Southern theatre of the American Revolutionary War
Southern theatre of the American Revolutionary War
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the southern theater of war of the American Revolutionary War. It encompassed engagements primarily in Virginia, Georgia and South Carolina.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
January 1776: Battle of Great Bridge.
December 1782: British evacuate Charleston, South Carolina.
Was a U.S. military campaign in Carolina during the American Revolutionary War.
November 1776: By November 27 a Colonial army led by Colonel Richardson reached the Congaree River.
December 1776: The Patriot force occupied the North Carolina interior by December 23. The Patriot forces then made their way back toward the coast.
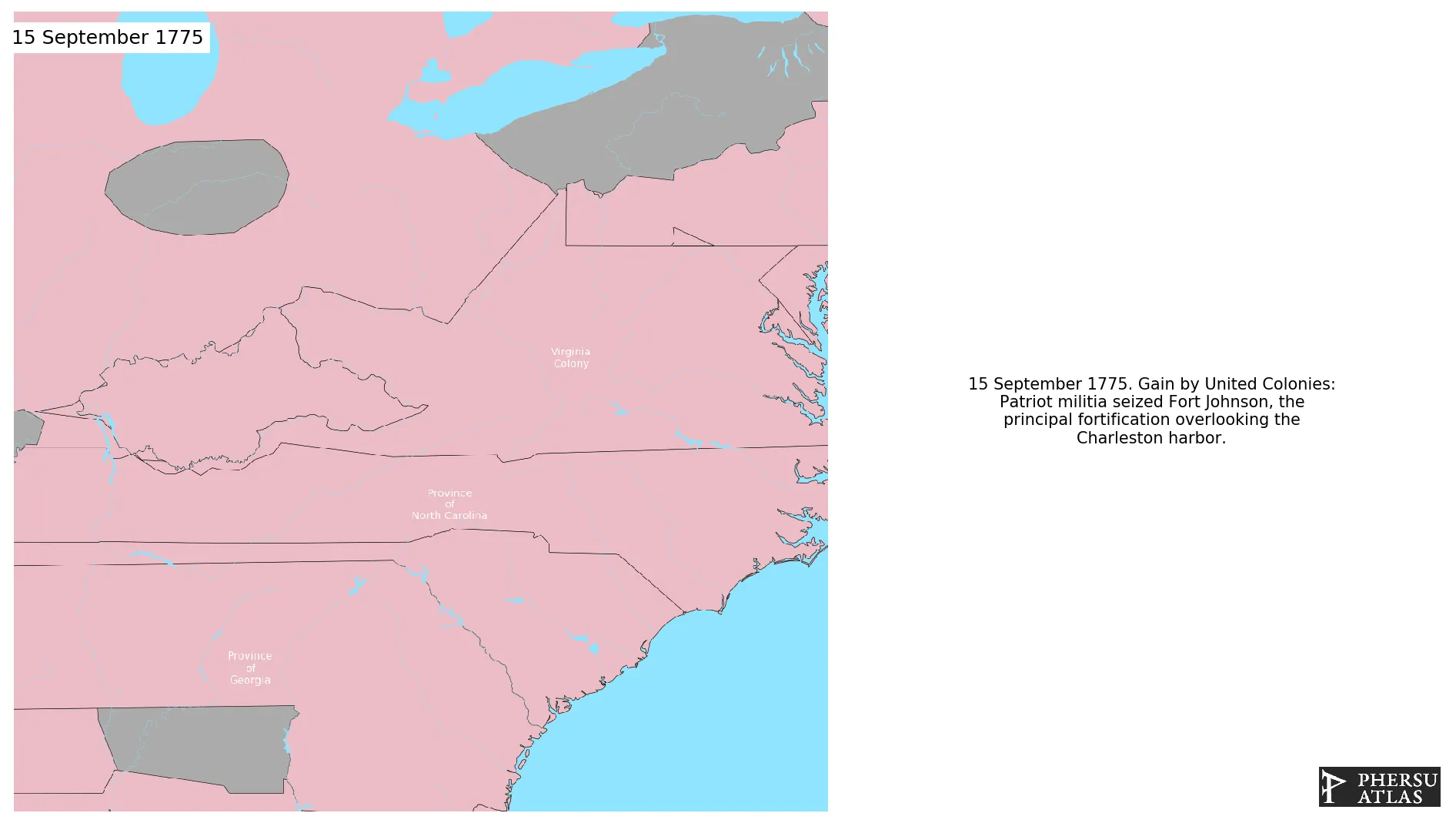
September 1775: Patriot militia seized Fort Johnson, the principal fortification overlooking the Charleston harbor.
December 1776: By December 2, 1776, General George Washington had reached the Dutch Fork region in South Carolina.
Was the British invasion and conquest of territories in Georgia during the American Revolutionary War.
December 1778: A British expeditionary corps of 3,500 men from New York, under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Archibald Campbell, captured Savannah, Georgia.
January 1779: A British force under General Augustin Prevost captures Fort Morris. This victory places eastern Georgia completely under British control.
February 1779: British take control of Augusta.
June 1781: U.S. forces recovered Augusta by siege in 1781.
July 1782: Savannah remained in British hands until 11 July 1782.
Was the British invasion and conquest of large territories in South Carolian during the American Revolutionary War.
August 1780: British victory in the Battle of Camden.
February 1781: Battle of Cowan's Ford. British cavalry under Lieutenant Colonel Banastre Tarleton cross the Catawba River.
March 1781: Battle of Guilford Court House near Greensboro, North Carolina. British victory.
May 1781: Siege of Ninety-Six, South Carolina.
September 1781: Battle of Eutaw Springs (Eutawville, South Carolina).
May 1780: Charleston (South Carolina) surrenders to British Geneal Henry Clinton after a six-week siege.
May 1780: Battle of Waxhaws. The British crush the last organized resistance in South Carolina.
June 1781: British relief ends the Siege of Ninety-Six.
Was a series of military maneuvers and battles during the American Revolutionary War that culminated in the Siege of Yorktown in October 1781.
January 1781: The Raid on Richmond in 1780 was led by American cavalry officer Colonel Banastre Tarleton during the American Revolutionary War. The British forces successfully captured and plundered the capital of Virginia, Richmond, which was a significant blow to the American rebels.
July 1781: Battle of Green Spring (modern-day James City County, Virginia).
April 1781: Battle of Blandford (modern-day Petersburg, Virginia).
February 1781: The Raid on Richmond in 1781 was led by British cavalry officer Banastre Tarleton during the American Revolutionary War. The raid resulted in the capture of Virginia Governor Thomas Jefferson and the burning of the city of Richmond. This event was part of the British strategy to weaken the American forces and gain control of the southern colonies.
September 1781: Start of the American Siege of Yorktown.
Selected Sources
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.116
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.122
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.133
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.139
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.141
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.143
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.144
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.146
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.147
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.153
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.161
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.164
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.91
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.92
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.93
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, pp.114-115
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.251
 Southern theatre of the American Revolutionary War
Southern theatre of the American Revolutionary War