Phase 2: Sweden Defending itself
Phase 2: Sweden Defending itself
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the second phase of the Great Northern War. It consisted in the counterattack of all the countries that Sweden had invaded during the first phase of the war.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
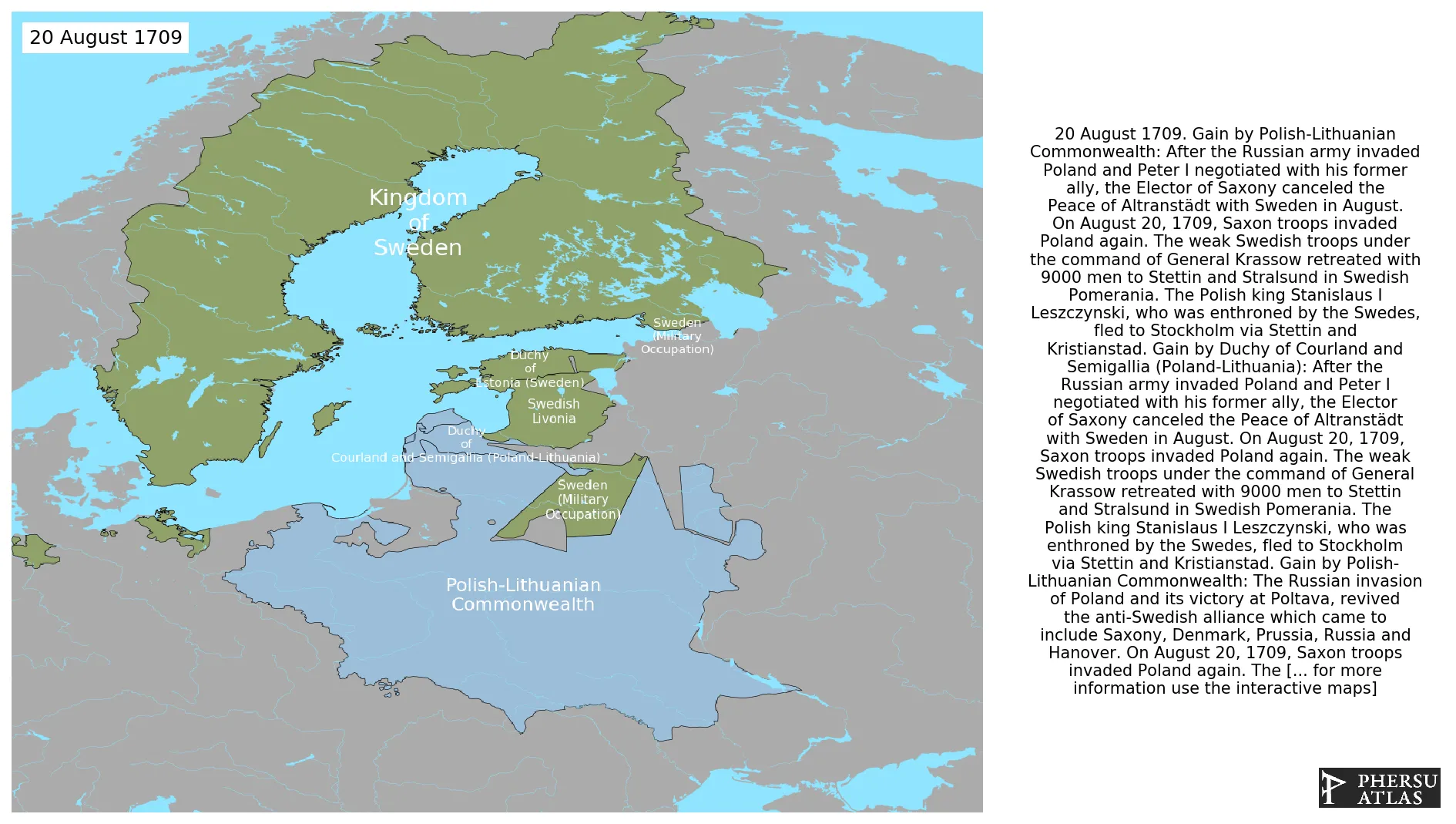
August 1709: After the Russian army invaded Poland and Peter I negotiated with his former ally, the Elector of Saxony canceled the Peace of Altranstädt with Sweden in August. On August 20, 1709, Saxon troops invaded Poland again. The weak Swedish troops under the command of General Krassow retreated with 9000 men to Stettin and Stralsund in Swedish Pomerania. The Polish king Stanislaus I Leszczynski, who was enthroned by the Swedes, fled to Stockholm via Stettin and Kristianstad.
August 1709: The Russian invasion of Poland and its victory at Poltava, revived the anti-Swedish alliance which came to include Saxony, Denmark, Prussia, Russia and Hanover. On August 20, 1709, Saxon troops invaded Poland again. The weak Swedish troops under the command of General Krassow retreated with 9000 men to Stettin and Stralsund in Swedish Pomerania. The Polish king Stanislaus I Leszczynski, who was enthroned by the Swedes, fled to Stockholm via Stettin and Kristianstad.
Was the Danish invasion of Schonen (in Sweden) during the Great Northern War.
January 1710: In December, Denmark controlled almost all of central Skåne with the exception of Malmö and Landskrona.
April 1710: After the Battle of Helsingborg, the Danish units were so weakened that they left Scania and embarked for Denmark. By March 5, the last remains of the Danish army left Scania after intentionally slaughtering all their horses and sabotaging their cannons by spiking them.
Was the theatre of war of northern Germany in the second phase of the Great Northern War.
August 1711: On August 29, 1711, Danish troops under the command of their king invaded Damgarten in Swedish Pomerania.
October 1712: In 1712, Ottersberg and Verden were occupied by Kurhannover, led by Elector George Louis. The occupation was a response to the Danish increase in power, as Kurhannover did not want to be cut off from the sea again. This move was part of the ongoing power struggles and territorial disputes in the region during that time.
January 1712: The conflict in Wismar in 1712 ended with the withdrawal of the Danish corps led by Lieutenant General Jørgen Rantzau on January 19. This marked a victory for the Swedish forces in the region during the Great Northern War.
January 1712: Frederick IV of Denmark withdrew to Wismar and Mecklenburg on January 7, 1712, leaving the territories he had occupied in Swedish Pomerania.
September 1712: End of Polish-Lithuanian siege of Stralsund.
February 1710: Russian storming of Elbing (today: Elbląg).
August 1711: Danish-Norwegian forces put Wismar under siege.
September 1711: From September 7, 1711, Stralsund was besieged by the Danish-Norwegian army.
July 1712: Wismar was occupied by the Danish army.
September 1712: In 1712, the Danish army, led by King Frederick IV, invaded the Swedish Duchy of Verden. The city of Stade was handed over to the Danes on September 6, 1712.
October 1712: On October 1, 1712, Bremerland fell as well. With that, the whole of Bremen-Verden was conquered by Denmark.
November 1712: Until 7 November 1712 Wismar unsuccessfully besieged by a Danish corps.
May 1713: Magnus Stenbock was surrounded in Tönning in February 1713 with 11,000 men by a superior force of Danish, Russian and Saxon troops and, after a three-month siege, was forced to capitulate on May 16, 1713.
September 1713: By summer 1713 Sweden left all territories in Mecklenburg.
October 1713: A few days after the handover, the Allies agreed with Prussia in the Treaty of Schwedt, which was to take over the city as a neutral occupying power and was allowed to keep it in the future for a payment of 400,000 Reichstaler. After paying this sum, Prussian troops marched into Stettin on October 6, 1713.
November 1713: In the meantime, apart from Stralsund and the enclave of Wismar, Swedish Pomerania had been completely conquered by the allied Danes, Russians and Saxons or occupied by Prussia as a neutral power.
May 1715: Following Prussian and Hanoverian occupation, Denmark ceded Bremen-Verden to Hanover on May 2, 1715 in exchange for a compensation payment.
June 1712: Polish-Lithuanian forces besiege Stralsund.
September 1713: The city of Stettin surrendered to Polish-Lithuanian forces.
January 1713: On January 31, 1713, Russian troops pushed the Swedish army into the Tönning fortress belonging to Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorf.
Was a Russian military campaign against the territories occupied by Sweden in eastern Europe and the Baltic during the Great Northern War.
March 1710: Siege of Vyborg.
July 1710: Siege of Riga (1709).
July 1710: Siege of Kexholm.
July 1710: Siege of Pernau.
August 1710: Siege of Pernau.
September 1710: Siege of Kexholm.
October 1710: Reval (today Tallinn) is besieged and taken by the Tsardom of Russia, along with Livonia and Estonia as all the Swedish forts had been conquered.
January 1711: Capitulation of Arensburg (now Kuressaare) in present-day Estonia to the Tsardom of Russia.
August 1710: Reval (today Tallinn) is besieged and taken by the Tsardom of Russia, along with Livonia and Estonia as all the Swedish forts had been conquered.
June 1710: Siege of Vyborg.
January 1711: Conquest of the island of Ösel by the Russians.
Was a Russian military campaign against the Ottoman Empire during the Great Northern War.
July 1711: Siege of Brăila.
July 1711: Battle of Stănileşti: the joint Moldavian and Russian troops, the former under the command of Cantemir and the latter under Peter the Great and Boris Sheremetev, were surrounded and forced to surrender (on 22 July) to the larger Ottoman army.
July 1711: In 1711 the mouth of the Don was lost in favor of Turkey according to the Prut peace.
July 1711: The conflict was ended on 21 July 1711 by the Treaty of the Pruth that stipulated the return of Azov to the Ottomans.
Was a Swedish military campaign in Holstein during the Great Northern War.
February 1713: The Swedish army leaves Altona.
December 1712: The Swedish army moved on to Rostock and took the city.
December 1712: Swedish forces defeated Danish forces at Galdebusch (20 December 1712).
January 1713: Swedish general Magnus Stenbock takes the city of Altona after a siege. Subsequently the Swedish army burnt the city down ("Einäscherung von Altona").
Was a Russian military campaign in Finland, at the time part of Sweden, during the Great Northern War.
May 1713: In 1713, during the Great Northern War, Tsar Peter the Great's Russian forces landed near Helsingfors (now Helsinki). The Swedish commander Georg Lybecker preemptively burned the city to prevent its capture, leading to its eventual occupation by the Tsardom of Russia.
May 1713: On the evening of May 22, 1713, Russian marines unopposed landed near the city of Borgå (modern-day Porvoo).
October 1713: Battle of Pälkäne.
March 1714: The Battle of Storkyro was a decisive victory for the Russian forces led by Tsar Peter the Great over the Swedish army in Finland. The defeat led to the complete occupation of Finland by the Tsardom of Russia in 1714.
August 1714: The whole of Åland was under Russian control.
Was the theatre of war on the border between Sweden and Norway in the second phase of the Great Northern War.
December 1714: In the fall of 1714, Russian troops led by Tsar Peter the Great landed near Umeå, Sweden. The Swedish garrison quickly abandoned the city after a brief skirmish, marking the beginning of the Tsardom of Russia's military occupation of the territory.
Was a joint Danish, Prussian and Polish military campaign in Pomerania during the Great Northern War.
April 1716: The Siege of Wismar in 1715 was part of the Great Northern War. The Swedish forces, led by General Carl Gustav Rehnskiöld, defended the city against the coalition of Danish, Polish-Lithuanian, and Prussian troops. The siege ended in 1716 with the territory of Wismar being divided among the victorious powers.
June 1715: The Siege of Wismar in 1715 was part of the Great Northern War. The city was besieged by the forces of Tsar Peter the Great of Russia, leading to its surrender and subsequent division of the territory between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark, and Prussia.
December 1715: Surrender of the Swedish garrison of Stralsund Fortress on December 23, 1715.
August 1715: Storming of the Peenemünder Schanze.
November 1715: The Allies succeeded in conquering Rügen on November 17th.
Was a Swedish invasion of Denmark-Norway during the Great Northern War.
July 1716: After the burning of the fleet by the Danes, the Swedish army was forced to return to Sweden in July.
November 1718: The Siege of Fredrikshald in 1718 was a military conflict between the forces of King Charles XII of Sweden and the Norwegian fortress town of Fredrikshald. The siege resulted in the death of King Charles XII and the territory of Fredrikshald falling under Swedish military occupation.
December 1718: The Siege of Trondheim in 1718 was part of the Great Northern War between Sweden and Denmark-Norway. The Swedish forces, led by King Charles XII, successfully captured the city of Trondheim, leading to a military occupation of the territory.
December 1718: The Siege of Fredrikshald in 1718 was a military conflict between Sweden and Denmark-Norway. The Swedish King Charles XII was killed during the siege, leading to the territory of Fredrikshald being ceded to Denmark-Norway as part of the peace treaty.
January 1719: The Siege of Trondheim in 1719 was part of the Great Northern War between Sweden and Denmark-Norway. Swedish forces, led by King Charles XII, unsuccessfully attempted to capture the city of Trondheim in Norway, which was then part of Denmark-Norway. The siege ended with the territory going back to Denmark-Norway.
April 1716: Oslo conquered by sweden.
Was a Danish invasion of Sweden during the Great Northern War.
July 1719: The Danish captured Marstrand.
Was the Russian invasion of Sweden during the second phase of the Great Northern War.
Selected Sources
Bradford, J.C. (2004): International Encyclopedia of Military History, Routledge, p. 554
Poten, B. (1879): Handwörterbuch der gesamten Militärwissenschaften, Velhagen & Klasing, p. 202
 Phase 2: Sweden Defending itself
Phase 2: Sweden Defending itself