Phase 1: Swedish Dominance
Phase 1: Swedish Dominance
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the first phase of the Great Northern War, characterized by Swedish victories.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
April 1700: Danish troops set out on March 17, 1700 and occupied several places in Holstein-Gottorf.
Was the Livonian-Estonian theatre of war in the first phase of the Great Northern War.
June 1704: In early June 1704, Dorpat (Tartu) was surrounded by Russian forces.
July 1701: Battle of the Dvina: the Saxons were repulsed by the Swedish army led by King Charles XII.
November 1700: Battle of Narva (30 November 30, 1700): the Swedish troops crushed the numerically superior Russian army.
July 1704: On July 14, 1704, the city of Tartu fell into Russian hands.
August 1704: Russian forces captured Narva.
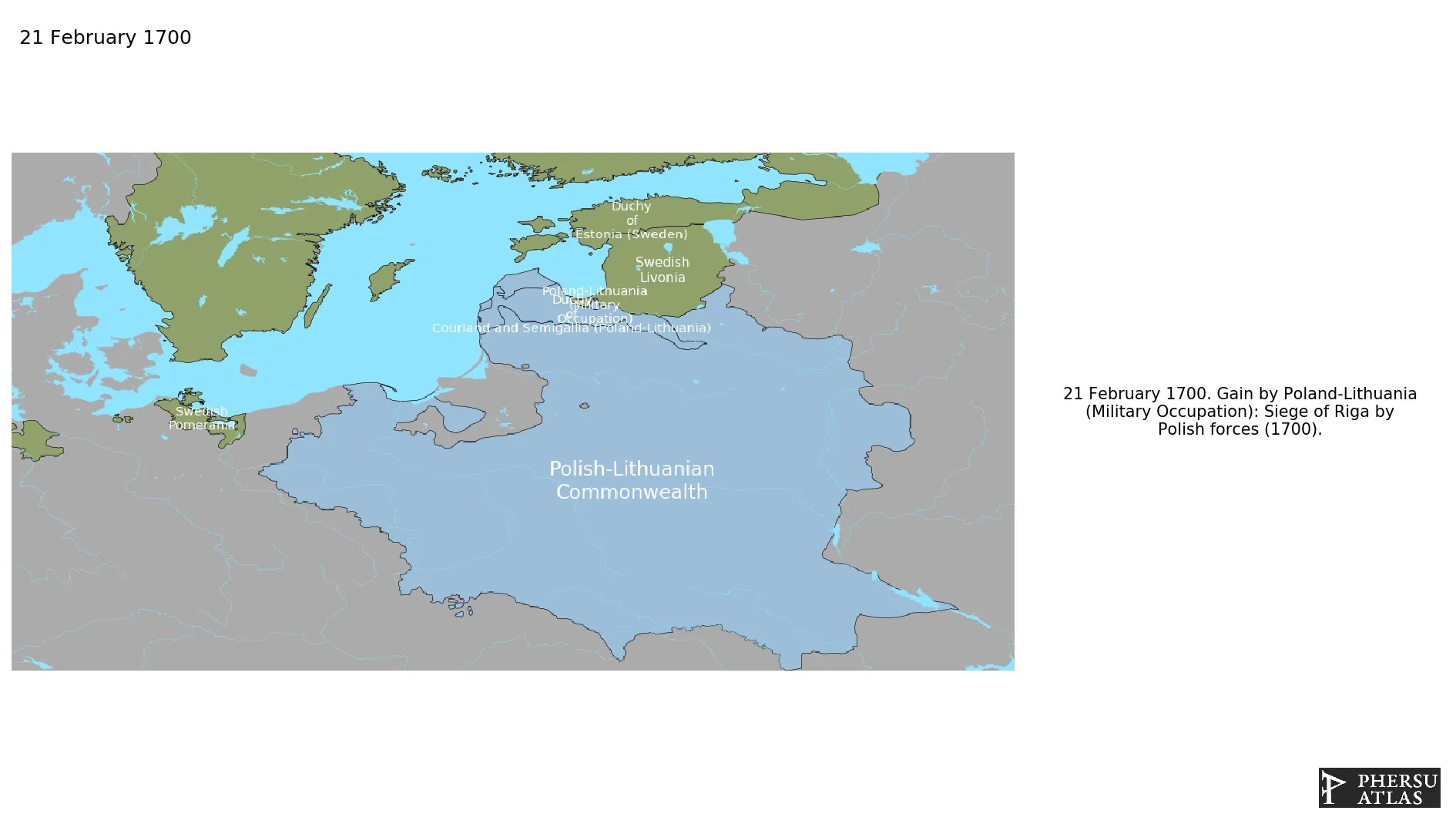
February 1700: Siege of Riga by Polish forces (1700).
March 1700: The Saxons took neighboring Dünamünde (March 13-15, 1700) and renamed it Augustusburg during th occupation.
October 1700: In mid-September, a Russian advance guard advanced into Swedish territory, and on October 4, 1700, the main Russian army with about 35,000 soldiers began the siege of Narva.
October 1700: Polish forces besieged the castle of Kokenhausen from autumn 1700 and conquered it on October 17, 1700.
January 1702: On December 30, 1701, Russian forces defeated the Swedish Livonian army in the Battle of Erastfer.
January 1702: After the victorious Russians had plundered Erastfer and nearby regions, they withdrew again as they feared an attack by Swedish forces.
July 1702: Battle at Hummelshof.
December 1702: The Russian army retreated to Pskov without occupying the territory conquered in Livonia.
June 1704: Siege of Narva (1704).
August 1705: Mitau is besieged by the Tsardom of Russia.
August 1702: Since the remaining Swedish forces were too weak to oppose the Russians in open battle, Wolmar and Marienburg as well as the rural areas of Livonia fell into Russian hands in August.
June 1704: Battle of Wesenberg.
September 1705: Mitau is besieged by the Tsardom of Russia.
Was the Danish theatre of war in the first phase of the Great Northern War.
August 1700: A Swedish army of 10,000 landed on Zealand under the protection of their ship guns.
April 1700: Danish troops entered Tönning.
August 1700: Charles XII of Sweden attacked Denmark by land and sea, forcing the country to sign a peace treaty. The rulers of Sweden and Denmark signed the Peace of Travendal (August 18, 1700), which restored the status quo ante.
August 1700: The Swedish army, having landed on Zealand, marched against Copenhagen.
Was a military campaign initiated by Sweden during the Great Northern war. The goal of the campaign was the overthrow of Augustus II the Strong, who was at the same the Elector fo Saxony and the King of Poland-Lithuania.
July 1702: Battle of Klissow.
November 1705: Since Count Ogiński was unsuccessful in his continued struggle on August II's side, the Swedish party finally gained the upper hand in Lithuania.
January 1707: Moreover, in 1706 a Russian army had invaded and occupied western Poland.
September 1706: In the summer of 1706, Charles XII of Sweden with his troops from eastern Poland, on August via Silesia into the Electorate of Saxony. The Swedes conquered the electorate step by step and crushed all resistance.
September 1706: Having pursued Augustus of Saxony in his homeland, the Swedish King forced Augustus to sign the Altranstadt Peace Treaty on 24 september 1706. The Elector of Saxony renounced the Polish crown "forever" and dissolved the alliance with Russia.
October 1705: As a result of the Battle of Rakowitz, Stanislaus Leszczyński was crowned the new Polish king on October 4, 1705 in Warsaw. […] Only Greater Poland, West Prussia, Mazovia and Lesser Poland submitted to him, while Lithuania and Volhynia continued to support Augustus II and Peter I.
January 1702: King Charles XII of Sweden took Mitau, the capital of the Duchy of Courland, and thus took the whole Duchy.
May 1702: Charles XII of Sweden and his army marched against Warsaw, which surrendered without a fight on May 14, 1702.
July 1702: Charles XII of Sweden occupied Kraków on July 31, 1702. Sweden now controlled the residence city of Warsaw and the coronation city of Kraków.
May 1703: Battle of Pultusk (1703).
May 1703: Siege of Thorn (1703).
October 1703: The Swedes under King Charles XII. conquered the fortress of Thorn after a month-long siege.
January 1704: The city of Posen was conquered by the Swedes in 1703.
September 1704: Swedish storming of Lviv.
October 1704: In 1704, during the Great Northern War, Western Prussia was occupied by Sweden under the leadership of King Charles XII. The successful military occupation of the territory led to other cities in the region submitting to the Swedish king out of fear and admiration for his military prowess.
October 1704: The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth captured Warsaw (1704).
November 1704: Battle of Tillendorf.
December 1704: In 1704, during the Great Northern War, Tsar Peter the Great of Russia led a large army into Belarus, capturing key cities like Vilnius, Minsk, and Grodno. This military occupation marked a significant expansion of Russian influence in the region.
March 1706: Siege of Lyakavichy.
November 1709: The fishing village of Råå falls under Danish-Norwegian military occupation.
April 1706: Battle of Klezk.
March 1706: Battle in Nyasvizh.
May 1706: Siege of Lyakavichy.
Was the Ingrian theatre of war in the first phase of the Great Northern War.
November 1706: Russian forces ended the siege of Vyborg and left the area.
October 1708: Battle of Koporje.
September 1708: Battle of the Neva.
October 1702: Siege of Nöteborg.
October 1702: Russian conquest of Nöteborg (actual Shlisselburg) after a siege.
April 1703: Siege of Nyenschanz.
May 1703: Siege of Nyenschanz.
October 1706: Russian forces started besieged the city of Vyborg.
July 1708: Sack of Porvoo by Russian forces.
August 1708: The Russians leave Porvoo.
May 1703: Naval battle at the mouth of the Neva. the Neva was now fully controlled by Russian forces.
July 1703: The rest of Ingermanland including Jaama and Koporje could also be occupied by the Russians within a few weeks after taking Nyenschantz by a Russian infantry command under Major General Nikolai von Werdin.
Was the Swedish invasion of the Tsardom of Russia during the first phase of the Great Northern War.
July 1708: In 1708, during the Great Northern War, King Charles XII of Sweden halted the advance of the Swedish main army at Mogilev, awaiting General Lewenhaupt's reinforcements and supply trains from Livonia. This strategic decision was crucial for the Swedish military occupation of Mogilev.
July 1708: Battle of Golovchin.
August 1708: On August 21, the Swedes occupied Chemikow on the Sosh River.
July 1709: The troops around King Karl of Sweden reached the Bug River on July 17, 1709. The pasha gave Ochakov permission to enter the Ottoman Empire, ending Charles XII's Russian campaign in a catastrophic defeat against Tsar Peter the Great of Russia.
July 1709: The troops around King Karl reached the Bug on July 17, where the pasha gave Ochakov permission to enter the Ottoman Empire. This ended Charles' Russian campaign in a catastrophic defeat.
October 1707: On September 7, 1707, it crossed the Polish border near Steinau an der Oder. Menshikov's army avoided battle and withdrew from the western part of Poland.
January 1708: In mid-January 1708, King Charles XII of Sweden led his army out of Masuria and arrived in Grodno on January 28, 1708. The Swedish military occupation of Grodno was part of their campaign during the Great Northern War against the Russian Empire.
March 1708: Tsar Peter, who met with Menshikov not far from the city, considered the strength of the Russian army too weak to be able to stop the Swedish army there and ordered a further retreat to the Lithuanian-Russian border […] The Swedish advance lasted until the beginning February until the army of Charles XII. moved into winter camp near the Lithuanian town of Smorgon.
June 1708: After the start of the summer campaign on June 1st, the Swedish army crossed the Berezina on June 18th. The Russian forces were able to elude an attempted evasion by the Swedes and withdrew behind the next river barrier, the Drut.
August 1708: When the main Swedish army crossed the Dnieper in the first week of August, Lewenhaupt's army had still not arrived.
September 1708: Battle of Molyatichi.
September 1708: Finally, King Charles XII of Sweden decided to call off the march on Moscow. When he left Tatarsk in mid-September 1708, it marked the end of Sweden's military occupation of the territory.
September 1708: Swedish General Lewenhaupt reached the Dnieper River. The crossing took a week, allowing the Russian forces to close in and eventually chase the Swedes.
January 1709: In 1709, during the Great Northern War, Weprik was besieged and stormed by Swedish forces under the command of King Charles XII. The siege resulted in the territory falling under Swedish military occupation.
February 1709: Battle of Krasnokutsk.
April 1709: Siege of Poltava.
July 1709: The Swedish force was decisively defeated by Peter the Great of Russia at Poltava near the River Dnieper.
July 1709: The Swedish force was decisively defeated by Peter the Great of Russia at Poltava near the River Dnieper. Charles XII of Sweden fled to Turkish Moldavia.
December 1708: Siege and storming of Weprik.
Selected Sources
Bradford, J.C. (2004): International Encyclopedia of Military History, Routledge, p. 553
Bradford, J.C. (2004): International Encyclopedia of Military History, Routledge, p. 554
Poten, B. (1879): Handwörterbuch der gesamten Militärwissenschaften, Velhagen & Klasing, p. 195
Poten, B. (1879): Handwörterbuch der gesamten Militärwissenschaften, Velhagen & Klasing, p. 196
Poten, B. (1879): Handwörterbuch der gesamten Militärwissenschaften, Velhagen & Klasing, p. 197
 Phase 1: Swedish Dominance
Phase 1: Swedish Dominance