Ahom Kingdom
Ahom Kingdom
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a late medieval kingdom in the Brahmaputra Valley in Assam. It maintained its sovereignty for nearly 600 years having successfully resisted Mughal expansion in Northeast India. The Kingdom later fell to the British East India Company after the First Anglo-Burmese War.
Establishment
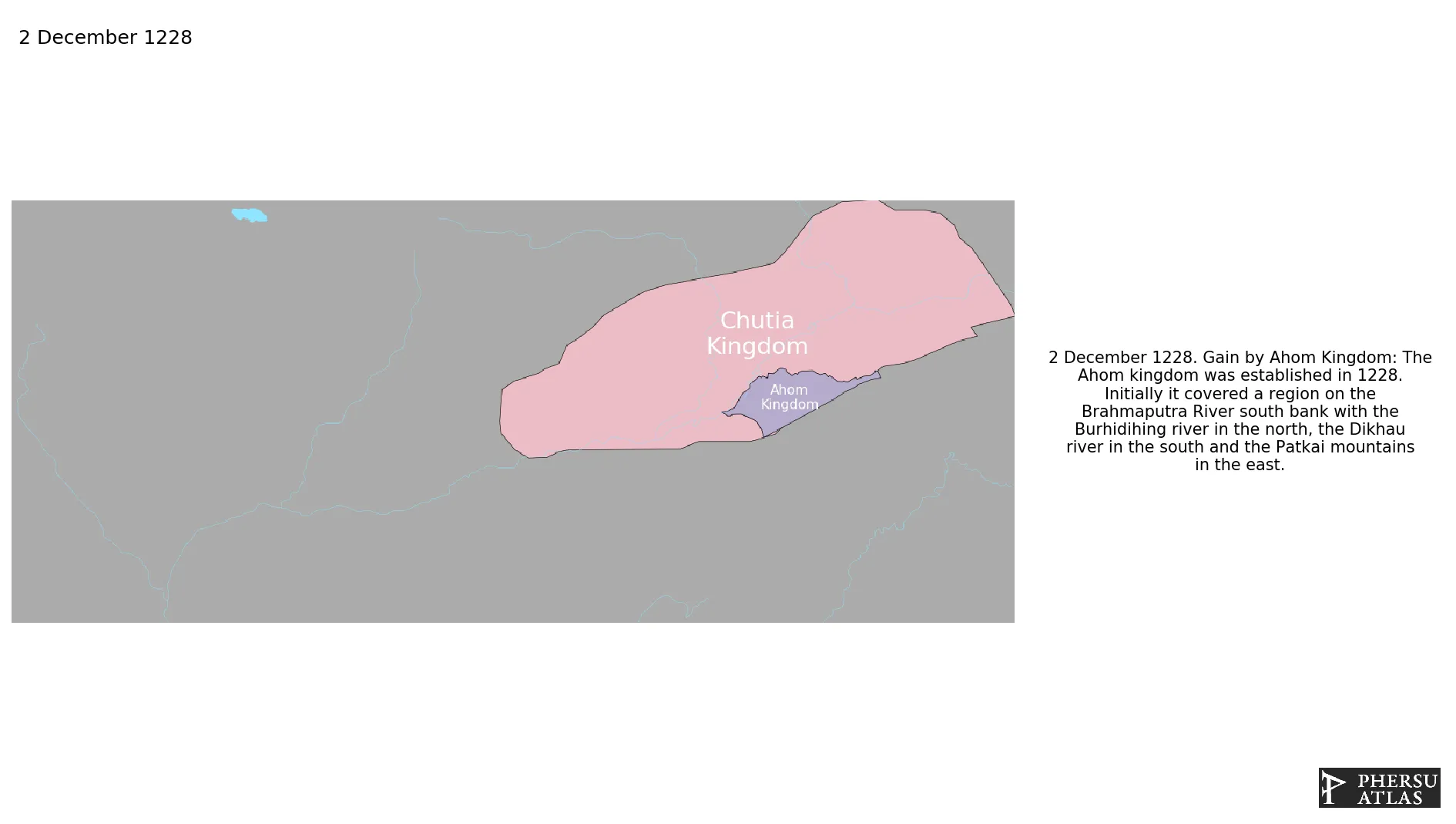
December 1228: The Ahom kingdom was established in 1228. Initially it covered a region on the Brahmaputra River south bank with the Burhidihing river in the north, the Dikhau river in the south and the Patkai mountains in the east.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
A series of conflicts between the Mughal Empire and the Ahom Kingdom in Assam.
November 1615: In 1615, the Mughal Empire, led by Emperor Jahangir, reached the confluence of the Brahmaputra and the Bharali rivers facing Samdhara.
November 1615: In 1615, the Mughal Empire, led by Emperor Jahangir, reached the confluence of the Brahmaputra and the Bharali rivers facing Samdhara.
December 1615: In November 1615, Abu Bakr, a Mughal general, attacked Kajali, an Ahom frontier post. The Ahoms, led by their ruler Swargadeo Pratap Singha, were defeated in a short skirmish and fled, leaving behind their war boats and the fort.
April 1616: The Ahoms reoccupied Samdhara at the mouth of Bharali.
December 1637: The Mughals entered Kamrup proper. The decisive defeat inflicted by the imperialists on Balinarayan and the Ahoms in November 1637 turned the tide of fortune in favour of imperialists. The whole of Kamrup was then re-annexed to the Pan-Mughalia.
January 1651: Koch Bihar falls under Ahom control through dynastic alliance.
January 1659: Aurangzeb, after ascending on the throne of Delhi, ordered Mir Jumla to invade Cooch Behar.
March 1662: Siege of Simalugarh.
March 1662: Mir Jumla entered the Ahom capital Garhgaon.
April 1662: Mir Jumla entered Assam in the beginning of 1662.
October 1662: With the progress of monsoon, the Ahoms easily recovered all the country east of Lakhau. Only Garhgaon and Mathurapur remained in the possession of Mughals.
February 1663: A treaty was concluded at Ghilajharighat in January 1663, according to which the Ahoms ceded western Assam to the Mughals.
November 1667: Itakhuli and the contiguous garrison of Guwahati fell into the hands of the Ahoms.
January 1680: Laluksola Borphukan was an influential military commander in the Ahom Kingdom of Assam. In 1679, he conspired with the Mughal Empire and betrayed Guwahati, leading to its capture by the Mughals. This event marked a significant shift in power dynamics in the region.
September 1682: Battle of Itakhuli: With this win, the Ahoms recovered Sarkar Kamrup from the Mughals.
Expansion during the rule of Aurangzeb in the Mughal Empire.
January 1663: On one occasion in 1662, the Mughals under Mir Jumla occupied the capital, Garhgaon.
February 1663: In 1662, the Mughal Empire, led by Mir Jumla, captured the capital city of Garhgaon.
Were a series of Burmese invasions of the Kingdom of Assam in the first halph of the XIX century.
3.1.First Burmese invasion (Assam)
Was a Burmese invasion of the Kingdom of Assam.
April 1817: The first battle between the Ahom Kingdom and Burma took place at Ghiladhari.
May 1817: The Burmese army left Assam in April 1817.
3.2.Second Burmese invasion (Assam)
Was a Burmese invasion of the Kingdom of Assam.
February 1819: Phulpanisiga, located in present-day Assam, India, was the site of a confrontation in 1819 between the Burmese army and the forces led by Jaganath Dhekial Phukan, a prominent historical figure in Assamese history.
March 1819: The Assam army, instead of pursuing the defeated Burmese, returned to the Ahom capital Jorhat leading to much confusion and panic. Failing to instill confidence, Ruchinath Burhagohain and Purandar Singha sailed down to Guwahati, and the Burmese army was able to occupy the capital two days later.
January 1820: The Burmese contingent returned to Burma, leaving all occupied regions to the Ahom Kingdom.
3.3.Third Burmese invasion (Assam)
Was a Burmese invasion of the Kingdom of Assam.
March 1821: In 1819, Bagyidaw became the king of Burma and decided to annex Assam. He sent Mingimaha Tilwa, a Burmese military commander, to Assam in February 1821 to carry out the military occupation of the Kingdom of Assam.
January 1822: Guwahati conquered by Ahom Kingdom.
March 1822: Ahom king Sudingphaa pitched his camp at Mahgarh, near Jorhat.
May 1822: Mingi Maha Bandula attacked and defeated the forces of Chandrakanta in April 1822. Chandrakanta then fell back to Guwahati.
August 1822: He was defeated and had to further retreat into the British territory. After this victory, the Burmese declared Mingimaha Tilwa the Raja of Assam and brought an end to the sovereign Ahom rule in Assam.
January 1513: The Ahoms annexed the Habung region (which was a part of Chutia kingdom).
January 1521: The Chutiyas again attacked the Ahoms in 1520 and occupied the areas up to Namdang and Mungkhrang.
January 1523: King Suhungmung extended the Ahom Kingdom to the mouth of the Tiphao River, where a new fort was constructed.
January 1523: In 1522, the Ahoms fought back, re-occupied their lost territories and erected a fort at Dibrumukh.
January 1524: The Chutia Kingdom fell in 1523 to the Ahom Kingdom after a series of conflicts.
January 1537: In 1536, the Ahom Kingdom, led by King Suklenmung, launched an attack on the Kachari capital in Dimapur. The city was sacked, forcing the Dimasa people to retreat south and establish their new capital in Maibang.
January 1617: The eastern kingdom of Koch Hajo was absorbed into the Ahom kingdom.
January 1627: Ngawang Namgyalm the founder of the Bhutanese state, consolidates control over western Bhutan.
January 1641: By 1640 Bhutan reached its current borders.
January 1661: Conquests of the Ahom Kingdom by 1660 (based on maps).
February 1663: In 1662, the Mughal Empire, led by Mir Jumla, captured the capital city of Garhgaon.
January 1672: After the Battle of Saraighat, the Ahoms not only fended off a major Mughal invasion but extended their boundaries west, up to the Manas river.
January 1707: The Ahom king invaded Maibong and destroyed its forts in 1706.
February 1707: The Ahom king invaded Maibong and destroyed its forts in 1706.
January 1761: Expansion of the Ahom Kingdom by 1769.
January 1785: In 1784, the British East India Company, represented by Warren Hastings, turned over the Bengal Duars territory to the Kingdom of Bhutan. The boundaries of the territory were poorly defined, leading to disputes between the two parties.
Disestablishment
January 1822: Guwahati conquered by Ahom Kingdom.
March 1822: Ahom king Sudingphaa pitched his camp at Mahgarh, near Jorhat.
May 1822: Mingi Maha Bandula attacked and defeated the forces of Chandrakanta in April 1822. Chandrakanta then fell back to Guwahati.
August 1822: He was defeated and had to further retreat into the British territory. After this victory, the Burmese declared Mingimaha Tilwa the Raja of Assam and brought an end to the sovereign Ahom rule in Assam.

 Ahom Kingdom
Ahom Kingdom