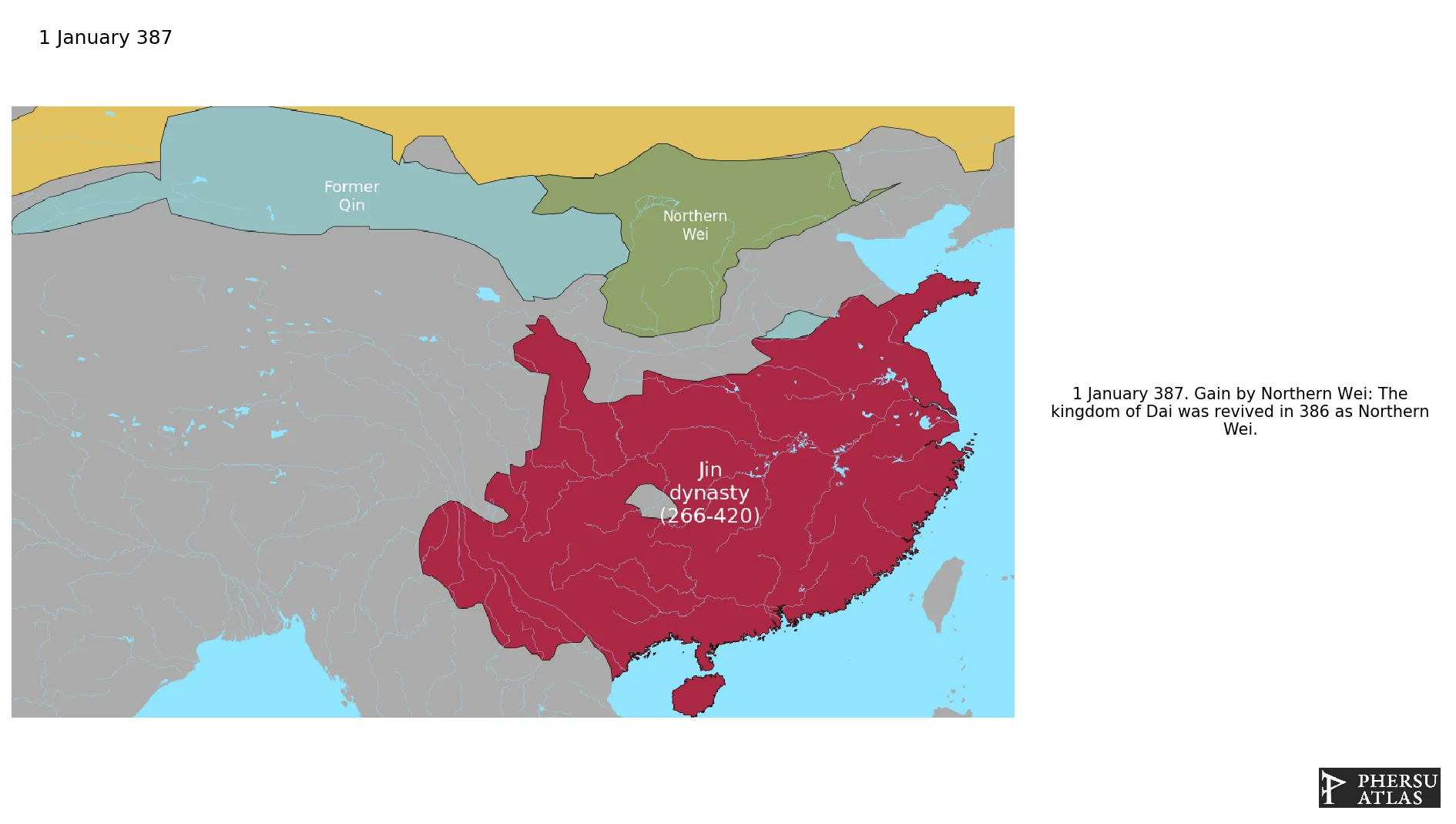
Northern Wei
Northern Wei
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was one of the Northern Dynasties during the Chinese Period of the Northern and Southern Dynasties.
Establishment
January 387: The kingdom of Dai was revived in 386 as Northern Wei.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military campaigns by Northern Wei, a Chinese polity during the Northern and Southern dynasties Era, that led to the conquest of northern China.
January 437: Northern Yan was conquered by Northern Wei in 436.
January 440: Northern Liang was conquered by Northern Wei in 439.
January 440: The Northern Wei Dynasty unified northern China in 439.
January 451: The Wei lured the Liu Song to cross the Yellow River, and then flanked them, destroying the Eastern army. As the Liu Song armies retreated, the provinces south of the Yellow River were devastated by the Wei army. Only Huatai, a fortified city, held out against the Wei. However, the economic damage was immense. The barbarian troops laid waste to the provinces they had temporarily occupied.
January 392: In 391, Tuoba Gui, a prominent ruler of the Northern Wei dynasty, achieved a significant victory by defeating the Rouran tribes in the Ordos region. During this battle, he successfully killed the Rouran chief, Heduohan, which led to the Rouran tribes fleeing westward in retreat.
January 397: In 395, the Northern Wei dynasty, led by Emperor Taiwu, defeated the Later Yan dynasty northeast of Liangcheng. Following this victory, in 396, Bing Province was taken from Later Yan by Northern Wei, consolidating their control over the region.
January 398: Northern Liang was founded by Duan Ye in 397.
January 399: Yan lost Zhongshan and Pingcheng to Northern Wei by 398.
January 408: Xia was a Xiongnu kingdom founded by Helian Bobo in 407.
January 410: Western Qing was revived in 409.
January 423: Sizhou (司州, central Henan) and Yanzhou (兗州, modern western Shandong) and most cities in Song's Qing Province (青州, modern central and eastern Shandong) fell to the Wei army.
January 424: Northern Wei troops were eventually forced to withdraw after food supplies ran out. Wei forces also stalled in their siege of Hulao, defended by the capable Liu Song general Mao Dezu (毛德祖), but were meanwhile able to capture Luoyang and Xuchang (許昌, in modern Xuchang, Henan) in spring 423.
January 427: Northern Wei attacked Xia in 426 and captured Chang'an.
January 429: Xia retook Chang'an in 428.
January 431: In fall 430, while Helian Ding was engaging the Western Qin, the Northern Wei made a surprise attack on the new Xia capital Pingliang and conquered the kingdom.
January 431: Under Emperor Wen, the Liu Song economy prospered during the rule of Yuanjia (Chinese: 元嘉之治), a period noted for its prosperity in the 400 years of conflict between the Han and Tang dynasties. However, the emperor's martial abilities were not equal to his father, and his inability to crush the remaining barbarian states allowed Northern Wei to complete the unification of the North, to the detriment of Liu Song.
January 449: The Kingdom of Couchi is restored but split into three kingdoms: Wudu, Wuxing and Yinping.
February 451: The Wei lured the Liu Song to cross the Yellow River, and then flanked them, destroying the Eastern army. As the Liu Song armies retreated, the provinces south of the Yellow River were devastated by the Wei army. Only Huatai, a fortified city, held out against the Wei. However, the economic damage was immense. The barbarian troops laid waste to the provinces they had temporarily occupied.
January 506: Until spring 505, Xinyang and Hanzhong were fallen to the Northern Wei.
January 507: In spring 506, Wei Rui, a general fo the Liang Dynasty, was able to capture Hefei.
May 526: In spring 525, the Northern Wei general Yuan Faseng (元法僧) surrendered the key city of Pengcheng (彭城, in modern Xuzhou, Jiangsu) to Liang.
September 526: However, in summer 525, Emperor Wu's son Prince Xiao Zong (蕭綜), grew suspicions that he was actually the son of Southern Qi's emperor Xiao Baojuan (because his mother Consort Wu was formerly Xiao Baojuan's concubine and had given birth to him only seven months after she became Emperor Wu's concubine), surrendered Pengcheng to Northern Wei, ending Liang's advances in the northeast.
January 527: Shouyang fell to Liang troops .
November 534: In 534, the Northern Wei dynasty split into two states: Eastern Wei and Western Wei. The territory of Western Wei included parts of present-day northern China. This division was a result of a power struggle between the ruling family members of the Northern Wei dynasty.
November 534: Northern Wei split into two states in 534.
Disestablishment
November 534: Northern Wei split into two states in 534.
November 534: In 534, the Northern Wei dynasty split into two states: Eastern Wei and Western Wei. The territory of Western Wei included parts of present-day northern China. This division was a result of a power struggle between the ruling family members of the Northern Wei dynasty.
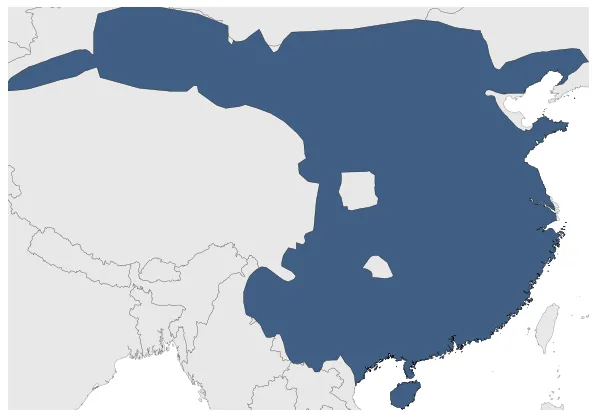
 Northern Wei
Northern Wei