Maurya Empire
Maurya Empire
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
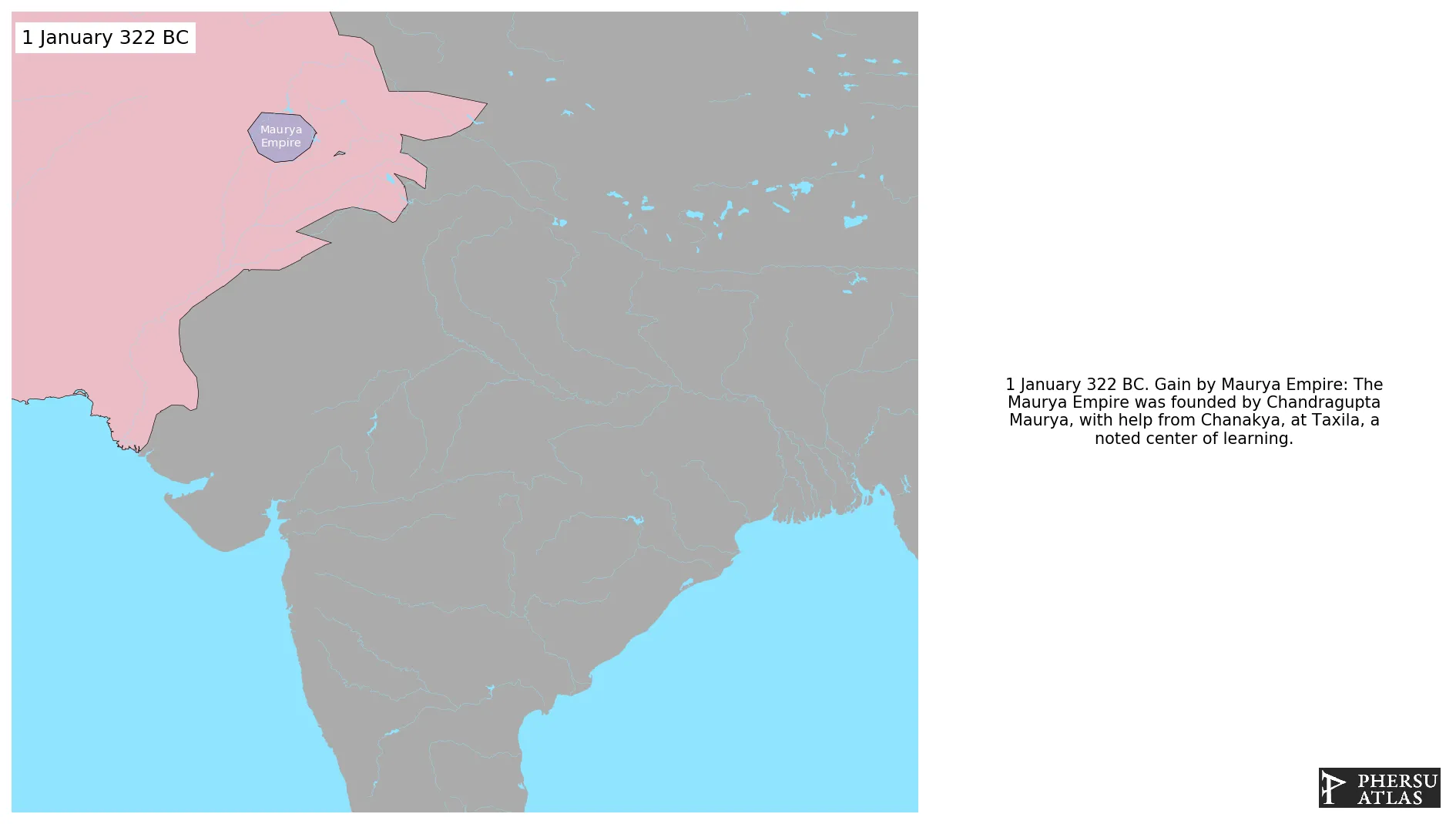
Was an Iron Age empire in India centered in Magadha that controlled the northern Indian Subcontinent at its greatest extent. It was founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE.
Establishment
January 322 BC: The Maurya Empire was founded by Chandragupta Maurya, with help from Chanakya, at Taxila, a noted center of learning.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Military campaign of Chandragupta Maurya, founder of the Mauryan Empire.
January 321 BC: The last Nanda king was overthrown by Chandragupta Maurya, the founder of the Maurya Empire, and the latter's mentor Chanakya.
January 316 BC: Expansion of the Magadha Kingdom until 317 BC.
January 316 BC: The Greek generals Eudemus and Peithon ruled in the Indus Valley until around 317 BC, when Chandragupta Maurya (with the help of Chanakya, who was now his advisor) orchestrated a rebellion to drive out the Greek governors, and subsequently brought the Indus Valley under the control of his new seat of power in Magadha.
January 299 BC: The Kingdom of Avanti was disestablished c. 300 BC.
January 299 BC: Chandragupta's son Bindusara extended the rule of the Mauryan empire towards southern India. The famous Tamil poet Mamulanar of the Sangam literature described how areas south of the Deccan Plateau which comprised Tamil country was invaded by the Maurya army using troops from Karnataka.
1.1.Seleucid-Mauryan war
Was a ware waged by the Seleucid Kingdom to conquer back former Macedonian Satrapies in the Indus Valley from the Mauryan Empire.
January 302 BC: Expansion of the Magadha Kingdom until 301 BC.
January 302 BC: Later Eudemus took over Taxila briefly, however he was killed by Malayketu after which Chandragupta Maurya conquered Alexander's satraps in the sub-continent by BC, and joined hands with Porus earlier, in around 322 BC. Some state that after Alexander's departure from India, Takshashila became a free kingdom, and that's when Porus conquered Takshashila and there, he may have killed Taxiles. However, it still remains unsure what happened to Taxiles, and whether he was deposed or assassinated.
January 302 BC: It seems probable that Oxyartes must have died before the Seleucus's diplomatic/military foray into South Asia, as Seleucus ceded Paropamisadae to Chandragupta Maurya without any mention of Oxyartes.
January 302 BC: The emerging and expanding Mauryan Empire came into conflict with Seleucus over the Indus Valley. Seleucus invaded the Punjab region of India, confronting Chandragupta Maurya. Maurya finally gained all the macedonian satrapies in the Indus valley.
January 300 BC: After the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, Chandragupta led a series of campaigns in 305 BC to retake satrapies in the Indus Valley and northwest India. When Alexander's remaining forces were routed, returning westwards, Seleucus I Nicator fought to defend these territories. Not many details of the campaigns are known from ancient sources. Seleucus was defeated and retreated into the mountainous region of Afghanistan.
The two rulers concluded a peace treaty in 303 BC, including a marital alliance. Under its terms, Chandragupta received the satrapies of Paropamisadae (Kamboja and Gandhara) and Arachosia (Kandhahar) and Gedrosia (Balochistan). Seleucus I received the 500 war elephants that were to have a decisive role in his victory against western Hellenistic kings at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC.
Military campaign of Bindusara, king of the Mauryan Empire.
January 279 BC: Bindusara, who inherited the Maurya Empire when he was just 22 years old, extended his empire to the southern part of India, as far as what is now known as Karnataka. He conquered almost all of the Indian peninsula (he is said to have conquered the 'land between the two seas' - the peninsular region between the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea).
January 272 BC: Expansion of the Magadha Kingdom until 273 BC.
Was fought in ancient India between the Maurya Empire and the state of Kalinga, an independent feudal kingdom located on the east coast.
January 264 BC: The Kalinga War was fought in ancient India between the Maurya Empire under Ashoka and the state of Kalinga. Kalinga was annexed by Mauryan Empire.
Diodotus, the satrap of Bactria founded the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom when he seceded from the Seleucid Empire around 250 BC.
January 249 BC: Diodotus, the satrap of Bactria founded the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom when he seceded from the Seleucid Empire around 250 BC.
January 299 BC: The kingdom of Gangaridai is established in the Ganges Delta.
January 249 BC: The history of the Kuninda Kingdom is documented from around the 2nd century BC. They are mentioned in Indian epics and Puranas. One of the first kings of the Kuninda was Amoghbhuti, who ruled in the mountainous valley of the Yamuna and Sutlej rivers (in today's Uttarakhand and southern Himachal in northern India).
January 249 BC: The confederation of the Kambojas may have stretched from the valley of Rajauri in the south-western part of Kashmir to the Hindu Kush Range; in the south-west the borders extended probably as far as the regions of Kabul, Ghazni and Kandahar, with the nucleus in the area north-east of the present day Kabul, between the Hindu Kush Range and the Kunar river, including Kapisa possibly extending from the Kabul valleys to Kandahar.
January 199 BC: Soon after the death of emperor Ashoka, the Mauryan Empire declined and the eastern part of Bengal became the state of Samatata.
January 199 BC: The Deva dynasty of Saketa was a dynasty of kings who ruled in the area of the city of Ayodhya, Kosala, in India from the 2nd century BC.
January 199 BC: The Mahameghavahanas were an ancient ruling dynasty of Kalinga after the decline of the Maurya Empire.
January 189 BC: As Mauryan power declined, the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom based in modern Afghanistan declared its independence from the Seleucid Empire, and quickly seized ancient Peshawar around 190 BC.
January 184 BC: The Shunga dynasty was established by Pushyamitra Shunga, after taking the throne of the Maurya Empire.
January 184 BC: After being absorbed into the Mauryan Empire (322-185 BC), Panchala regained its independence.
Disestablishment
January 179 BC: In 180 BC, Brihadratha Maurya, was killed by his general Pushyamitra Shunga in a military parade without any heir. Hence, the great Maurya empire finally ended, giving rise to the Shunga Empire.
Selected Sources
Schwartzberg,J. E. (1992): A Historical Atlas of South Asia, Minneapolis (USA), Plate III.B.4b (p.18) and Plate XIV.1a-c (p.145).
 Maurya Empire
Maurya Empire