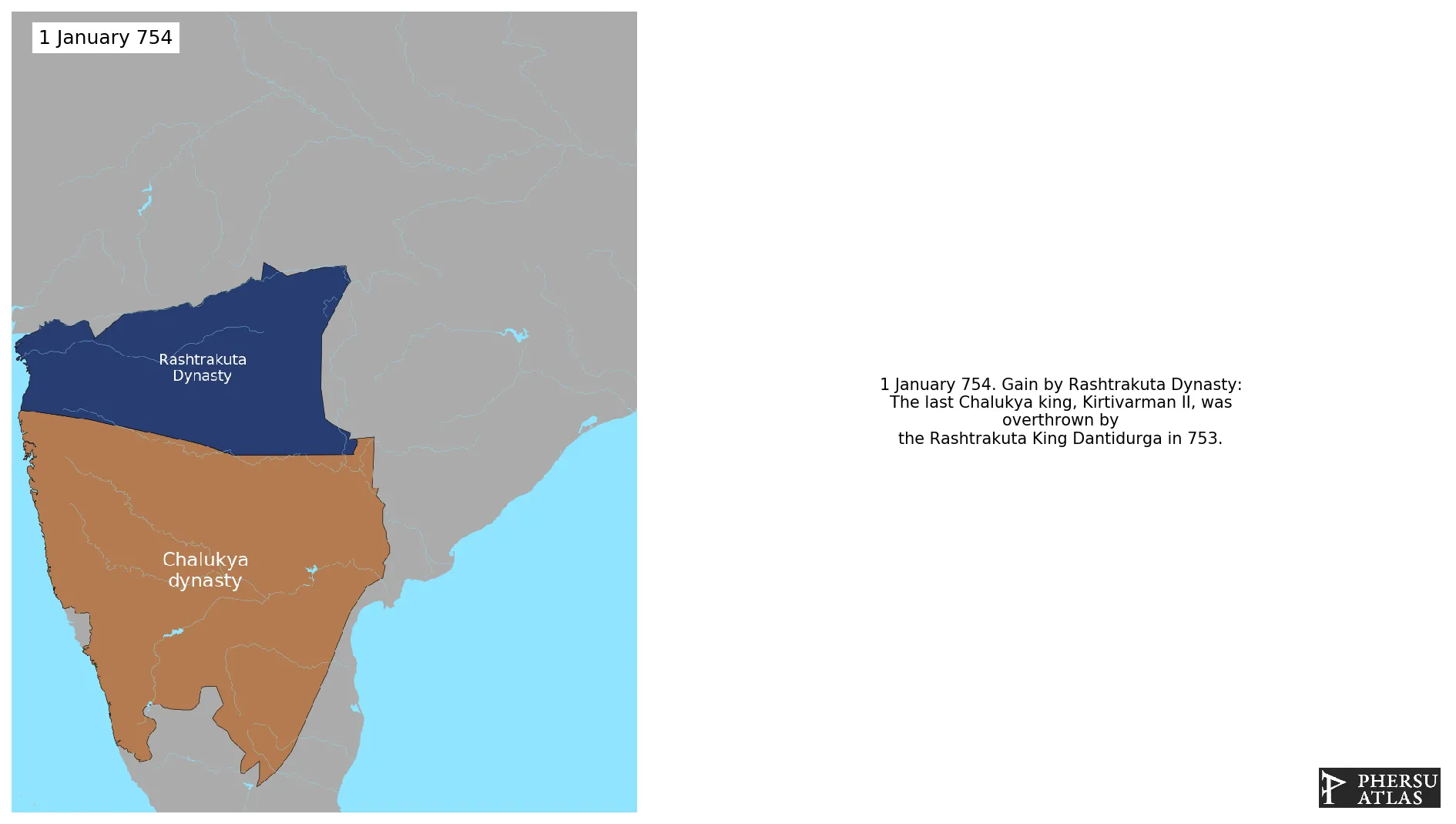
Rashtrakuta Dynasty
Rashtrakuta Dynasty
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a dynasty that overthrew the Chalukya Dynasty and then ruled large parts of southern, central and westend India from the VIII century.
Establishment
January 754: The last Chalukya king, Kirtivarman II, was overthrown by the Rashtrakuta King Dantidurga in 753.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Events
January 758: Though he conquered the Chalukyan Empire, it is clear from the Vakkaleri inscription of 757 that the Chalukyan Emperor Kirtivarman II retained control over his southern provinces up to the year 757.
January 758: Avanijanashraya is best known for repulsing an Arab invasion from the Umayyad Caliphate near Navsari, a feat recorded in his 738-739 inscription. After his reign, the history of this Chalukya branch is uncertain: their territory subsequently came under the Rashtrakuta control.
January 761: Siladitya V probably had tried to recover Malwa as one of his grant (760 CE) is made from military camp at Godraka (Godhra). He must have failed to recover Malwa but nonetheless recovered the Khetaka (Kheda) region.
January 766: North Konkan was ruled by the Shilahara Dynasty between 765 and 1029.
January 801: From his capital in Mayurkhandi in Bidar district, Govinda III conducted his northern campaign in 800 C.E. He successfully obtained the submission of Gurjara-Pratihara Nagabhata II, Dharmapala of Pala Empire and the incumbent puppet ruler of Kannauj, Chakrayudha.
January 801: King Shivamara II is mostly known for his wars with the Rashtrakuta Dhruva Dharavarsha, his subsequent defeat and imprisonment, his release from prison and eventually his death on the battle field.
January 801: Vatsraja was defeated by the Dhruva Dharavarsha of the Rashtrakuta dynasty, who conquered Malwa.
January 807: Dharmapala was forced to surrender and to seek alliance with the Rashtrakuta emperor Govinda III, who then intervened by invading northern India and defeating Nagabhata II.
January 811: Vatsraja was succeeded by Nagabhata II (805-833), who was initially defeated by the Rashtrakuta ruler Govinda III (793-814), but later recovered Malwa from the Rashtrakutas.
January 813: Historical evidence suggests that between 808-812 CE, the Rashtrakutas expelled the Gurjara-Pratiharas from the Malwa region.
January 815: Dharmapala gained control over North India after Govinda III left for the Deccan.
January 820: The Ganga resistance continued through the reign of Rashtrakuta Govinda III and by 819, a Ganga resurgence gained them partial control over Gangavadi under King Rachamalla.
January 837: Barwani State was a state in India from 836 AD. The seat was at Barwani.
January 841: Mihira Bhoja (c. 836-886) expanded the Pratihara dominions west to the border of Sind, east to Bengal, and south to the Narmada.
January 915: The Gurjara Pratihara ruler Mahendrapala I was experiencing some family feuds and this gave Indra III an opportunity to attack Kannauj in the Ganges - Yamuna doab.
January 917: The Rashtrakutas were actually able to hold Kannauj until c.916.
January 926: The Chandelas initially ruled as feudatories of the Gurjara-Pratiharas of Kanyakubja. Harsha's son Yashovarman (r. c. 925-950 CE) continued to acknowledge the Pratihara suzerainty, but became practically independent.
January 936: The Chalukyas of Vengi defeated the Rashtrakuta emperor Govinda IV and expanded their territories, achieving the maximal extent of their empire.
January 941: The territory was ruled by King Gandaraditya of the Shilahara Dynasty from 940 to 1215. The Shilahara Dynasty was a prominent ruling family in the region during that time.
January 951: Butuga II ascended the throne in 938 with the help of Rashtrakuta Amoghavarsha III (whose daughter he married). He helped the Rashtrakutas win decisive victories in Tamilakam in the battle of Takkolam against the Chola Dynasty. With this victory, the Rashtrakutas took control of modern northern Tamil Nadu. In return for their valour, the Gangas were awarded extensive territories in the Tungabhadra river valley.
January 951: While the Pandyas and the Rashtrakutas were busy engaging the Pallavas, with the Gangas and the Simhalas (Sri Lanka) also in the mix, the Cholas emerged from the Kaveri delta and took on the chieftains of Thanjavur.
January 971: The Chalukyas of Lata were an Indian dynasty, which ruled the Lata region of present-day Gujarat during 10th and 11th centuries. They ruled as feudatories of the Western Chalukyas in their early years.
January 973: Paramara King Siyaka Harsha attacked and conwuered Manyakheta, the capital of the Rashtrakutas.
February 973: Paramara King Siyaka Harsha attacked and conwuered Manyakheta, the capital of the Rashtrakutas.
January 974: Tailapa II, a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta ruling from Tardavadi province in modern Bijapur district, declared himself independent and established the Western Chalukya Empire.
Disestablishment
January 983: With the fall of the Rashtrakutas, their feudatories and related clans in the Deccan and northern India declared independence. The Western Chalukyas annexed Manyakheta.
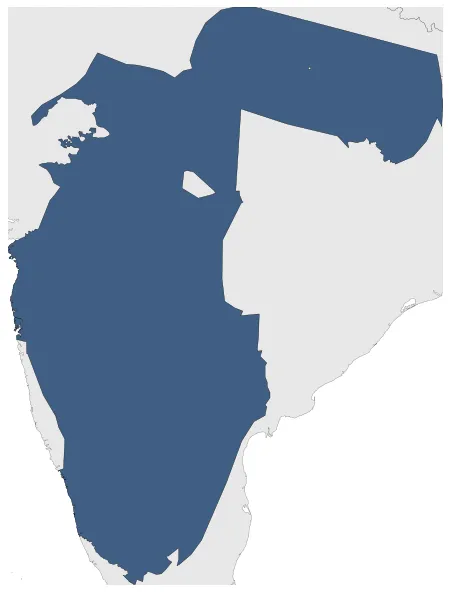
 Rashtrakuta Dynasty
Rashtrakuta Dynasty