If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Were a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
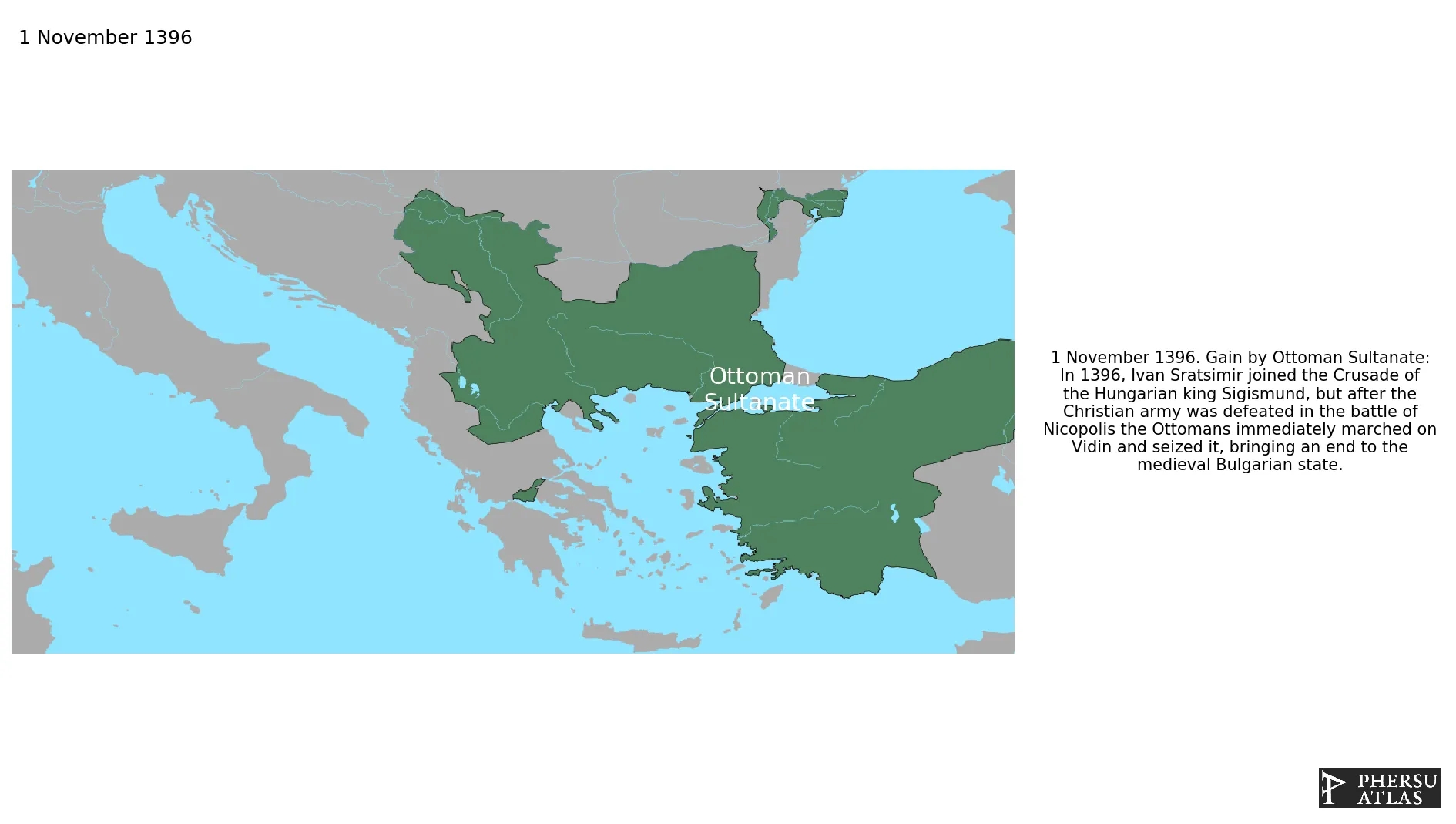
Was a battle between a crusader army of allied countries (Hungary, Croatia, Bulgaria, Wallachia, France, Venice and others) and the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman victory led to the end of the Second Bulgarian Empire.
Saw the Ottoman Empire under Sultan Murad II capture the city of Thessalonica.
March 1430: Ottoman capture of Thessalonica.
Was a war between the Republic of Venice and the ottoman Empire. Several Venetian territories were captured and annexed by the Ottomans.
January 1471: Negroponte was taken by the Turks.
January 1479: The Venetian-controlled territory of Lezhë (Alessio) was conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1478.
January 1480: Lefkada Island (Santa Maura) was a Venetian colony from 1362 to 1479, 1502 to 1503, and 1684 to 1797. In 1479, the territory was taken over by the Ottoman Empire. The Venetians were a powerful maritime republic based in Venice, Italy, known for their trade and military strength in the Mediterranean.
January 1469: In 1468, Athens was conquered by the Republic of Venice under the leadership of the Venetian general Bartolomeo Contarini. The city remained under Venetian control for a brief period before being captured by the Ottoman Empire in 1458.
January 1471: Pteleos was a Venetian colony from 1322 to 1470. In 1470, the territory was conquered by the Ottoman Empire under the leadership of Mehmed the Conqueror, marking the end of Venetian rule in the region.
January 1469: The Venetian commander Vettor Capello conquered Methone, Imbros, Thassos, Samothrace.
January 1479: Lemnos reverted to Ottoman control in accordance with the 1479 Treaty of Constantinople.
January 1469: After the death of the Albanian national hero Scanderbeg, the Republic of Venice seized the strategic city of Croia (Kruja) in 1468.
April 1463: The governor of the Morea, Isa-Beg Ishaković, took the Venetian-held town of Argos by treason.
August 1463: In early August, the Venetians retook Argos.
December 1463: In 1463, Matthias Corvinus, the King of Hungary, captured over sixty fortified places in Bosnia and successfully took the capital city of Jajce after a 3-month siege on 16 December.
January 1464: While of all Venetian territories in the Morea, Nauplia persisted longest in her possession, and was surrendered to the Ottomans in 1540 after the conclusion of the Third Ottoman-Venetian War.
January 1464: Preveza (Prevesa) was a Venetian colony from 1401 to 1463. In 1463, it was conquered by the Ottoman Empire. The Venetians regained control from 1684 to 1699 and again from 1717 to 1797.
May 1466: In April 1466, Vettore Cappello, the most vociferous proponent of the war, replaced Loredan as Captain General of the Sea. Under his leadership, the Venetian war effort was reinvigorated: the fleet took the northern Aegean islands of Imbros, Thasos and Samothrace.
October 1478: Croia fell into Muslim hands.
January 1479: Venetian colony of Drisht (Drivasto) in the periods 1393-1423 and 1442-1478.
April 1464: The Ottoman army razed the Hexamilion, and advanced into the Morea. Argos fell.
January 1470: In 1469, Athens was conquered by the Ottoman Empire, ending its brief period as part of the Venetian colonial Empire.
3.1.Treaty of Constantinople (1479)
Was a treaty between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire.
April 1479: Shkodër succumbed to the Ottomans in 1479.
Was a war between the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice for control of the lands that were contested between the two parties in the Aegean Sea, Ionian Sea, and the Adriatic Sea.
May 1503: The Ottomans abandoned Naples of Románia, Navarino, Malvasia, Kefalonia and Zakynthos.
January 1502: In 1501 the Ottomans led by Feriz Beg captured Durazzo in Venetian Albania.
September 1500: Ottoman conquest of Modone.
January 1500: Nafpaktos (Lepanto) is occupied by the Ottomans.
September 1500: Tinos and Mykonos conquered by Ottoman Empire.
December 1500: Siege of the Castle of Saint George or Siege of Cephalonia
January 1501: Cephalonia and Ithaca were conquered by the Venetians in December 1500.
October 1501: Santa Maura conquered by the Venetians.
January 1502: The city of Lezhë was again under the control of the Republic of Venice.
January 1504: End of the Venetian rule of Lefkada Island (Santa Maura).
January 1507: In 1506, Lezhë (Alessio) was conquered by the Ottoman Empire.
Was one of the Ottoman-Venetian wars which took place during the 16th century.
January 1539: The Venetians loose the Sporades to the Ottomans.
August 1539: Siege of Castelnuovo.
January 1539: Venice agreed to cede Morea to the Ottomans.
January 1538: In 1537 the Duchy of the Archipelago became a tributary of the Ottoman Empire.
January 1538: Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent attacked the Venetian colonies, conquering Corfu, Clissa, Syra, Stampalia, Patmos, Naxos, Andros.
January 1538: Venetian Aegina (Egina), 1451-1537.
September 1538: In the summer of 1538 the Ottomans turned their attention to the remaining Venetian possessions in the Aegean capturing the islands of Andros, Naxos, Paros, and Santorini, as well as taking the last two Venetian settlements on the Peloponnese Monemvasia and Navplion.
October 1538: Cefalonia conquered by Ottoman Empire.
January 1539: Northern Sporades conquered by the Ottomans.
January 1539: Venetian Karpathos Island (Scarpanto) and Kasos Island (Caso), 1306-1538.
Was a war of the Ottoman Empire against the Republic of Venice and the Holy League.
January 1572: Venetian Ulcinj (Dulcigno), 1405-1571.
March 1573: The new treaty confirmed the new state of affairs: Cyprus became an Ottoman province.
January 1574: In 1573, the Holy League fleet failed to sail altogether. Instead, Don John attacked and took Tunis.
January 1572: Venetian Bar (Antivari), 1443-1571.
6.1.Ottoman conquest of Cyprus
Was an Ottoman military campaign that resulted in the annexion of Cyprus, a Venetian possession at the time.
July 1570: The Ottomans landed unopposed at Salines, near Larnaca on the island's southern shore.
September 1570: The fortress of Kyrenia surrendered without resistance to the Ottoman Empire.
September 1570: The Siege of Nicosia in 1570 was part of the Ottoman–Venetian War (1570–1573). The Ottoman forces, led by Lala Mustafa Pasha, besieged the city of Nicosia, which was then under Venetian control. The siege lasted for seven weeks, resulting in the fall of the city to the Ottoman Empire on September 9.
Was a war between the Republic of Venice and her allies (among them the Knights of Malta, the Papal States and France) against the Ottoman Empire and the Barbary States.
January 1647: Ottoman occupation of Novigrad.
August 1657: The Ottoman fleet proceeded to recover Lemnos.
January 1670: During the Cretan War (1645-1669), Cres Island was briefly occupied by the Ottoman Empire. However, in 1669, the territory was transferred to the Republic of Venice, which ruled over Cres Island and the neighboring Lošinj Islands until 1797.
January 1670: End of the Ottoman occupation of Krk Island and Pag Island.
January 1646: During the Cretan War (1645-1669), Cres Island was briefly occupied by the Ottoman Empire. The war was fought between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire over control of the island of Crete. The Ottoman occupation of Cres lasted until the end of the war in 1669.
November 1657: Tenedos conquered by Ottoman Empire.
July 1656: The Venetians seize Tenedos.
August 1656: Lemnos conquered by Republic of Venice.
January 1646: Ottoman occupation of Crete.
January 1648: Venice reconquers Tenin (Knin) from the Ottomans.
January 1649: Knin (Tenin) is conquered by the Ottomans.
7.1.Ottoman invasion of Crete
Was the Ottoman invasion and occupation of Crete, a Venetian possession at the time.
June 1645: The Ottomans, led by Sultan Ibrahim, landed on the coast 15 miles west of Canea in 1645. The local militia, led by Venetian commander Francesco Morosini, retreated as the Ottomans began their military occupation of the territory.
August 1645: The Ottoman army advanced to the city of Canea itself, which fell.
September 1669: Siege of Candia.
October 1646: The venetian attempt to break the Ottoman blockade of Rettimo led to the fall of the city in 1646.
June 1647: Gazi Hüseyin Pasha, the local commander, conquered the eastern half of Crete, except for the fortress of Siteia.
April 1648: By the beginning of 1648, all of Crete, except Candia and a few strongholds like the island of Gramvousa, was in Ottoman hands.
January 1654: In 1653, the Ottomans took the island fortress of Selino in Suda Bay.
7.2.War in Dalmatia
Was the Dalmatian theatre of the Cretan War (1645-1669).
January 1648: Venetian commander Leonardo Foscolo seized several forts and retook Novigrad, temporarily captured the fortress of Knin and took Klis.
July 1646: The supposedly impregnable fortress of Novigrad surrendered.
January 1647: The Ottomans launched a large-scale attack in 1646, and made some significant gains, including the capture of the islands of Krk, Pag and Cres.
7.3.Cretan War (1645-1669) Peace Treaty
Was the peace treaty between the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice that ended the Cretan War (1645-1669). Venice aknowledged the loss of Crete. At the same time the borders of the Venetian possession in Dalmatia were officially established with the Nani Line, and Venice had some territorial gains in Dalmatia.
January 1672: In 1671, the territory of Nani Line was acquired by the Republic of Venice. This expansion in Dalmatia was part of Venice's efforts to strengthen its control in the region, following the end of the war.
October 1671: The Nani line (later called the Purchase Vecchio) was the border line established in Dalmatia on October 30 1671 between the Venetian and Ottoman possessions, following the War of Candia.
January 1672: The peace treaty between Venice and the Sublime Porte was signed two years after the loss of Candia, in 1671, sanctioning the definitive loss of Crete for the Venetians, even though they were allowed to keep only the fortress-islands of Gambusa, Suda and Spinalonga.
Was a war between the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice, part of the Great Turkish War. Venice succesfully invaded and occupied the Peloponnese.
Was a war between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire.
9.1.Ottoman conquest of the Venetians possessions in Greece
Was the Ottoman invasion of Venetian-held Peloponnese.
September 1715: Gathered their remaining forces at Methoni (Modon). However, being denied effective support from the sea by Delfin's reluctance to endanger his fleet by engaging the Ottoman navy, the fort capitulated.
January 1716: Venice conquered Kythira Island (Cerigo) and Antikythera Island (Cerigotto).
July 1715: After only nine days of siege, the Ottomans exploded a mine under the bastions of Palamidi and successfully stormed the fort.
June 1715: The Ottoman army crossed the Isthmus of Corinth and entered the Morea. The citadel of Acrocorinth, which controlled the passage to the peninsula, surrendered after a brief siege.
July 1715: The Ottoman Fleet, numbering 80 warships under Canum Hoca, captured the last Venetian possessions in the Aegean, the islands of Tinos and Aigina.
September 1715: The Ottomans then advanced to the southwest, where the forts of Navarino and Koroni were abandoned by the Venetians.
January 1716: Tinos conquered by Ottoman Empire.
January 1716: Poros, along with Methana, Troezen, and Epidaurus, was part of the Venetian Colony from 1484 to 1715. In 1715, the territory was taken over by the Ottoman Empire. This marked the end of Venetian control in the region.
Was a war between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire between 1714 and 1718. It was the last conflict between the two powers, and ended with an Ottoman victory and the loss of Venice's major possession in the Greek peninsula, the Peloponnese (Morea).
July 1718: The Mocenigo line (later called the Acqui Nuovissimo) was the border line established in Dalmatia in 1721 between the Venetian and Ottoman possessions, following the Peace of Passarowitz of 21 July 1718.
July 1718: The Mocenigo line (later called the Acqui Nuovissimo) was the border line established in Dalmatia in 1721 between the Venetian and Ottoman possessions, following the Pace of Passarowitz of 21 July 1718.
 Ottoman-Venetian Wars
Ottoman-Venetian Wars