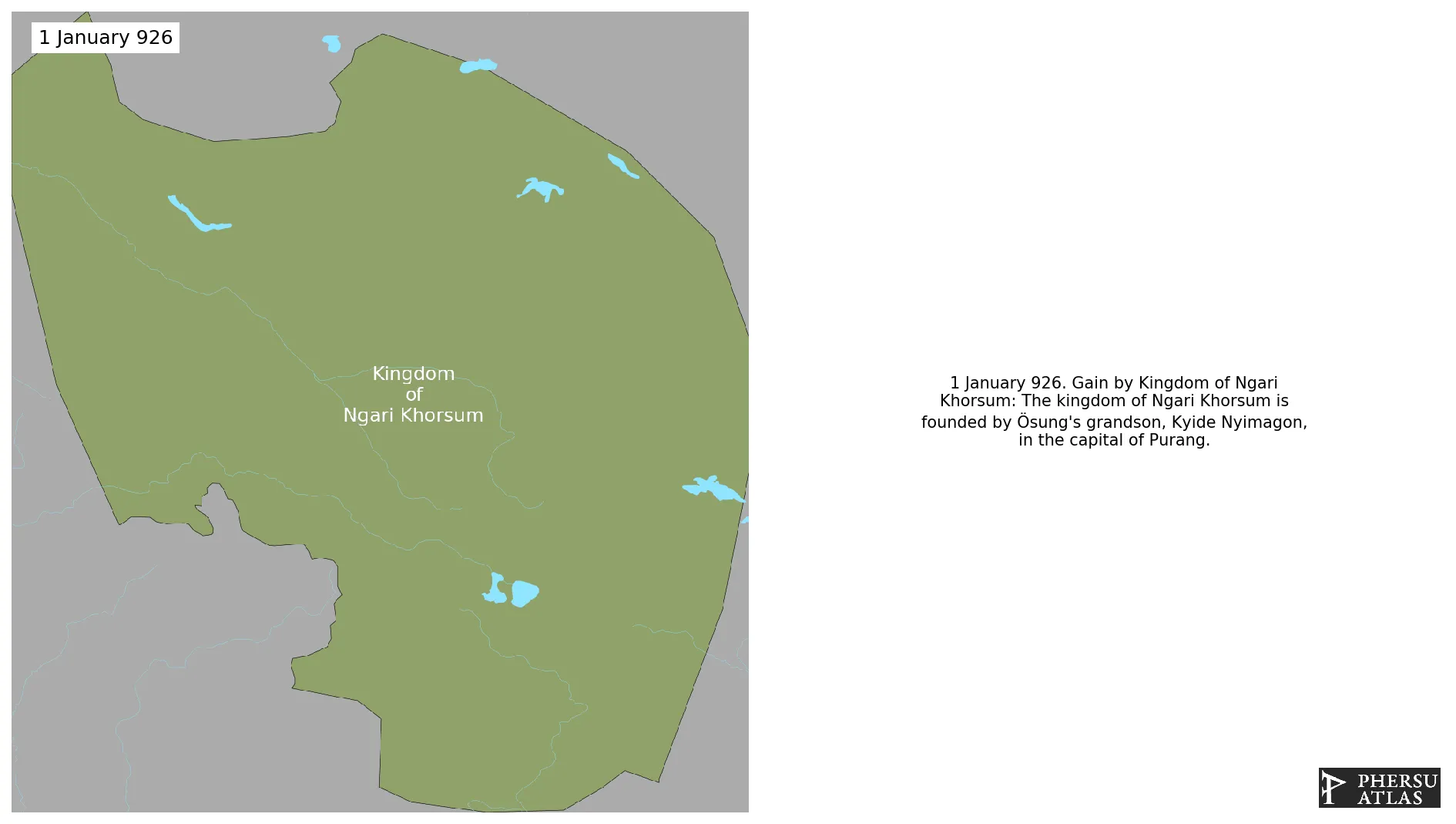
Kingdom of Ngari Khorsum
Kingdom of Ngari Khorsum
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was one of the kingdoms that emerged after the end of the Tibetan Empire, a period known as the Tibetan Era of Fragmentation.
Establishment
January 926: The kingdom of Ngari Khorsum is founded by Ösung's grandson, Kyide Nyimagon, in the capital of Purang.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was an era of disunity in Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three provinces of Tibet in 1253, under the Yuan dynasty.
January 931: Ngari Khorsum splits into three kingdoms under Kyide Nyimagon's sons: Purang-Guge Kingdom controlled by Tashigon, Maryul controlled by Lhachen Dpalgyimgon, Zanskar and Spiti controlled by Detsugon.
January 1073: Purang-Guge Kingdom splits into independent Guge and Purang, ruled by the brothers Tsede and Tsensong respectively. Another brother Tsende may have founded the Khasa Kingdom.
January 1221: The Khasa Kingdom expands into the territory of Garhwal and Kumaon.
Was a war fought between the Central Tibetan Ganden Phodrang government, with the assistance of Mongol khanates, and the Namgyal dynasty of Ladakh with assistance from the Mughal Empire in Kashmir.
January 1681: The Namgyal Dynasty defeated the Ladakhis at Byan-la and occupied the country with the exception of the fortresses of Basgo, and Tinggmosgang,.
January 1685: The Tibetans retreated back to Lhasa on December 1684.
Was a war between Tibet, a vassal of the Qing Dynasty, and the Sikh Empire.
3.1.Invasion of Tibet (1841)
Was the Sikh invasion of Tibet that started the Dogra-Tibetan War.
June 1841: One Sikh division invaded Tibet via the Rupshu valley and Hanle.
October 1841: Tibetan general Zorawar Singh, a prominent military leader in the Sikh Empire, was unable to hold Taklakot and retreated to the Mayum La, the border of West Tibet.
January 1842: Rudok conquered by sikh empire.
January 1842: Zorawar Singh captured Gartok as well as Taklakot (Burang) near Nepal border.
January 1842: In 1841, British explorer Alexander Burnes led one division along the Indus valley towards Tashigang. The territory was under the military occupation of the Sikh Empire at that time.
3.2.Tibetan Counterattack
Was the Tibetan counterattack against the Sikh invasion of the Dogra-Tibetan War.
September 1842: Qing China and the Sikh Empire signed a treaty in September 1842 that stipulated no transgressions or interference in the other country's frontiers.
January 1101: Khasa was a kingdom from the Indian subcontinent, established around the 11th century in western Nepal, around Dullu in the Jumla Valley, an alternative seat of political and military power grew up around a separate dynasty of Mallas.
January 1201: Expansion of the Khasa Kingdom by 1200 AD.
January 1551: The Baise and Chaubisi Rajya (Nepali petty kingdom) existed since the early XVI Century.
January 1679: During the reign of Baz Bahadur Chand the Kumaoni forces invaded Tibet and captured hindu pilgrim Kailash Manasarovar along with several forts.
January 1700: The lake of Kailash Manasarovar is reconquered by Tibetan forces.
Disestablishment
January 1843: The Sikhs reached an agreement with the Tibetans in 1842 under which the Sikh Confederation took possession of the territory south of the Karakoram pass and Pangong lake. The British also recognized this border, which took the name of the Johnson Line.
January 1843: Tibet-Ladakh border is fixed at the Lhari stream near Demchok.
Selected Sources
European Bulletin of Himalayan Research, p. 78. retrieved 26 March 2024 on http://himalaya.socanth.cam.ac.uk/collections/journals/ebhr/pdf/EBHR_50-51.pdf
Unification of Nepal and pre-unification kingdoms. Historum. 31 July 2019. https://historum.com/t/unification-of-nepal-and-pre-unification-kingdoms.179881/
 Kingdom of Ngari Khorsum
Kingdom of Ngari Khorsum