Mong Mao
Mong Mao
This article is about the specific polity Mong Mao and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an ethnic Tai state that controlled several smaller Tai states or chieftainships along the frontier of what is now Myanmar, China, the states of Northeast India of Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh, principally set in the Dehong region of Yunnan with a capital near the modern-day border town of Ruili/Meng Mao. It was conquered by Burma in 1563.
Establishment
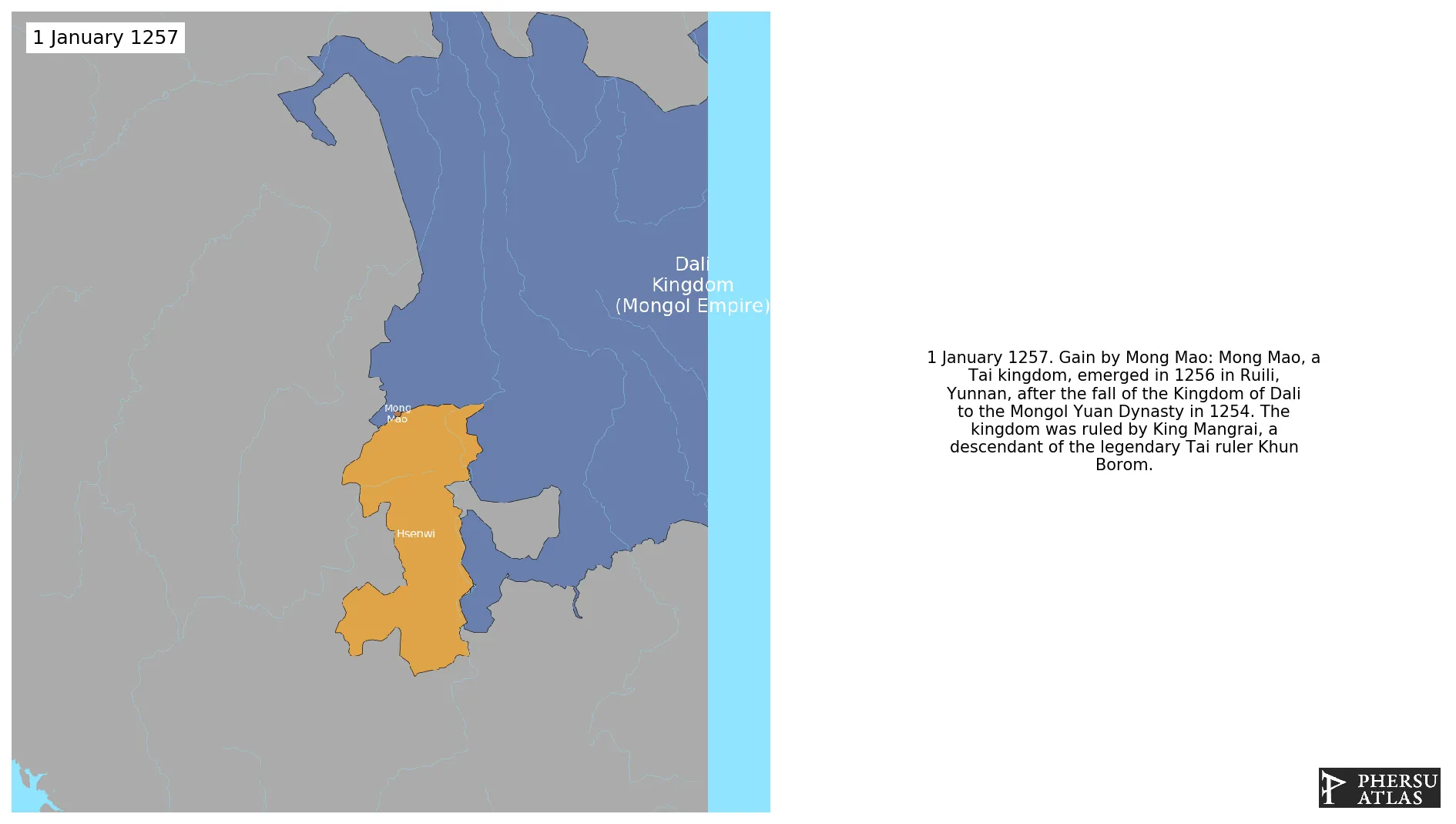
January 1257: Mong Mao, a Tai kingdom, emerged in 1256 in Ruili, Yunnan, after the fall of the Kingdom of Dali to the Mongol Yuan Dynasty in 1254. The kingdom was ruled by King Mangrai, a descendant of the legendary Tai ruler Khun Borom.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
A military conflict waged between the Ming dynasty and the previously subordinate Shan state of Mong Mao.
January 1389: After a military conflict waged between the Ming dynasty and Mong Mao, the latter was forced to accept Ming suzerainty.
January 1343: In 1342, the Maw troops, led by King Thado Minbya of Ava, breached the northern territory of the Sagaing Kingdom. This incursion led to the territory falling under the control of the Mong Mao Kingdom, a powerful state in the region at the time.
February 1343: Maw troops breached northern Sagaing territory in 1342.
January 1351: Despites the opposition of the Yuan dynasty, Mong Mao conquered several surrounding states.
January 1357: In 1356-57, Maw troops led by King Thado Minbya of Ava again raided the northern part of Sagaing Kingdom, resulting in the territory falling under the control of the Mong Mao kingdom.
February 1357: In 1356-57, the troops of King Thado Minbya of Ava, led by General Maw, launched a raid on the northern part of the Sagaing Kingdom. This incursion was part of the ongoing conflict between the Ava and Sagaing Kingdoms for control of the region.
January 1360: In 1359, the Yawnghwe state was founded with the ritual name Kambosarattha. This territory was located in present-day Myanmar.
January 1363: Led by King Thado Minbya of Sagaing Kingdom, the raid in 1362-63 was a devastating attack by the Mong Mao forces. The invasion resulted in the complete overrun of the Sagaing countryside, causing widespread destruction and loss of life.
February 1363: Led by King Thado Minbya of Ava, the raid in 1362-63 targeted the Sagaing Kingdom, resulting in the complete overrun of the Sagaing countryside. This military campaign was part of the ongoing power struggles between the Ava and Sagaing Kingdoms in Myanmar.
January 1364: In Winter 1363-early 1364, the forces of King Thado Minbya of Sagaing Kingdom were invaded by the Mong Mao army led by King Nawrahta. The siege of Sagaing marked a significant conflict between the two kingdoms in Southeast Asia.
February 1364: In Winter 1363-early 1364, the forces of King Thado Minbya of Ava invaded Sagaing Kingdom, laying siege to the territory. King Thado Minbya was a prominent ruler of the Ava Kingdom, while Sagaing was ruled by King Thado Kyaw. The conflict between the two kingdoms was a result of territorial disputes and power struggles in the region.
Disestablishment
January 1389: After a military conflict waged between the Ming dynasty and Mong Mao, the latter was forced to accept Ming suzerainty.
 Mong Mao
Mong Mao