First Macedonian War
First Macedonian War
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a war fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218-201 BC) against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
January 212 BC: Lissos was besieged and successfully taken by King Philip V of Macedon.
January 204 BC: In the First Macedonian War (214-205 BC), Oiniadai was lost again.
Was a military campaign led by Philip V of Macedon in Illyria during the first Macedonian War.
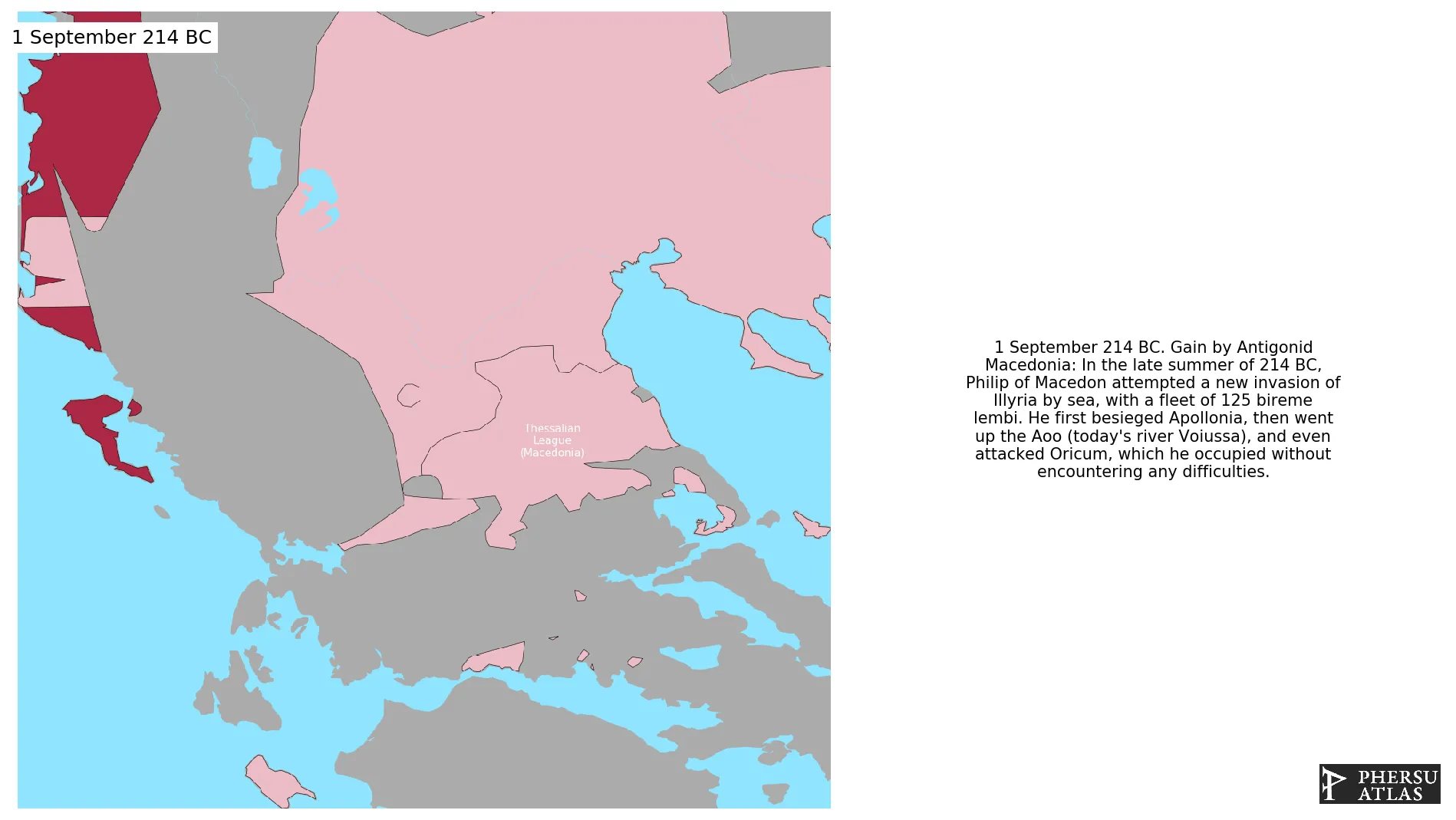
September 214 BC: In the late summer of 214 BC, Philip of Macedon attempted a new invasion of Illyria by sea, with a fleet of 125 bireme lembi. He first besieged Apollonia, then went up the Aoo (today's river Voiussa), and even attacked Oricum, which he occupied without encountering any difficulties.
January 213 BC: Roman general Levinus set off with the fleet and army towards Oricum, managing to conquer the city after a brief battle against the garrison left by Philip V of Macedon.
January 211 BC: Philip of Macedon finally managed to gain access to the Adriatic by capturing the city of Lissus and its citadel.
Was a Roman military campaign in Greece led by Marcus Valerius Laevinus during the first Macedonian War.
January 207 BC: The Macedonians took Thronium, followed by Tithronium and Drymaea north of the Cephissus river, at that point controlling all of Locris.
January 204 BC: After another season of fighting, in 206 BC, the members of the Aetolian League surrendered and, without the consent of Rome, signed a separate peace on the terms imposed on them by Philip of Macedon. With no more allies in all of Greece, but having nonetheless achieved their objective of preventing Philip from helping Hannibal, the Romans were now willing to sign peace. A treaty was signed at Phoenix in 205 BC, the so-called Peace of Phoenix, thus ending the First Macedonian War.
January 209 BC: A treaty was signed by the Romans with the Aetolians in 211 BC. The territories conquered by the Romans in Greece would go to them. Roman general Laevinus took possession of Zakynthos.
January 210 BC: The region was conquered by the Aetolians.
January 209 BC: The Romans conquered three cities of Acarania: Eniade, Nasos and Acarnanus, which he returned to the Aetolians.
January 209 BC: Corinth was assaulted by the Romans via sea and by the Aetolians via land. The assault from the sea was better managed as it was carried out by the Roman fleet, armed with various types of siege engines and war machines. In a few days, the city surrendered and handed itself over to the Aetolians. According to the agreement, the spoils of war went to the Romans.
January 209 BC: The Macedonian king probably took Phalara.
January 209 BC: Conquests of Attalus of Pergamon.
January 207 BC: In 208 BC the Roman fleet, made up of 35 ships from Pergamon and 25 Roman ships, failed to conquer Lemnos, but instead occupied and plundered the hinterland of the island of Peparethos, present-day Skopelos.
January 207 BC: Philip of Macedon managed to destroy Thermos, the capital of the Aetolians (207 BC).
January 207 BC: Macedonian conquest of Oreus.
Selected Sources
Piganiol, A. (1989): Le conquiste dei romani, Milan (Italy), p. 236
Piganiol, A. (1989): Le conquiste dei romani, Milan (Italy), p. 237
Polybius: The Histories, IX, 39
Polybius: The Histories, VIII, 15-16
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita, XXVIII, 5
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita,XXVI, 24.15-16
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita, XXIV, 40.1-3
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita, XXIV, 40.4-6
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita, XXVI, 26.1-4
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita, XXVIII, 8.
 First Macedonian War
First Macedonian War