Data
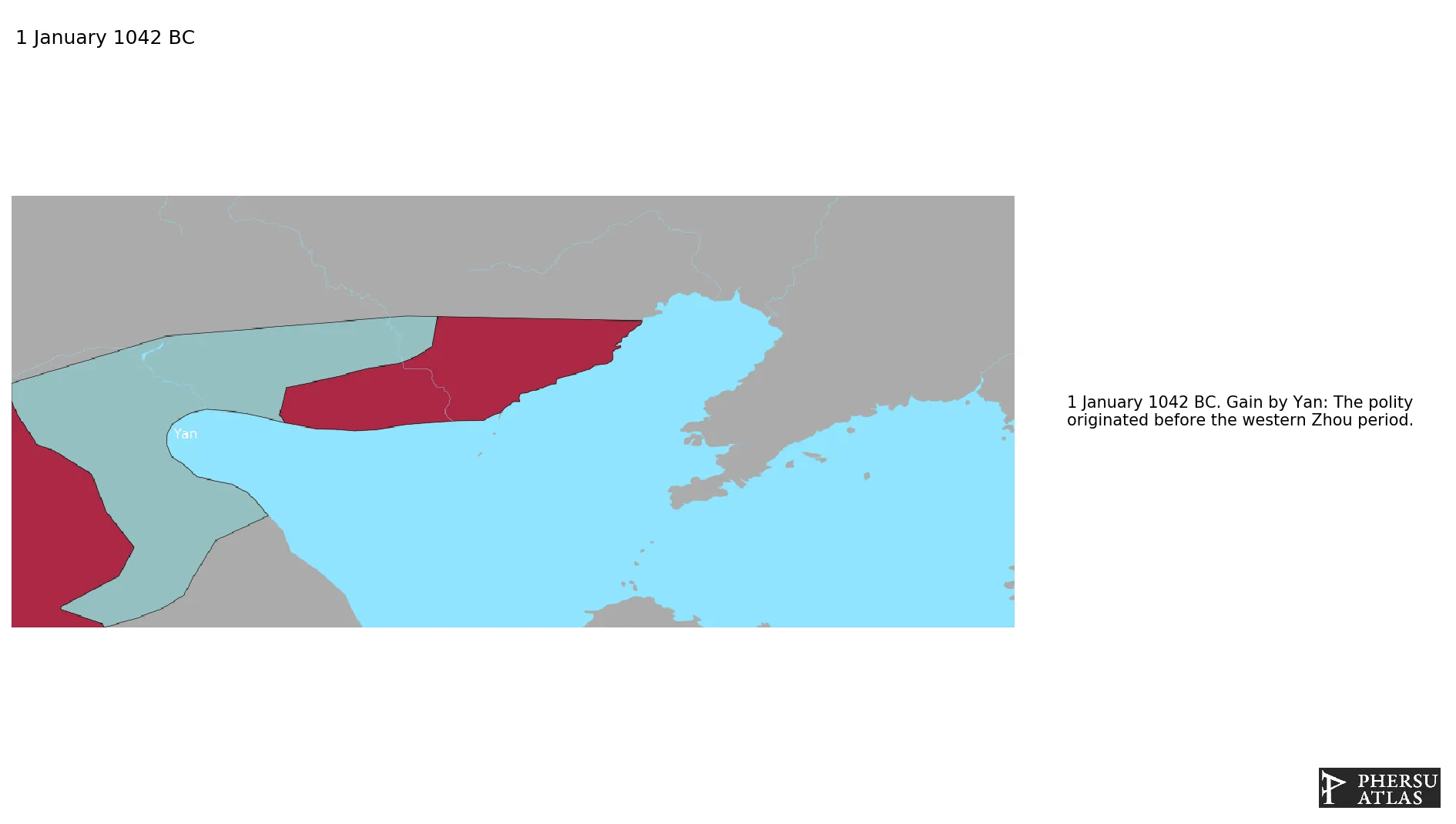
Name: Yan
Type: Polity
Start: 1042 BC
End: 204 BC
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Yan
Yan
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was one of many small polities that existed during the Chinese Spring and Autumn Period. It originated before the Zhou Dynasty or at the beginning of its existence.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Rebellion of the Three Guards
Was a civil war, instigated by an alliance of discontent Zhou princes, Shang loyalists, vassal states and other non-Zhou peoples against the Western Zhou government.
1.1.Annexation of external allies of the Three Guards
After crushing the rebellion of the three guards the Duke of Zhou conquered the regions of Feng and Pugu, that were allied with the rebels.
2. Gojoseon-Yan War
The Yan feudal state invaded the Gojoseon kingdom resulting in Yan's conquest of the Liaodong Peninsula from Gojoseon.
3. Qin´s wars of unification
Were a series of military campaigns launched in the late 3rd century BC by the Qin state against the other six major Chinese states, leading to the unification of China under the Qin dynasty.
Was a military campaign by the Qin Dynasty that led to the conquest of the state of Dai.
Was a military campaign by the Qin Dynasty that led to the conquest of the state of Yan.
4. Liu Bang´s Insurrection against the Qin dynasty
Was an insurrection in the Qin Empire that lead to its demise.
5. Chu-Han Contention
Was a war between the two most powerful successors of the Qin Dynasty, Western Chu and Han, won by the latter which was able to reunite China.