Roman-Parthian War of 161-166
Roman-Parthian War of 161-166
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a war fought between the Roman and Parthian Empires over Armenia and Upper Mesopotamia.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
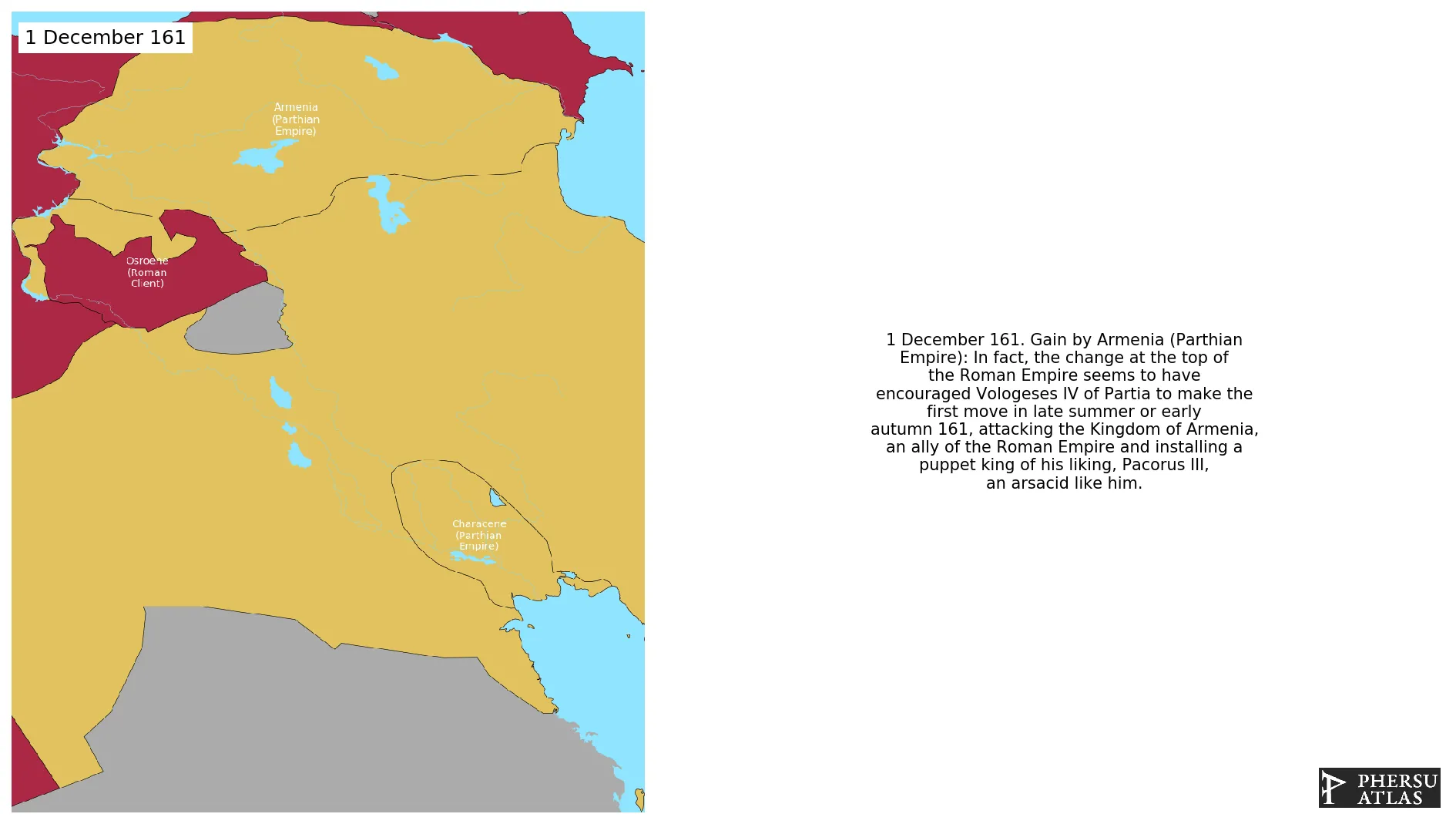
December 161: In fact, the change at the top of the Roman Empire seems to have encouraged Vologeses IV of Partia to make the first move in late summer or early autumn 161, attacking the Kingdom of Armenia, an ally of the Roman Empire and installing a puppet king of his liking, Pacorus III, an arsacid like him.
January 162: The Parthians attacked the entire frontier of Cappadocia and Syria, defeated many of the local garrisons, bringing destruction even under the walls of Antioch and captured the border fortress of Edessa.
January 164: In 163, the Parthians intervened in Osroene, a client state of the Romans located in Mesopotamia, east of Syria, with the capital Edessa. They deposed the Roman client king, Mannus, and replaced him with their own client king.
January 164: Roman occupation of Dausara and Nicephorium.
January 164: The legions I Minervia and V Macedonica, under the command of the legates Marcus Claudius Fronto and Publius Marzio Verus, who served under Marcus Statius Priscus, achieved numerous military successes, penetrating deeply into Armenia, and inflicted a heavy defeat on the Parthians, conquering the Armenian capital , Artaxata.
January 165: In 164 AD, Pacorus, the Parthian ruler of Armenia, was deposed. The former Roman consul of Emesa, Gaius Julius Soemus, who had been deposed by Vologeses, was then crowned as the new tributary king of Armenia under Roman rule.
January 166: In 165 AD, the city of Edessa in Osroene was reoccupied by the Roman client king Manno. This event marked the reinstatement of Manno as the ruler of Osroene under Roman authority.
January 166: Avidio Cassio was a Roman general who served as the legatus legionis of legio III Gallica. Dura Europos was a strategic city located on the Euphrates River. The battle fought near Dura Europos in 165 AD was significant in the Roman Empire's campaign in the region.
January 166: Avidius Cassius reached the twin metropolises of Mesopotamia: Seleucia on the right bank of the Tigris and Ctesiphon on the left. Ctesiphon was taken and its royal palace burned. The citizens of Seleucia opened the gates to the invaders, but the city was burned anyway, leaving a shadow on the conduct of Cassio and the reputation of Lucio Vero.
January 167: Avidius Cassius was a Roman general and usurper who invaded the territory of the Medes, located beyond the Tigris River, in 166 AD. This demonstrated the military might of the Roman Empire under his command.
January 168: The Nisibis area remained part of the roman empire.
January 166: In 165 AD, the Roman forces, led by Emperor Lucius Verus and his generals, launched a military campaign in the East. They used a pincer movement strategy to capture strategic fortress-cities along the Euphrates, including Dausara, Edessa, Carrhae, and Nisibis, expanding the Roman Empire's territory.
January 168: The plague, which broke out during the last year of the campaign, however forced the Romans to withdraw from the newly conquered territories.
 Roman-Parthian War of 161-166
Roman-Parthian War of 161-166