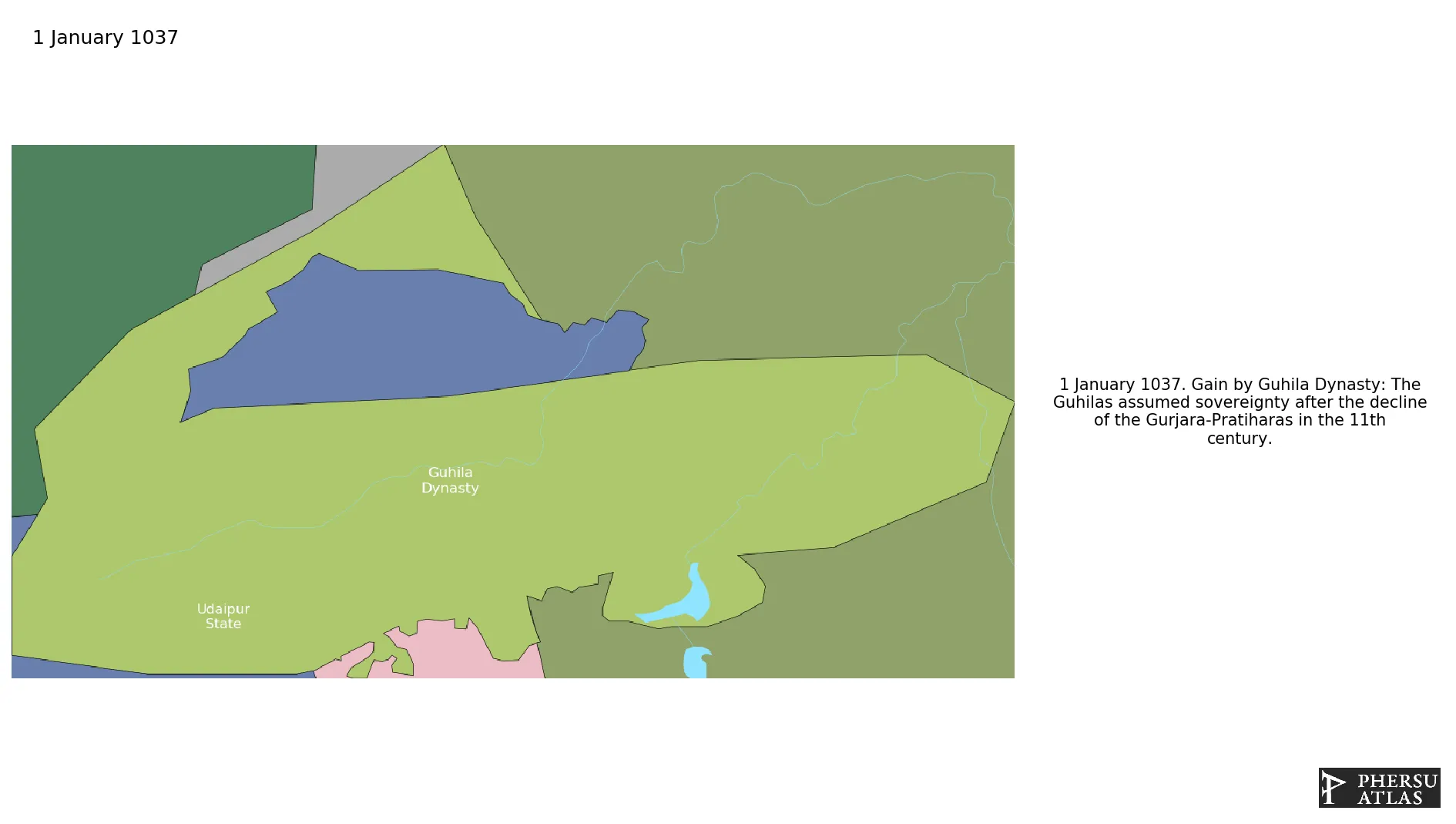
Guhila Dynasty
Guhila Dynasty
This article is about the specific polity Guhila Dynasty and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a dynasty in India that assumed the control of Mewar (a region of Rajasthan, India) after the decline of the Gurjara-Pratiharas in the XI century.
Establishment
January 1037: The Guhilas assumed sovereignty after the decline of the Gurjara-Pratiharas in the 11th century.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Events
January 1151: In the mid-12th century, the Guhila dynasty divided into two branches. The senior branch (whose rulers are called Rawal in the later medieval literature) ruled from Chitrakuta (modern Chittorgarh).
January 1207: In 1193 the Ghurid Sultan Muhammad conquered Delhi and left a slave lieutenant Qutab-ud-din Aybak, in charge when he returned to Afghanistan. When Muhammad was assassinated in 1206, Aybak declared independency and established the Mamluk Dynasty of the Sultanate of Delhi.
January 1221: Iltutmish of Delhi conquered Multan and Bengal from contesting Muslim rulers, as well as Ranthambore and Siwalik from Hindu rulers.
January 1227: Foundation of the Jodhpur Kingdom, also known as Kingdom of Marwar.
January 1243: Later the region was governed by Rao Deva, who took over Bundi from Jaita Meena in 1242, renaming the surrounding area as Haravati or Haroti. For the next two centuries, the Hadas of Bundi were the vassals of the Sisodias of Mewar and ruled by the title of Rao.
January 1616: In 1615, after four decades of skirmishing, Mewar and the Mughals entered into a treaty under which Mewar territory under the Mughals' possession was returned in exchange for the crown prince of Mewar attending the Mughal court and Mewar providing a force of 1,000 horsemen to the Mughals.
January 1632: In 1631, Kota state seceded from Bundi State under the rule of Rao Madho Singh.
January 1732: Gwalior state was a semi-autonomous Maratha state. It was centered in modern-day Madhya Pradesh, arising due to the rise of the Maratha Empire and fragmentation of the Mughal Empire.
January 1734: Sardargardh state Bantva was a princely state founded in 1733 by Khan Shri Sherzamankhanji Babi youngest son of Nawab Saheb Salabat Muhammadkhan Babi of Junagadh State, on the Kathiawar peninsula in Gujarat, India.
Disestablishment
January 1807: Nawab Muhammad Amir Khan (1769-1834), an adventurer and military leader of Pashtun descent, established the Tonk State. Amir Khan rose to be a military commander in the service of Yashwantrao Holkar of the Maratha Empire in 1798. In 1806, Khan received the state of Tonk from Yashwantrao Holkar.
Selected Sources
Middleton, J. (2005): World Monarchies and Dynasties, Volumes 1-3, Routledge, p. 644

 Guhila Dynasty
Guhila Dynasty