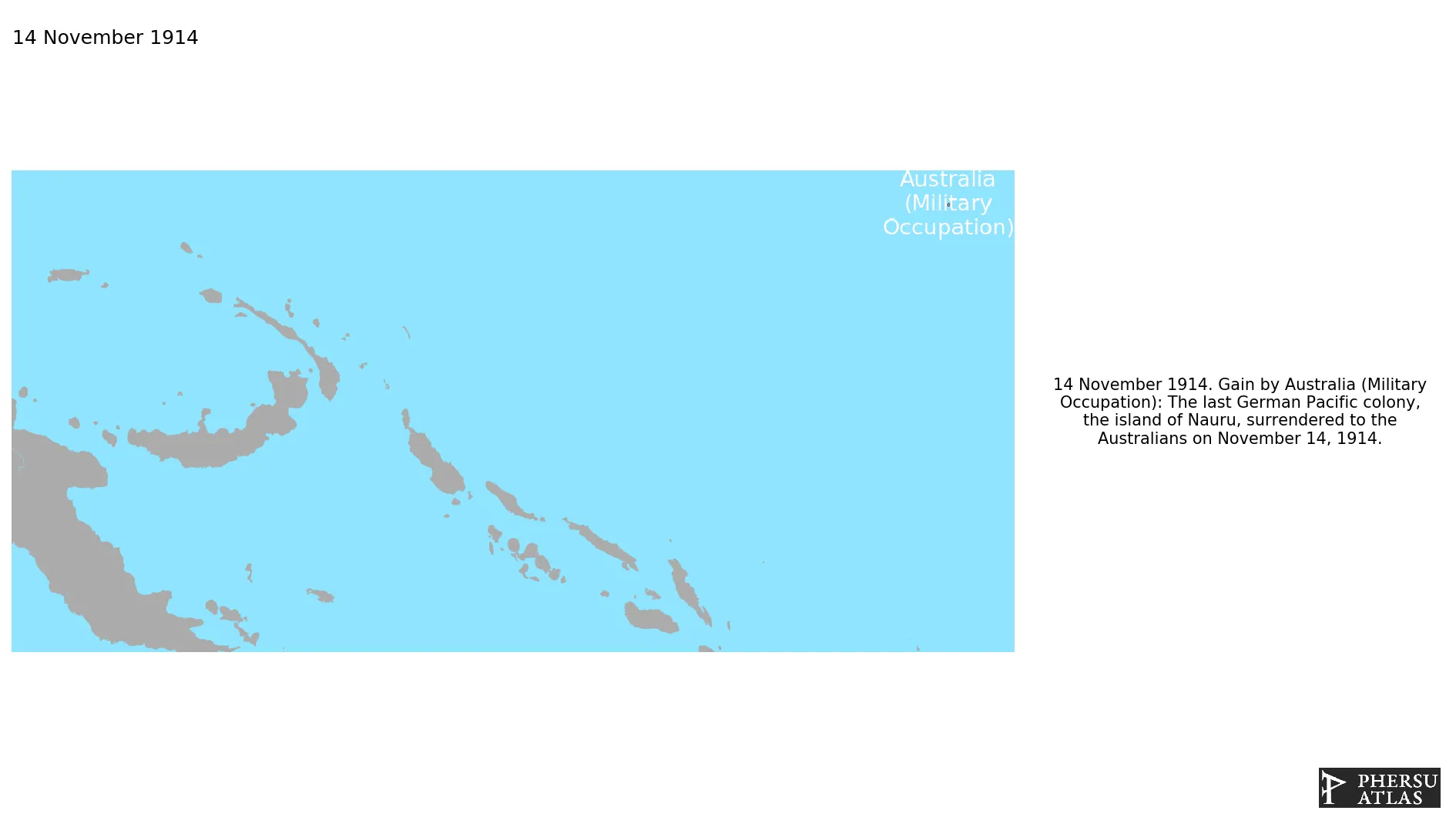
November 1914: The last German Pacific colony, the island of Nauru, surrendered to the Australians on November 14, 1914.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
1.1.World War I Pacific Theatre
Was the Pacific theatre of World War I.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
2.1.World War II (Asia & Pacific)
Was the East Asian, South Asian and Pacific theatre of World War II.
2.1.1.New Guinea Campaign
Was a military campaign that started when Japan invaded the island of New Guinea.
September 1942: By September 1942 most of New Guinea island is occupied by Japan.
2.1.1.1.Kokoda Track Campaign
A series of battles fought between July and November 1942 by the Japanese invaders and the Allies, in what was then the Australian Territory of Papua.
August 1942: Isolated and under attack, the Japanese withdrew from Kokoda during the night of 9 August.
August 1942: Japanese attack Maroubra Force at Deniki in strength, forcing it back beyond Isurava, 5 miles from Deniki.
October 1942: Australian forces advanced to Kokoda Trail, in the vicinity of Eora Creek, where fighting continued with the Japanese.
November 1942: Australian 16th Brigade forces Japanese from Oivi toward Kumusi River mouth.
December 1942: Gona is taken by the Australians. Japanese sustain heavy casualties while trying unsuccessfully to withdraw from Gona to Giruwa.
January 1943: Australian forces capture Buna on 2 January 1943.
2.1.1.2.Battle of Milne Bay
Was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II in the Australian Territory of Papua.
September 1942: Australian forces defeat the Japanese who leave Milne Bay.
2.1.1.3.Markham and Ramu Valley - Finisterre Range campaign
Was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II in the Australian Territory of New Guinea.
September 1943: Australian amphibious assault at Scarlet Beach.
September 1943: Australian forces take Kaipit.
October 1943: Battle of Dumpu.
January 1944: Battle of Shaggy Ridge.
April 1944: Australian forces enter Madang, from which enemy has withdrawn.
2.1.1.4.Salamaua-Lae campaign
Was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II in the Australian Territory of New Guinea.
September 1943: The Japanese garrison at Salamaua withdrew and it was captured by Austrlian forces.
September 1943: Australian forces continue to advance toward Lae.
2.1.1.5.Huon Peninsula campaign
Was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II in the Australian Territory of New Guinea.
October 1943: The Australian army takes control of Finschhafen and its airfield.
November 1943: Sattelberg falls to troops of Australian 9th Division.
January 1944: US Army landing at Saidor.
2.1.1.6.New Britain campaign
Was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II in the Australian Territory of New Guinea.
January 1944: Battle of Cape Gloucester.
March 1944: Battle of Talasea.
October 1944: Australian conquest of Cape Hoskins.
December 1944: Japanese conquest of Bialla Plantation.
December 1944: Australian conquest of Cape Koas.
December 1944: Australian conquest of Sampun.
January 1945: Australian conquest of Lolobau island, Ea Ea.
January 1945: Australian conquest of Kiep.
February 1945: Japanese conquest of Baia.
February 1945: Australian conquest of Kalai.
March 1945: Australian conquest of Tol.
September 1945: Following the Surrender of Japan in 1945, civil administration of Papua and New Guinea was restored, and under the Papua New Guinea Provisional Administration Act (1945-46), Papua and New Guinea were combined in an administrative union.
2.1.1.7.Admirality Islands Campaign
Was a series of battles in the New Guinea campaign of World War II in which the United States Army's 1st Cavalry Division took the Japanese-held Admiralty Islands.
March 1944: Australian advances during the Admirality Admirality Islands Campaign by March 6.
March 1944: Australian advances during the Admirality Admirality Islands Campaign by March 7.
March 1944: Australian advances during the Admirality Admirality Islands Campaign by March 8.
March 1944: Australian advances during the Admirality Admirality Islands Campaign by March 9.
March 1944: Austrlian conquest of Butjuo Luo Islands.
March 1944: Australian conquest of Lugos.
March 1944: Australian advances during the Admirality Admirality Islands Campaign by March 16.
March 1944: Australian advances during the Admirality Admirality Islands Campaign by March 17.
March 1944: Austrlian forces overrun Lorengau.
March 1944: Australian conquest of Rossum.
May 1944: The Admirality Islands Campaign is officially terminated by the Austrlian Sixth Army. The Islands are fully occupied.
2.1.2.Operation Cartwheel
Was a major military operation of the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul.
June 1943: Unopposed allied landings on Woodlark and Kiriwina Islands.
March 1944: Allied landing on Emirau.
2.1.2.1.Bougainville campaign
Was a series of land and naval battles of the Pacific campaign of World War II between Allied forces and the Empire of Japan on the Island of Bougainville and its surroundings.
November 1943: At 7:30 a.m. on November 1, Rear Admiral Theodore S. Wilkinson's Task Force 31 began landing Gen. Allen H. Turnage's 3rd Marine Division in Empress Augusta Bay in the Cape Torokina sector.
November 1943: The bulk of the US 73rd Division landed in Empress Augusta Bay.
December 1944: The Australians captured Pearl Ridge in December 1944.
August 1945: The last Japanese forces on Bougainville also surrendered as their country had six days earlier.
January 1915: In 1914, Nauru, also known as Pleasant Island, became part of the British Western Pacific Territories.
Disestablishment
January 1945: Australian conquest of Lolobau island, Ea Ea.
January 1945: Australian conquest of Kiep.
February 1945: Japanese conquest of Baia.
February 1945: Australian conquest of Kalai.
March 1945: Australian conquest of Tol.
August 1945: The last Japanese forces on Bougainville also surrendered as their country had six days earlier.
September 1945: Following the Surrender of Japan in 1945, civil administration of Papua and New Guinea was restored, and under the Papua New Guinea Provisional Administration Act (1945-46), Papua and New Guinea were combined in an administrative union.
Selected Sources
MacArthur, D. (1994): Reports of General MacArthur: The Campaigns of MacArthur in the Pacific. Volume 1, Center of Military History (Retrieved on https://www.history.army.mil/books/wwii/MacArthur%20Reports/MacArthur%20V1/), p. 139
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 188
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 194
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.115
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.133
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.135
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.136
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.138
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.143
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.149
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.159
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.181
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.49
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.54
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.59
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.65
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.73
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.81
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.52-53
.svg.png.webp)
.png.webp)
 Australia (Military Occupation)
Australia (Military Occupation)