Cretan War (1645-1669)
Cretan War (1645-1669)
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a war between the Republic of Venice and her allies (among them the Knights of Malta, the Papal States and France) against the Ottoman Empire and the Barbary States.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
November 1657: Tenedos conquered by Ottoman Empire.
July 1656: The Venetians seize Tenedos.
August 1656: Lemnos conquered by Republic of Venice.
January 1646: Ottoman occupation of Crete.
January 1648: Venice reconquers Tenin (Knin) from the Ottomans.
January 1649: Knin (Tenin) is conquered by the Ottomans.
January 1647: Ottoman occupation of Novigrad.
August 1657: The Ottoman fleet proceeded to recover Lemnos.
January 1670: During the Cretan War (1645-1669), Cres Island was briefly occupied by the Ottoman Empire. However, in 1669, the territory was transferred to the Republic of Venice, which ruled over Cres Island and the neighboring Lošinj Islands until 1797.
January 1670: End of the Ottoman occupation of Krk Island and Pag Island.
January 1646: During the Cretan War (1645-1669), Cres Island was briefly occupied by the Ottoman Empire. The war was fought between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire over control of the island of Crete. The Ottoman occupation of Cres lasted until the end of the war in 1669.
Was the Ottoman invasion and occupation of Crete, a Venetian possession at the time.
September 1669: Siege of Candia.
October 1646: The venetian attempt to break the Ottoman blockade of Rettimo led to the fall of the city in 1646.
June 1647: Gazi Hüseyin Pasha, the local commander, conquered the eastern half of Crete, except for the fortress of Siteia.
April 1648: By the beginning of 1648, all of Crete, except Candia and a few strongholds like the island of Gramvousa, was in Ottoman hands.
January 1654: In 1653, the Ottomans took the island fortress of Selino in Suda Bay.
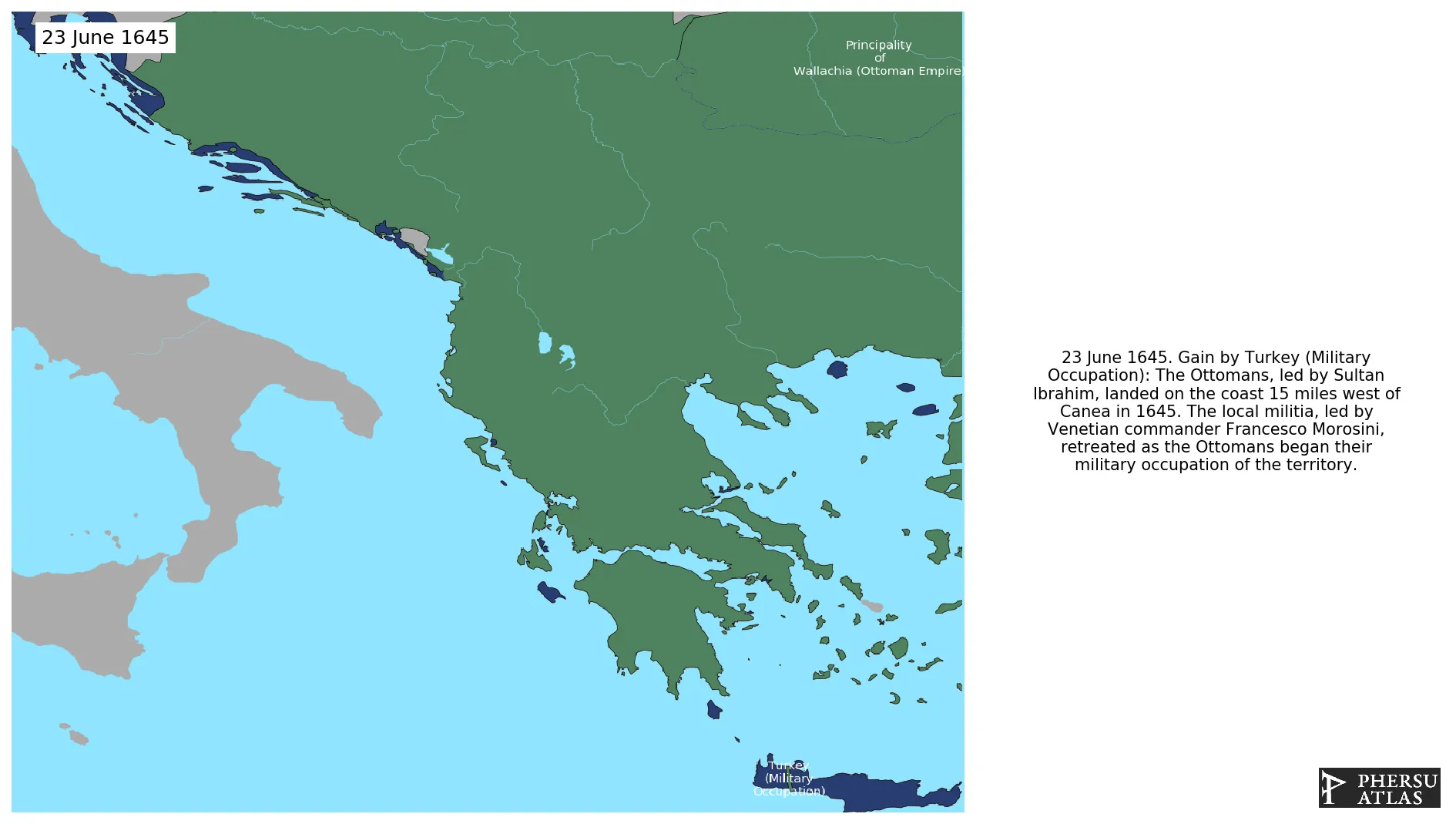
June 1645: The Ottomans, led by Sultan Ibrahim, landed on the coast 15 miles west of Canea in 1645. The local militia, led by Venetian commander Francesco Morosini, retreated as the Ottomans began their military occupation of the territory.
August 1645: The Ottoman army advanced to the city of Canea itself, which fell.
Was the Dalmatian theatre of the Cretan War (1645-1669).
July 1646: The supposedly impregnable fortress of Novigrad surrendered.
January 1647: The Ottomans launched a large-scale attack in 1646, and made some significant gains, including the capture of the islands of Krk, Pag and Cres.
January 1648: Venetian commander Leonardo Foscolo seized several forts and retook Novigrad, temporarily captured the fortress of Knin and took Klis.
Was the peace treaty between the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice that ended the Cretan War (1645-1669). Venice aknowledged the loss of Crete. At the same time the borders of the Venetian possession in Dalmatia were officially established with the Nani Line, and Venice had some territorial gains in Dalmatia.
October 1671: The Nani line (later called the Purchase Vecchio) was the border line established in Dalmatia on October 30 1671 between the Venetian and Ottoman possessions, following the War of Candia.
January 1672: The peace treaty between Venice and the Sublime Porte was signed two years after the loss of Candia, in 1671, sanctioning the definitive loss of Crete for the Venetians, even though they were allowed to keep only the fortress-islands of Gambusa, Suda and Spinalonga.
January 1672: In 1671, the territory of Nani Line was acquired by the Republic of Venice. This expansion in Dalmatia was part of Venice's efforts to strengthen its control in the region, following the end of the war.
 Cretan War (1645-1669)
Cretan War (1645-1669)