Anglo-Burmese Wars
Anglo-Burmese Wars
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Were a series of wars between the British Empire and the Konbaung dynasty of Burma. After the third and last war, Burma was annexed to British India.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the first of a series of wars between the British Empire and the Konbaung dynasty of Burma. Burma lost territories in Assam, Manipur, and Arakan.
1.1.Western theatre (First Anglo-Burmese War)
Was a British military campaign in western Burma during the First Anglo-Burmese War.
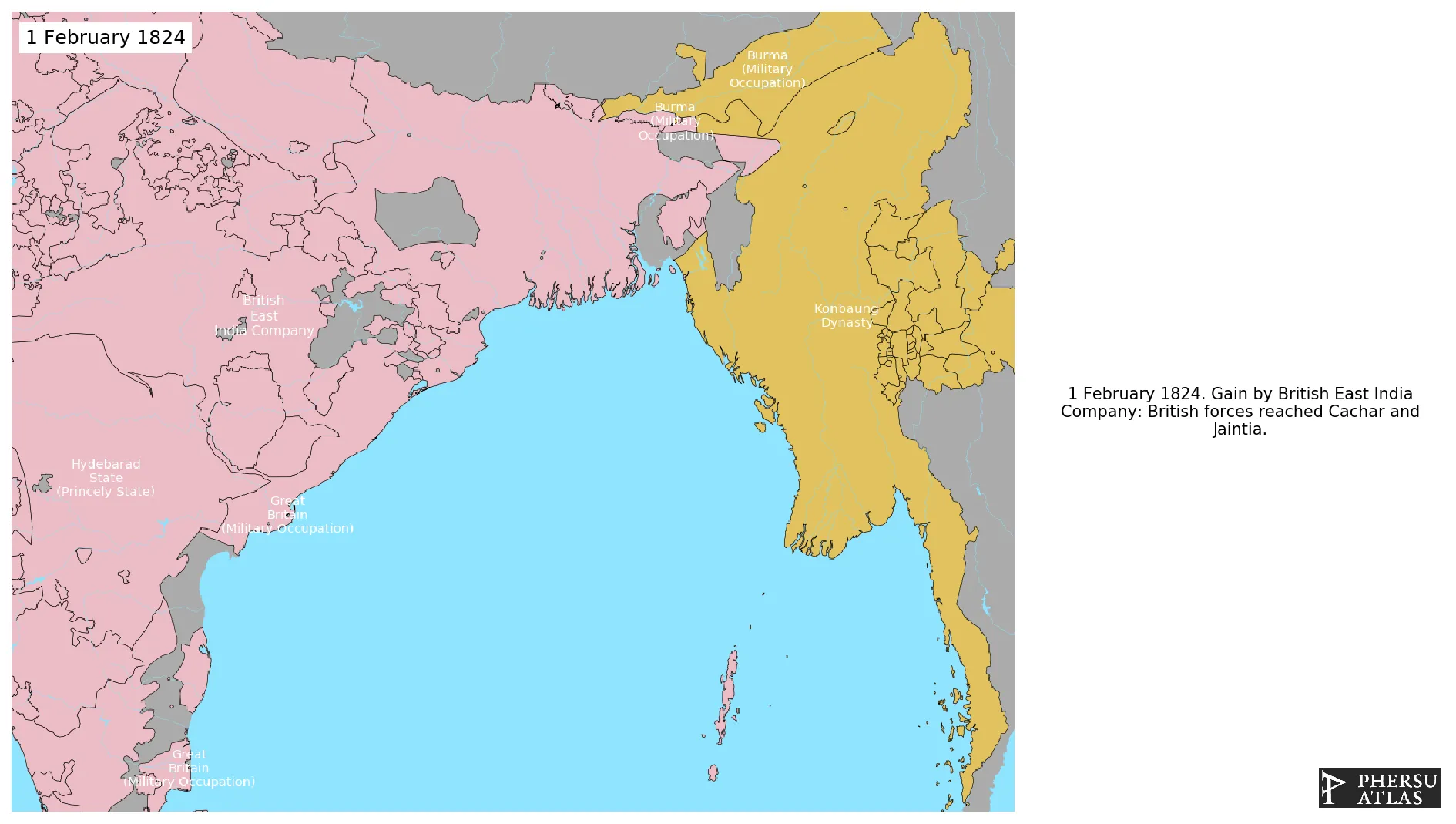
February 1824: British forces reached Cachar and Jaintia.
March 1824: Burmese general Thado Thiri Maha Uzana defeated the British units in Cachar and Jaintia in January 1824.
May 1824: Battle of Ramu.
1.2.Burma interior Campaign (First Anglo-Burmese War)
Was a British military campaign in the interior of Burma during the First Anglo-Burmese War.
April 1825: Battle of Danubyu.
May 1824: A British naval force of over 10,000 men (5,000 British soldiers and over 5,000 Indian sepoys) entered the harbour of Yangon (Rangoon), taking the Burmese by surprise.
November 1824: Burmese general Bandula commanded a force of 30,000 massed outside Yangon.
December 1824: The Burmese were driven out of their last remaining stronghold at Kokine.
January 1826: Battle of Prome.
February 1826: Battle of Prome.
February 1826: British army at Yandabo village, only 80 km from the capital Ava, the Burmese were forced to accept the British terms without discussion. According to the treaty, the Burmese agreed to: Cede to the British- Assam without any consent and approval of the Ahom Kingdom in their own region, Manipur, Rakhine (Arakan), and the Taninthayi (Tenasserim) coast south of the Salween River.
January 1826: With a large portion of the Burmese army dispersed at Prome, the British army led by Campbell advanced toward Ava unimpeded until they encountered a stockaded defence at Bagan.
May 1825: The British proceeded to occupy the rest of Arakan.
August 1824: The British launched attacks on Burmese lines, and by July 1824, had successfully pushed the Burmese towards Kamayut, 8 km from Shwedagon.
1.3.Treaty of Yandabo
Was the peace treaty that ended the First Anglo-Burmese War. .
February 1826: The Treaty of Yandabo ended the First Anglo-Burmese War. The treaty resulted in the cession of Assam, Manipur, Tripura, Rakhine, and Tenasserim to the British.
Was the first of a series of wars between the British Empire and the Konbaung dynasty of Burma. Burma lost the Pegu province (renamed Lower Burma by the British).
May 1852: Bassein was seized by the British on 19 May.
October 1852: British Major-General Godwin occupied Prome on 9 October.
April 1852: Shwedagon Pagoda conquered by great britain.
June 1852: Pegu, a city in Burma, was taken by British forces on 3 June 1852 during the Second Anglo-Burmese War. The British military occupation of Pegu marked a significant turning point in the conflict between the British Empire and the Burmese Kingdom.
January 1853: Lord Dalhousie was the Governor-General of India at the time, and King Pagan was the ruler of the province of Pegu. The British East India Company annexed Pegu in 1853 as part of their expanding colonial territories in India.
April 1852: Rangoon was occupied on the 12th by British forces led by General Godwin. This marked the beginning of British military occupation in the region, following the Second Anglo-Burmese War.
April 1852: In 1852, during the Second Anglo-Burmese War, the port of Martaban was taken by British forces led by General Godwin.
Was the last of a series of wars between the British Empire and the Konbaung dynasty of Burma. Burma was annexed to British India.
January 1886: The Shan States and Karenni States became princely states of the British Empire after the defeat of Burma in the Anglo-Burmese Wars.
November 1885: British General Harry Prendergast was ordered to conquer Upper Burma with 11,000 men, light boats and elephants. Also due to disagreements within the Burmese troops, Prendergast's troops reached the capital Mandalay on November 26 with little resistance and forced the king to abdicate.
3.1.British annexion of Burma
Annexion of the Konbaung Dynasty of Burma by British India after the Third Anglo-Burmese War.
November 1885: The British, led by General Sir Harry Prendergast, annexed the remaining territories of the Konbaung dynasty in Burma during the Third Anglo-Burmese War in 1885. This was in response to the growing influence of French Indochina in the region.
Selected Sources
Yawnghwe, C.T. (2010): The Shan of Burma: Memoirs of a Shan Exile, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, pp. 68-76
 Anglo-Burmese Wars
Anglo-Burmese Wars