Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville)
Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville)
This article is about the specific polity Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville) and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a sovereign state in Central Africa, created with the independence of the Belgian Congo in 1960. From 1960 to 1966, the country was also known as Congo-Léopoldville (after its capital) to distinguish it from its northwestern neighbor, which is also called the Republic of the Congo, alternatively known as "Congo-Brazzaville".
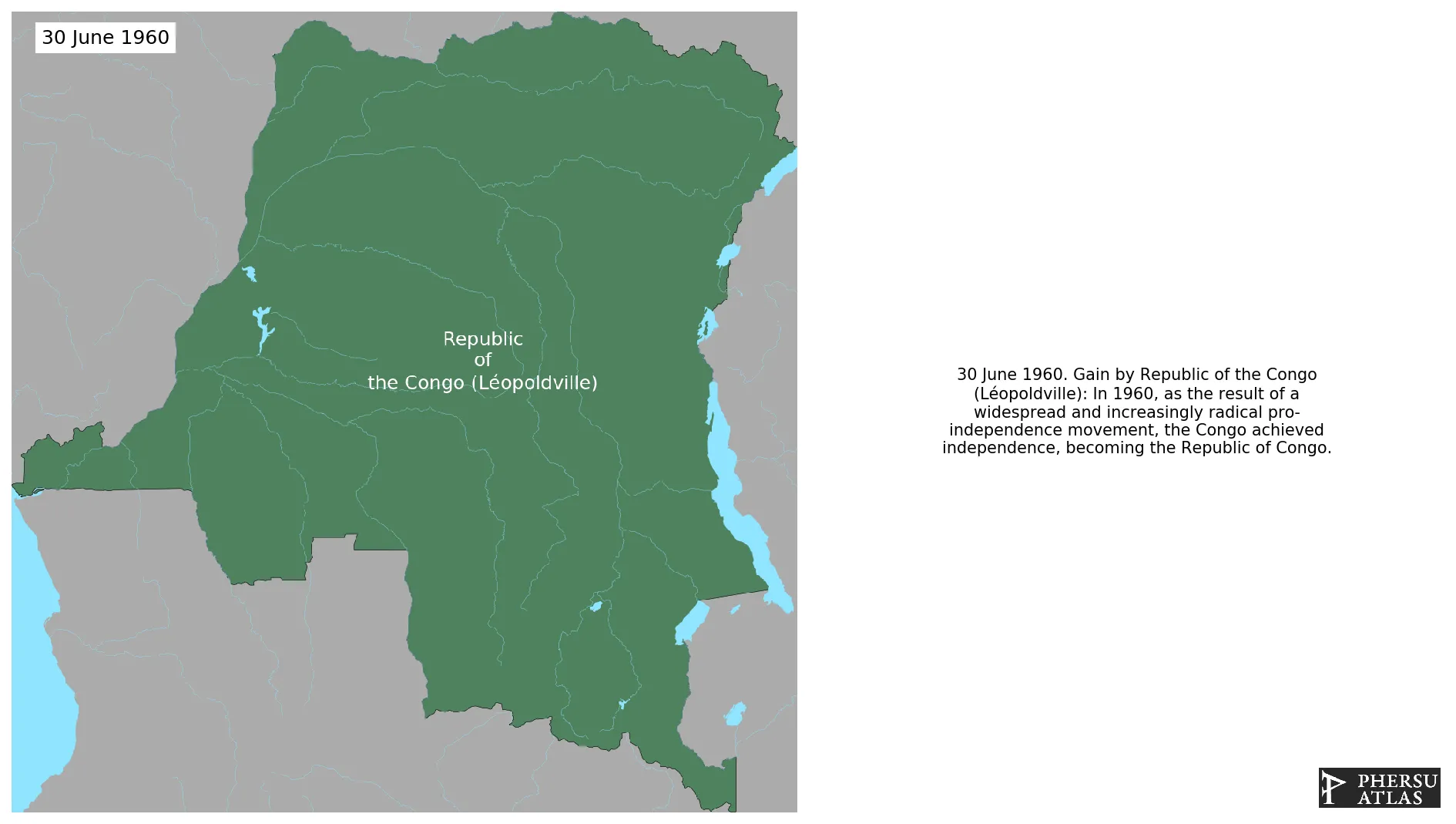
Establishment
June 1960: In 1960, as the result of a widespread and increasingly radical pro-independence movement, the Congo achieved independence, becoming the Republic of Congo.
July 1960: Moïse Tshombe, the leader of CONAKAT, declared the Congo's southern province of Katanga independent as the State of Katanga.
August 1960: Less than a month after the Katangese secession, on 8 August, a section of the region of Kasai situated slightly to the north of Katanga also declared its autonomy from the central government as the Mining State of South Kasai (Sud-Kasaï) based around the city of Bakwanga.
December 1960: Members of the MNC-L fled to Stanleyville where, led by Antoine Gizenga, they formed a rebel government in November 1960 in opposition to the central government in Léopoldville.
December 1960: Stanleyville troops occupied Bukavu.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Is a series of wars in the Democratic Republic of the Congo that started shortly after its independence from Belgium in 1960. The conflicts, that continue to this day, mainly consist of revolts against the central government caused by local ethnic secessionist movements.
1.1.Congo Crisis
Were a series of revolts against the central government of the newly established Republic of the Congo (modern-day Democratic Republic of the Congo). The war ended with Mobutu Sese Soko reuniting the country and establishing an authoritarian regime.
1.1.1.Secessionistic States (Congo Crisis)
At the beginning of the Congo crisis several territories declared their independence from the central government.
February 1961: The rival government, led by Moise Tshombe and supported by Belgium, reached its greatest territorial extent on 24 February 1961 when some of its forces briefly earned the allegiance of the Luluabourg garrison in the ongoing Congo Crisis.
January 1962: The rival government was not fully reintegrated into the Republic of the Congo until Gizenga was arrested in January 1962.
October 1962: Central government troops again arrived in Bakwanga to support the mutineers and help suppress the last Kalonjist loyalists, marking the end of South Kasai's secession.
December 1962: On 24 December 1962, UN troops and the Katangese Gendarmerie clashed near Élisabethville and fighting broke out. After attempts to reach a ceasefire failed, UN troops launched Operation Grandslam and occupied Élisabethville.
January 1963: In 1963, Indian UN troops, under the command of Commandant Pat Quinlan, occupied Jadotville in the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville) during the Congo Crisis. They were part of a peacekeeping mission but found themselves surrounded and outnumbered by Congolese troops and mercenaries.
January 1963: UN troops seized an abandoned gendarmerie base and secured Shinkolobwe.
January 1963: On 14 January, Indian troops found the last intact bridge into Kolwezi. After a brief fight with gendarmes and mercenaries they secured it and crossed over, stopping at the city outskirts to await further instruction.
January 1963: Tshombe surrendered his final stronghold of Kolwezi, effectively ending the Katangese secession.
1.1.2.Simba rebellion
Was a revolt part of the Congo Crisis that started in South Kivu (modern-day Democratic Republic of the Congo). The rebel leaders opposed the central government and most of them where Marxists.
May 1964: Pro-Simba forces successfuly revolted in the important harbor town of Albertville in late May.
May 1964: Fizi conquered by Simba Rebels.
May 1964: A small ANC detachment led by Louis Bobozo retook the town of Albertville.
June 1964: A third rebel force, independent of Soumialot, Gbenye, and Olenga, rebelled in northern Katanga in early June.
June 1964: When another rebellion broke out in the town, Soumialot's forces exploited the resulting chaos and captured Albertville.
June 1964: Kabila and Massengo's troops conquered the entire western shore of Lake Tanganyika, including Moba by late June.
July 1964: Christophe Gbenye and Nicholas Olenga rose in revolt in northeastern Congo, quickly expanding their army and territories. By June 1964, they held North Kivu, and southern Oriental Province.
July 1964: Simba conquest of Kindu.
July 1964: The Simbas continued to advance. By late July 1964, the insurgents controlled about half of the Congo.
August 1964: The Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville) is renamed Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Disestablishment
May 1964: Pro-Simba forces successfuly revolted in the important harbor town of Albertville in late May.
May 1964: Fizi conquered by Simba Rebels.
May 1964: A small ANC detachment led by Louis Bobozo retook the town of Albertville.
June 1964: A third rebel force, independent of Soumialot, Gbenye, and Olenga, rebelled in northern Katanga in early June.
June 1964: When another rebellion broke out in the town, Soumialot's forces exploited the resulting chaos and captured Albertville.
June 1964: Kabila and Massengo's troops conquered the entire western shore of Lake Tanganyika, including Moba by late June.
July 1964: Christophe Gbenye and Nicholas Olenga rose in revolt in northeastern Congo, quickly expanding their army and territories. By June 1964, they held North Kivu, and southern Oriental Province.
July 1964: Simba conquest of Kindu.
July 1964: The Simbas continued to advance. By late July 1964, the insurgents controlled about half of the Congo.
August 1964: The Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville) is renamed Democratic Republic of the Congo.
.svg.png.webp)
.png.webp)
 Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville)
Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville)