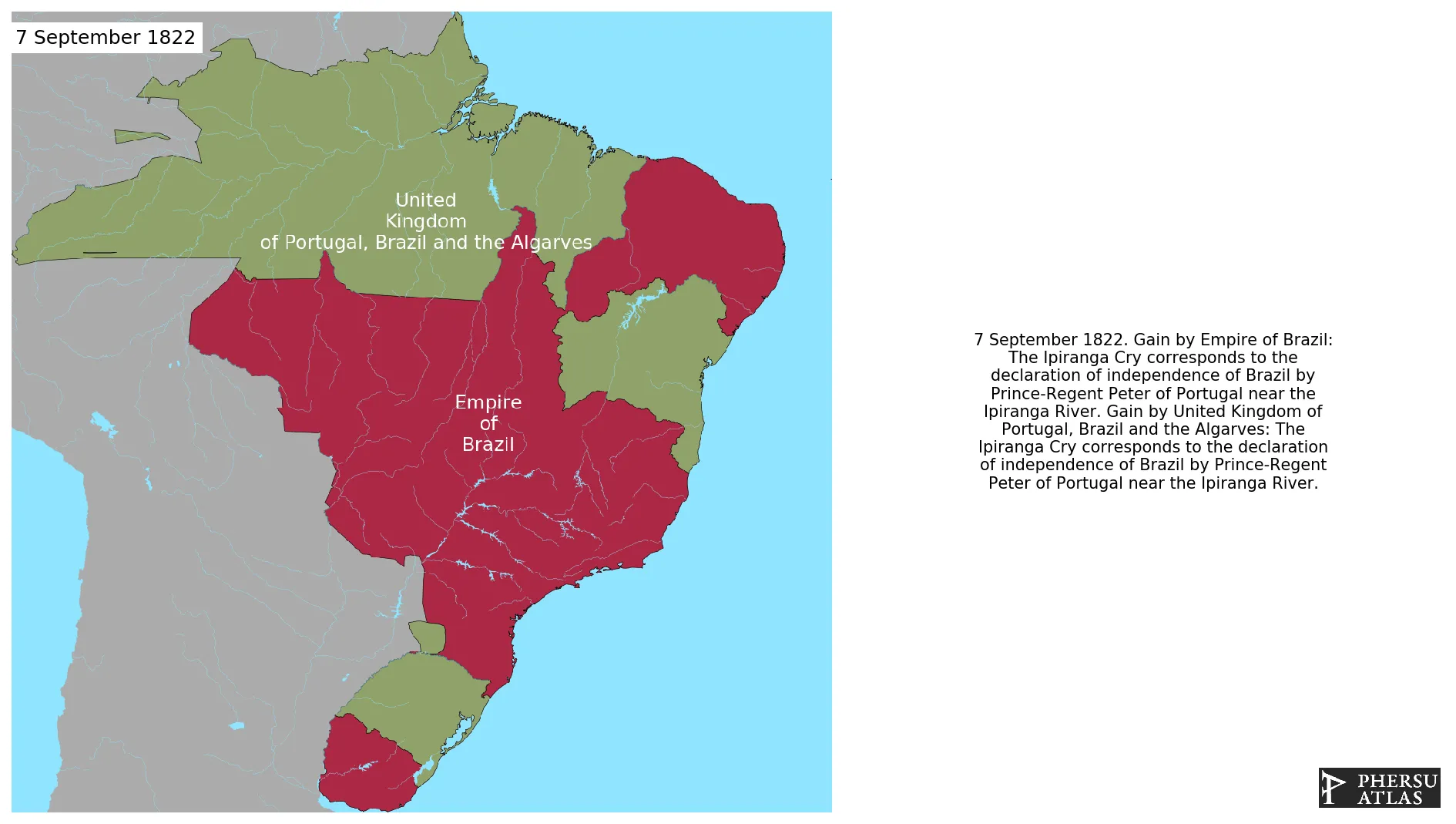
This article is about the specific polity Empire of Brazil and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the first form of the independent Brazilian state. It emerged from the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves in the first halph of the XIX century, the period of decolonization of South America.
Establishment
September 1822: The Ipiranga Cry corresponds to the declaration of independence of Brazil by Prince-Regent Peter of Portugal near the Ipiranga River.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the war of Brazil to become independent from the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves.
January 1823: Battle of Itaparica.
July 1823: Siege of Salvador.
July 1823: Siege of Caxias. The city fell to Brazilian forces.
December 1823: By November 1823, the whole of the north of Brazil was under Brazilian control.
March 1824: Siege of Montevideo (1823).
Was an armed conflict in the 1820s between the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata and the Empire of Brazil over Brazil's Cisplatina province. It resulted in the independence of Cisplatina as the Oriental Republic of Uruguay.
2.1.Treaty of Montevideo
The 1828 Treaty of Montevideo acknowledged the independence of the Cisplatina region from Brazil as the Republic of Uruguay.
August 1828: The 1828 Treaty of Montevideo acknowledged the independence of the Cisplatina under the name Eastern Republic of Uruguay.
During the Brazilian regency period (a decade of Brazilian history where there was no strong central power because the emperor was a minor) the degree of autonomy of the provinces was still not well defined and this led to a series of local secessions.
3.1.Cabanagem Revolt
Was a popular revolution and pro-separatist movement that occurred in the then province of Grão-Pará, Empire of Brazil.
January 1835: On the night the rebels attacked and conquered the city of Belém.
August 1835: Rebel forces were destroyed and retired toward the interior of Belém.
August 1835: Reorganizing their forces, the Rebels again attacked Belém on August 14. After nine days of battle, and suffering the death of Antônio Vinagre, they retook the capital.
May 1836: In March 1836, brigadier José de Sousa Soares Andréia attacked Bélem, as a result of which the rebel group decided to abandon the city in favor of resistance from the interior.
January 1841: The Cabanagem Revolt finally ended when amnesty was declared to the rebels, in 1839. In 1840 the last rebel group, under the leadership of Gonçalo Jorge de Magalhães, yielded.
3.2.Ragamuffin War
Was a Republican uprising that began in southern Brazil, in the province (current state) of Rio Grande do Sul in 1835. The revolt led to the creation of two secessionist states, the Riograndense Republic and the Juliana Republic.
3.2.1.Ragamuffin revolt
Was the initial phase of revolt of the Ragamuffin War.
September 1835: General Bento Gonçalves captured the capital, Porto Alegre, beginning an uprising against the perceived unfair trade reinforced by the provincial government.
June 1836: On the night of June 15 , 1836, with the help of a corrupt guard, the prisoners were released and, under the command of Marques de Sousa and with the help of Bento Manuel, the Imperials took over the city of Porto Alegre from the hands of the farroupilhas.
3.2.2.Secession of the Riograndense and Juliana Republics
Secession of the Riograndense and the Juliana Republic from Brazil during the Ragamuffin War.
September 1836: The Riograndense Republic was a de facto state that seceded from the Empire of Brazil roughly coinciding with the present state of Rio Grande do Sul. It was proclaimed on 11 September 1836, by General Antônio de Sousa Neto, as a direct consequence of the victory obtained by Gaúcho oligarchic forces at the Battle of Seival.
October 1836: Bento Manuel raised the “parliament” flag and Bento Gonçalves agreed to negotiate. The agreement was signed and signed on October 4.
April 1837: General Neto conquered Caçapava do Sul, an imperial refueling center.
March 1838: On March 9, 18 38 the farroupilhas invaded Lages , annexing the village to the Rio-Grandense Republic.
July 1839: The Farrapos, bypassing the imperial armada, managed to enter the Strait of the Capivari River and passed the boats ashore.
July 1839: Riograndense forces advanced from the Tomás José lagoon to the Tramandaí river.
July 1839: Finally, on July 14 , 1839, the lanes headed to Laguna to attack the neighboring province. On the coast of Santa Catarina, near the Araranguá River , a storm broke Farroupilha , miraculously saving a few rags, including Garibaldi himself.
July 1839: Laguna was taken by the Riograndense Republic, with help from the people of Laguna.
November 1839: The Juliana Republic was declared in the imperial Brazilian province of Santa Catarina on July 24, 1839, and lasted only until November 15, 1839.
December 1839: The Brazilian army retook Lages.
December 1839: In a close fight the loyalist troops were defeated by Brigadier Francisco Xavier da Cunha in Lages. The city reverted again to Riograndense control.
3.2.3.Brazilian Counterattack (Ragamuffin War)
Was the counterattack of the Brazilian government against the secessionist Riograndense Republic during the Ragamuffin War.
February 1839: Caçapava , the capital of the Republic since February 14 , 1839, considered impregnable because of the difficult access, was invaded by the imperials.
August 1839: In July, Farrapos lost São Gabriel.
February 1845: Treaty of Poncho Verde: The treaty offered the rebels a full amnesty, full incorporation into the imperial army and the choice of the next provincial president. All the debts of the Riograndense Republic were paid off by the Empire and a tariff of 25% was introduced on imported charque. The Riograndense and Juliana Republics remained in the Empire of Brazil and are now two states of the Federative Republic of Brazil.
Was a war fought between the Argentine Confederation and an alliance consisting of the Empire of Brazil, Uruguay, and the Argentine provinces of Entre Ríos and Corrientes, with the participation of the Republic of Paraguay as Brazil's co-belligerent and ally. The war was caused by disputes over the Platine region between Brazil and Argentina.
4.1.Allied invasion of Argentina
Was the invasion of Argentina by an alliance of countries led by Brazil during the Platine War.
January 1852: At the Battle of Alvarez Field the Allied vanguard defeated a force of 4,000 Argentines.
A series of armed conflicts between the leaders of Uruguayan independence.
February 1852: Montevideo was able to withstand the siege for nine years. When the British and French ceased their support in 1850 and signed an agreement with de Rosas, victory for the Blancos seemed certain. A revolt against de Rosas, led by Justo José de Urquiza, abruptly changed the situation. Oribe and his followers had to retreat in 1851 and the Colorados gained full control of Uruguay with the support of Brazil.
Was a war between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. The war began due to disputes over areas in the Platine region. Paraguay was militarly occupied by the Triple Alliance and lost around 30% of its territory to Argentina and Brazil.
6.1.Mato Grosso Campaign
Was a Paraguayan military campaign in Mato Grosso (Brazil) during the Paraguayan War.
January 1865: Resquín occupied the village of Nioaque.
February 1865: Continuing its advance into enemy territory, the column occupied the village of Miranda.
May 1865: Coxim was taken by the Paraguaians in April 1865.
6.2.Corrientes Campaign
Was the Paraguayan invasion of Corrientes during the Paraguayan War.
April 1865: Under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Antonio de la Cruz Estigarribia, Paraguayan forces crossed the Paraná near Encarnación to head south along the right bank of the Uruguay River.
June 1865: Estigarribia crossed the river and followed Duarte's advance from the Brazilian bank, entering São Borja e Itaqui.
August 1865: The city of Uruguayana was occupied by Paraguayan forces.
September 1865: Siege of Uruguaiana.
November 1865: Paraguayan military leader Francisco Isidoro Resquín carried out the withdrawal operations towards the northern bank of the Paraná throughout the month of October, which ended on 4 November.
6.3.Loizaga - Cotegipe Treaty
Was a treaty that ended the Paraguayan War between Paraguay and Brazil, with large territorial cessions from Paraguay to Brazil.
January 1872: The Loizaga - Cotegipe Treaty was a treaty of peace and borders signed in Asuncion between Paraguay and the Empire of Brazil.
August 1825: In 1825, the region of Tarija declared its independence from the United Provinces of the River Plate. This territory was then incorporated into the Republic of Bolivia, under the leadership of Simón Bolívar and Antonio José de Sucre.
August 1825: Uruguay broke away from Brazil on August 25, 1825, after numerous previous revolts. Independent Uruguay formed a regional federation with the United Provinces of Río de la Plata, today's Argentina: it was an annexation.
January 1827: Modern-day Uruguay is ccupied by Brasil in 1826.
January 1868: In an 1867 treaty with Empire of Brazil to secure water rights to the Atlantic Ocean, Bolivia ceded 102,400 square kilometers of territory, hoping to break Bolivia's isolation.
January 1868: The territory of Acre was assigned to Bolivia in 1867 by the Treaty of Ayacucho with Brazil.
July 1886: Counani was created on 23 July 1886 in the area that was disputed by France (as part of French Guiana) and Brazil in the late nineteenth century.
July 1886: French founding of the Republic of Independent Guiana, commonly referred to by the name of the capital Counani.
November 1889: Proclamation of the Brazilian Republic.
Disestablishment
November 1889: Proclamation of the Brazilian Republic.
.svg.png.webp)
 Empire of Brazil
Empire of Brazil