Wars of Ivan III
Wars of Ivan III
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Russian military campaign against the Khanate of Kazan by Ivan III.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
November 1480: The Great Stand on the Ugra River was a standoff between the forces of Akhmat Khan of the Great Horde, and the Grand Prince Ivan III of Muscovy in 1480 on the banks of the Ugra River, which ended when the Tatars departed without conflict. It is seen in Russian historiography as the end of Tatar/Mongol rule over Moscow.
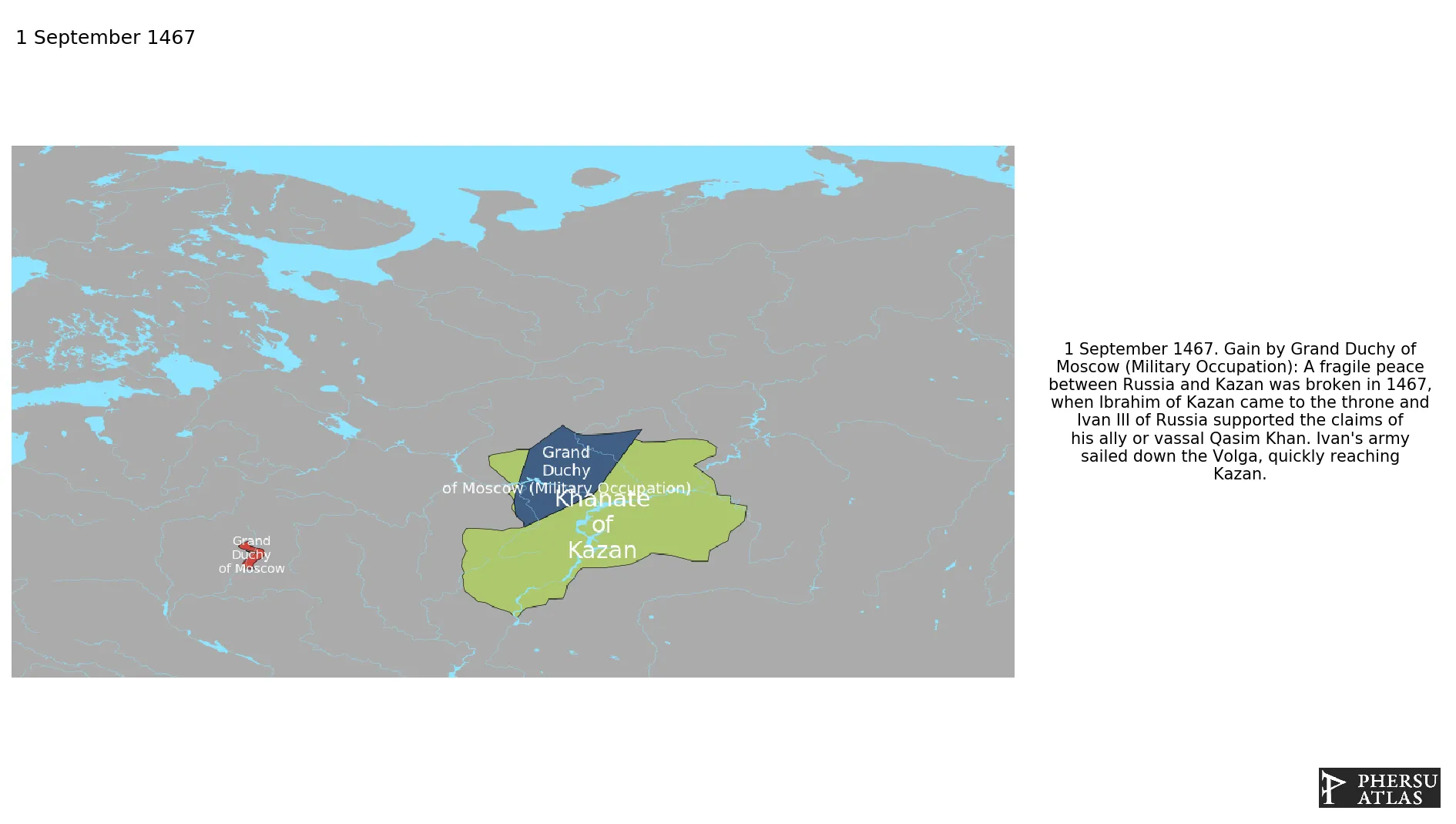
September 1467: A fragile peace between Russia and Kazan was broken in 1467, when Ibrahim of Kazan came to the throne and Ivan III of Russia supported the claims of his ally or vassal Qasim Khan. Ivan's army sailed down the Volga, quickly reaching Kazan.
December 1467: In 1467, during the reign of Ivan III of Russia, the Russian forces faced difficulties due to autumn rains and rasputitsa while trying to advance in the occupied regions, which eventually fell under the control of the Khanate of Kazan.
January 1468: In 1467, the campaign led by Ivan III of Russia against the Khanate of Kazan fell apart due to the lack of unity and military capability among the Russian forces.
January 1469: The Russians sailed down the Vyatka River and the Kama towards the Volga, pillaging merchant vessels on their way.
January 1470: In 1469, under the terms of the peace settlement, the Khanate of Kazan set free all the ethnic Christian Russians they had enslaved in the forty previous years. The Russians left the territories they had occupied in the Khanate of Khazan.
January 1470: In 1469, under the terms of the peace settlement, the Khanate of Kazan set free all the ethnic Christian Russians they had enslaved in the forty previous years. The Russian and Kazan forces left the territories they had occupied during the war.
January 1484: The Grand Duchy of Moscow gained the Elets principality (Елец) from Ryazan by an agreement.
January 1484: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1484.
January 1486: The Kholm Principality lasted until the annexation of the Tver principality of Moscow in 1486.
June 1487: The city of Kazan fell to the Russians on 9 June.
January 1488: The Russian leave all occupied regions of the Khanate of Kazan.
January 1500: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1500.
January 1501: The Putivl Principality is acquired by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1505: Ruza conquered by the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1506: A huge army of the Kazan and Nogai Tatars advanced towards Nizhny Novgorod and besieged the city.
January 1484: Ryazan completely annexed Pronsk in 1483 during the regency of Anna of Ryazan.
January 1486: The Mikulinskoe principality was ruled by Prince Ivan Mikulinsky until it was annexed by the Grand Duchy of Moscow in 1485. The annexation marked the end of Mikulinsky's rule and the incorporation of the territory into the expanding Moscow principality. It lasted until the annexation of the Tver principality of Moscow in 1486.
December 1469: In autumn 1469, Ivan III of Moscow launched a third invasion of the Kazan khanate. The Russian commander, Prince Daniil Kholmsky, besieged Kazan, leading to the territory falling under the military occupation of the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1484: Principality of Tver conquered by Grand Duchy of Moscow.
January 1495: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1495.
February 1469: Khazan Khan Ibrahim mounted a counter-offensive against the Russians, overran Vyatka, and forced local inhabitants into slavery for the duration of the campaign.
January 1468: When frosty winter came, the Russian generals launched an invasion of the northern Vyatka Region.
May 1487: Prince Kholmsky, also known as Ivan III of Russia, led the military occupation of Kazan in 1487. The city was a key stronghold of the Tatar Khanate and its capture was a significant victory for the Grand Duchy of Moscow in their expansion efforts.
January 1490: Expansion of the Grand Duchy of Moscow by 1490.
Was a war of the Grand Duchy of Moscow, in alliance with the Crimean Khanate, against the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Ruthenia in alliance with the Golden Horde Khan Akhmat.
Was a border war which occurred between the Grand Duchy of Moscow and the Kingdom of Sweden.
August 1495: In 1495, Ivan III of Russia sent Princes Daniil Shchenya and Vasily Shuisky to besiege the Swedish castle of Viborg.
November 1495: The siege of Viborg in 1495 was led by Tsar Ivan III of Russia against the Kingdom of Sweden. The castellan who set the powder on fire was Knut Posse, a Swedish nobleman defending the city. The Muscovites were forced to retreat after the explosion, ending the siege.
January 1497: In 1496, Hämeenlinna was severely devastated by Russian generals Vasily Kosoy and Andrey Chelyadnin during the military occupation of Finland by Russia.
January 1497: Svante Nilsson, a Swedish nobleman and military leader, led the occupation of Ivangorod in 1496. Ivangorod was a strategically important fortress located on the border between Sweden and Russia.
February 1497: Russian forces leave Swedish Finland.
February 1497: In 1497, during the Russo-Swedish War, the Swedes, led by King Hans of Denmark, set the fortress of Ivangorod ablaze before sailing back to their homeland. This event marked a significant victory for the Grand Duchy of Moscow in their conflict with Sweden.
Was a war between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
3.1.Muscovite invasion
Was a Muscovite invasion of Lithuania.
3.2.Livonian Intervention alongside Lithuania
The Livonian Order joined the Second Muscovite Border War as an ally of Lithuania.
3.3.Truce (Second Lithuanian-Muscovite border war)
A six-year truce was concluded on the Feast of the Annunciation, ending the Second Muscovite Border War. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania lost approximately 210,000 square kilometres (81,000 sq mi), or a third of its territory.
Selected Sources
Атлас. 6 класс. История России с древнейших времен до XVI века (Atlas. 6th grade. History of Russia from ancient times to the 16th century.) , Дрофа Publisher (2015), Moscow (Russia), p. 23
 Wars of Ivan III
Wars of Ivan III