If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
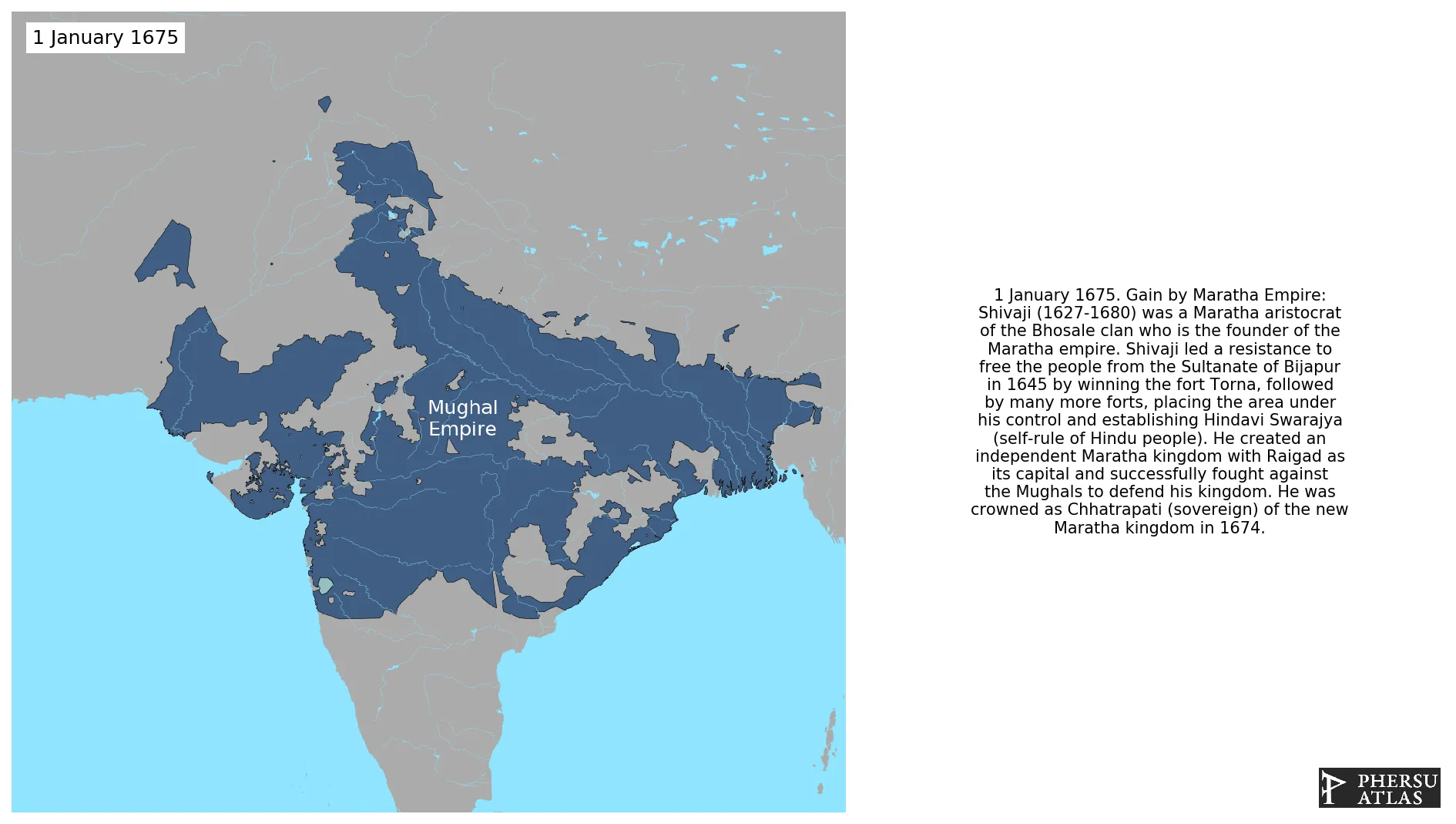
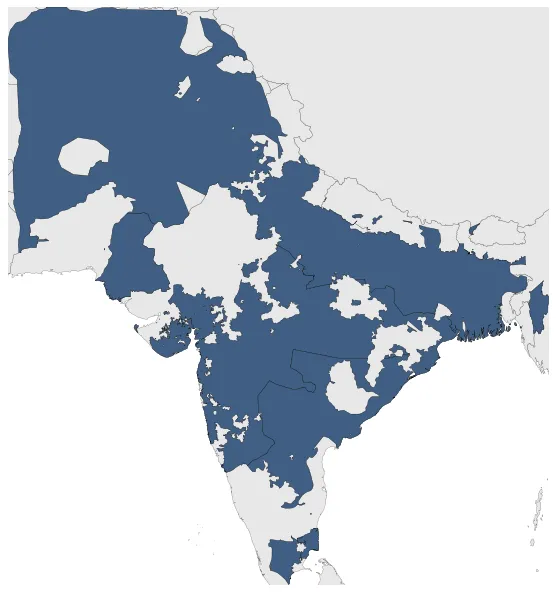
Maratha Empire
Establishment
January 1675: Shivaji (1627-1680) was a Maratha aristocrat of the Bhosale clan who is the founder of the Maratha empire. Shivaji led a resistance to free the people from the Sultanate of Bijapur in 1645 by winning the fort Torna, followed by many more forts, placing the area under his control and establishing Hindavi Swarajya (self-rule of Hindu people). He created an independent Maratha kingdom with Raigad as its capital and successfully fought against the Mughals to defend his kingdom. He was crowned as Chhatrapati (sovereign) of the new Maratha kingdom in 1674.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars fought between the Mughal Empire and the Maratha Empire.
January 1691: Aurangzeb himself had to come and Panhala was surrendered.
January 1698: Jinji Fort in modern day Tamil Nadu is besieged by the Mughal Empire.
April 1700: Prayagji Prabhu defended Satara for a good six months but surrendered in April 1700.
January 1701: The Marathas expanded eastwards into Mughal lands, capturing Hyderabad in 1700.
January 1705: By 1704 Aurangzeb conquered Torana, Rajgad and some other handful forts mostly by bribing maratha commanders.
January 1706: By 1705 end, Marathas had penetrated Mughal possession of Central India and Gujarat. Nemaji Shinde defeated Mughals on the Malwa plateau.
January 1706: A Marata army under the leadership of Nemaji Shinde, hit as far north as Bhopal. The second Maratha army, headed by Khanderao Dabhade, struck Bharoch and the west.
January 1707: In 1706, Mughals started retreating from Maratha dominions.
Expansion during the rule of Shahu I in the Maratha Empire.
January 1720: In 1719, an army of Marathas marched to Delhi after defeating Sayyid Hussain Ali, the Mughal governor of Deccan, and deposed the Mughal emperor. The Mughal Emperors became puppets in the hands of their Maratha overlords from this point on.
January 1723: Establishment of the Danish outpost of Eddowa.
January 1725: In 1724, Udaji Pawar captured Jhabua State, which remained under his control until 1726. Udaji Pawar was a prominent Maratha general who played a key role in expanding the Maratha Empire's territory. Jhabua State was eventually incorporated into the Maratha Empire as a result of this conquest.
January 1726: The Marathas made the first successful incursion into Mewar territory in 1725 and, subsequently, continued to exert increasing influence not only on Mewar but also surrounding states.
January 1729: Yanaon (Yanam) was a French colony in India. It was abandoned from 1728 to 1731 during a period of conflict between the French and the Mughal Empire.
January 1731: The Dutch abandoned their post in Draksharama in favour of Jaggernaikpoeram.
January 1734: In 1733 the British and Dutch convinced the Mughal general at Hugli to attack Bankipur. He attacked Bankipur and the garrison of only fourteen soldiers escaped and set sail for Europe.
January 1734: In 1733, Peshwa Bajirao of the Maratha Empire launched a campaign against the Siddis of Janjira. Bajirao's forces, however, did not take Janjira fort, though they captured much of the surrounding area; a favorable treaty gave the Marathas indirect control over virtually all of the Sidi's lands.
February 1734: After a month it was destroyed by the British and the French.
January 1738: In 1737 the island was captured by the Marathas,.
January 1738: In 1737, Marathas defeated the Mughals and the Nawab of Bhopal in the Battle of Bhopal, and started collecting tribute from the state.
May 1739: The fort was taken over by the Maratha Army in 1739, ending the Battle of Vasai.
September 1740: After the capture of Baçaim in 1740, a peace treaty was concluded, and on 18 September 1740, Chaul was ceded by treaty to the Marathas.
January 1741: In 1740, the Maratha forces, under Raghoji Bhosale, came down upon Arcot and defeated the Nawab of Arcot.
January 1743: The Marathas briefly controlled Jawhar in 1742, 1758 and 1761.
January 1745: Ahmadabad was abandoned in 1744.
Expansion during the rule of Nader Shah of the Afsharid Dynasty.
January 1741: In 1740, the Khanate of Bukhara was conquered by Nadir Shah, the Shah of Iran.
3.1.Nader Shah's invasion of the Mughal Empire
Was the invasion of India by the Afsharid ruler Nader Shah.
November 1738: Nader advanced to the river Indus before the end of year.
January 1739: The Afsharids advanced onto the Punjab and captured Lahore.
February 1739: Battle of Karnal.
March 1739: Nader Shah, the ruler of the Afsharid Dynasty, captured Delhi in 1739 after defeating the Mughal Empire. The keys to the capital were surrendered to him as a sign of submission and victory.
May 1739: Persian troops left Delhi in early May 1739.
Expansion during the rule of Prithvi Narayan Shah in the Gorkha Kingdom.
January 1747: Expansion of the Gorkha Kingdom under Prithvi Narayan Shah by 1746.
January 1749: Expansion of the Gorkha Kingdom under Prithvi Narayan Shah by 1748.
Expansion during the rule of Ahmad Shah Durrani in the Durrani Empire.
January 1748: In 1747, Peshawar was taken by Ahmad Shah Durrani, also known as Ahmad Shah Abdali, who was the founder of the Afghan Durrani Empire. Ahmad Shah Durrani was a prominent military leader who established the empire in the region.
January 1748: Kasur, a town in present-day Pakistan, was captured by Ahmad Shah Durrani, the founder of the Durrani Empire.
January 1750: In 1749 the Mughal ruler ceded sovereignty over much of north-west India to the Afghans.
January 1752: In 1751, the Afghan ruler Ahmad Shah Durrani of the Durrani Empire gained control of Kashmir. This marked the beginning of Durrani rule in the region, which lasted until the early 19th century.
January 1761: Shah Durrani, who was the founder of the Durrani Empire, sent an army to conquer the areas north of the Hindu Kush mountains, successfully uniting various tribes under his rule.
January 1762: The Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II (1759-1806) made futile attempts to reverse the Mughal decline but ultimately had to seek the protection of the Emir of Afghanistan, Ahmed Shah Abdali, which led to the Third Battle of Panipat between the Maratha Empire and the Afghans (led by Abdali) in 1761.
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
6.1.Indian Theatre (Seven Years' War)
Was the theatre of war of the Seven Years' War in the Indian Subcontinent.
6.1.1.Capture of Calcutta
The Mughal Empire captured British-held Calcutta during the Seven Years' War.
June 1756: The Siege of Calcutta was a battle between the Bengal Subah and the British East India Company on 20 June 1756. The Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-Daulah, aimed to seize Calcutta to punish the Company for the unauthorised construction of fortifications at Fort William.
6.1.2.Third Carnatic War
The outbreak of the Seven Years' War in Europe in 1756 resulted in renewed conflict between French and British forces in India.
January 1761: British occupation of Pondichéry.
Were a series of wars fought by the British East India Company in the Indian Subcontinent that resulted in the British conquest and colonial rule of the region.
7.1.Anglo-Mysore Wars
Were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company, Maratha Empire, Kingdom of Travancore, and the Kingdom of Hyderabad on the other. The fourth war resulted in the dismantlement of Mysore to the benefit of the East India Company, which took control of much of the Indian subcontinent.
7.1.1.First Anglo-Mysore War
Was a conflict in India between the Sultanate of Mysore and the East India Company.
February 1767: The war began in January 1767 when the Marathas, possibly anticipating movements by the nizam, invaded northern Mysore. They reached as far south as the Tunghabadhra River, before Haider entered into negotiations.
April 1767: In exchange for payments of 30 lakhs rupees the Marathas agreed to withdraw north of the Kistna River.
7.1.2.Second Anglo-Mysore War
Was a conflict between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company from 1780 to 1784.
January 1780: By 1779, Mysore ruler Haider Ali had captured parts of modern Tamil Nadu and Kerala in the south, extending the Kingdom's area to about 80,000 mi2 .
7.1.3.Third Anglo-Mysore War
Was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, the Kingdom of Travancore, the Maratha Empire, and the Nizam of Hyderabad. It was the third of four Anglo-Mysore Wars.
7.1.3.1.Allied advances
During the summer of 1790, a Maratha army of some 30,000 under the command of Purseram Bhow, accompanied by a detachment of British troops from Bombay invaded the Kingdom of Mysore.
October 1790: During the summer of 1790, a Maratha army of some 30,000 under the command of Purseram Bhow, accompanied by a detachment of British troops from Bombay, began marching toward Mysore. The first several Mysorean outposts surrendered in the face of the large army, and it made steady if slow progress until it reached Darwar in September.
May 1791: The Maratha army then continued to advance, reaching the Tungabhadra River in early May.
November 1791: In 1791, Purseram Bhow, a commander in the Maratha Empire, captured Hooly Honore and Shimoga in an attempt to recapture the Bednore district taken by Tipu Sultan's father, Hyder Ali, in a previous war.
7.1.3.2.Treaty of Seringapatam
Was the treaty that ended the Third Anglo-Mysore War. Mysore lost about one-half of its territories.
March 1792: Treaty of Seringapatam: Under its terms Mysore ceded about one-half of its territories to the other signatories. The Peshwa acquired territory up to the Tungabhadra River, the Nizam was awarded land from the Krishna to the Penner River, and the forts of Cuddapah and Gandikota on the south bank of the Penner. The East India Company received a large portion of Mysore's Malabar Coast territories between the Kingdom of Travancore and the Kali River, and the Baramahal and Dindigul districts. Mysore granted the rajah of Coorg his independence, although Coorg effectively became a company dependency.
7.1.4.Fourth Anglo-Mysore War
Was the fourth and final Anglo-Mysore war. After the war, the Kingdom of Mysore became a princely state in a subsidiary alliance with British India.
7.1.4.1.Partition of Mysore
After the loss of the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War, Mysore was occupied and partitioned. The remnant territories became a princely state of British India.
June 1799: After the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War, several Mysore territories were ceded to neighbour states.
7.2.Anglo-Maratha Wars
Was a series of wars fought between the British East India Company and Maratha Empire in India.
7.2.1.First Anglo-Maratha War
Was the first of three Anglo-Maratha Wars fought between the British East India Company and Maratha Empire in India. .
March 1775: The Treaty of Surat on 6 March 1775. According to the treaty, Raghunathrao ceded the territories of Salsette and Bassein (Vasai) to the British, along with part of the revenues from Surat and Bharuch districts.
March 1775: The British occupied Salsette Island in 1774.
March 1776: The Treaty of Purandhar (1 March 1776) annulled that of Surat, Raghunathrao was pensioned and his cause abandoned, but the revenues of Salsette and Broach districts were retained by the British.
November 1778: Following a treaty between France and the Poona Government in 1776, the Bombay Government decided to invade and reinstate Raghoba, a claimant to the Maratha throne. They sent a force under Col. Egerton, which reached Khopoli in 1778 during the First Anglo-Maratha War.
January 1779: The British East India Company made its way through the Western Ghats at Bhor Ghat and onwards toward Karla.
January 1779: Finally the British were forced to retreat back to Wadgaon, but were soon surrounded. The British surrendered and were forced to sign the Treaty of Wadgaon on 16 Jan. 1779, a victory for the Marathas.
February 1779: In 1779, British General Goddard led 6,000 troops to capture Ahmedabad's Bhadra Fort from the Marathas, marking a significant victory for the British East India Company in their expansion across India.
May 1782: The Treaty of Salbai was signed on 17 May 1782, by representatives of the Maratha Empire and the British East India Company after long negotiations to settle the outcome of the First Anglo-Maratha War. The borders were reverted to the status quo ante bellum and British forces left the occupied regions.
7.2.2.Second Anglo-Maratha War
Was the second conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. .
December 1802: Baji Rao, the last Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy, fled the Maratha invasion to British protection, and in December the same year concluded the Treaty of Bassein with the British East India Company, ceding territory for the maintenance of a subsidiary force.
October 1803: British forces took the pettah of Asirgarh Fort.
December 1803: Raghoji II Bhonsale of Nagpur signed the Treaty of Deogaon in Odisha with the British after the Battle of Argaon and gave up the province of Cuttack (which included Mughal and the coastal part of Odisha, Garjat/the princely states of Odisha, Balasore Port, parts of Midnapore district of West Bengal).
December 1803: On 30 December 1803, the Daulat Scindia signed the Treaty of Surji-Anjangaon with the British after the Battle of Assaye and Battle of Laswari and ceded to the British Rohtak, Gurgaon, Ganges-Jumna Doab, the Delhi-Agra region, parts of Bundelkhand, Broach, some districts of Gujarat and the fort of Ahmmadnagar.
January 1804: The British strategy included Wellesley securing the Deccan Plateau.
7.2.3.Third Anglo-Maratha War
Was the final and decisive conflict between the English East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India.
November 1817: In 1817, General Sir Thomas Hislop led the British East India Company troops, including Colonel Smith, to cross the river and establish positions at Ghorpadi during the Third Anglo-Maratha War in India.
January 1818: Battle of Koregaon.
January 1818: British commanders began arriving with reinforcements: Lieutenant Colonel Rahan on 29 November, Major Pittman on 5 December, and Colonel Doveton on 12 December. The British counterattack was severe and Appa Saheb was forced to surrender. The British lost 300 men, of which 24 were Europeans. The Marathas lost an equal number. A treaty was signed on 9 January 1818. Appa Saheb was allowed to rule over nominal territories with several restrictions. Most of his territory, including the forts, was now controlled by the British.
February 1818: British General Smith entered Satara and captured the royal palace of the Marathas.
February 1818: Mountstuart Elphinstone mentions the capture of Sinhagadh in his diary entry.
April 1818: General Smith's forces had taken the forts of Sinhagad and Purandar.
June 1818: Baji Rao surrendered to the British.
Expansion during the rule of Shahu II in the Maratha Empire.
January 1784: In 1780, Cambay was captured by the British Army under the leadership of General Goddard Richards during the First Anglo-Maratha War. However, the territory was later returned to the Maratha Empire in 1783 as a result of the Treaty of Salbai.
June 1790: Jaipur and Jodhpur, the two most powerful Rajput states, were still out of direct Maratha domination. So, Mahadji sent his general Benoît de Boigne to crush the forces of Jaipur and Jodhpur at the Battle of Patan.
January 1791: Korea State conquered by Maratha Empire.
January 1801: Piploda was reduced to a great extent and the thakur was forced to become a vassal of Amir Khan Pindari.
January 1801: Jigni State's size was much reduced during the Maratha invasion in the last half of the eighteenth century.
January 1801: Junagarh State was ruled by Mohammad Hamid Khanji I, who became a tributary to the Maratha Empire in 1800. However, in 1807, the territory came under British suzerainty during his reign.
January 1809: Sambalpur was invaded and occupied by the Marathas between 1808 and 1817.
Expansion during the rule of Rana Bahadur Shah in the Kingdom of Nepal.
January 1787: Based on the border of Nepal in 1782.
Expansion during the rule of Ranjit Singh in the Sikh Empire.
January 1802: The formal start of the Sikh Empire began with the unification of the Misls (states) by 1801, creating a unified political state.
10.1.Afghan-Sikh Wars
Were a series of military conflicts between the Durrani Empire and the Sikh Empire that took place mainly in the Punjab region.
January 1779: The city of Multan reverted to Afghan rule under the suzerainty of Nawab Muzaffar Khan in 1778.
January 1678: In the year 1677, Sivaji, routed the Bijapur forces and captured Jinji Fort.
January 1681: In 1680, the Maratha Empire, under the leadership of King Shivaji and his successors, expanded its territory to include a vast area in present-day India. This growth solidified the Marathas as a dominant power in the region during this time period.
January 1698: The Jagir (fiefdom), which was the forerunner of the state, was granted to Shankarji Narayan for his services as the Pant Sachiv, one of the eight hereditary Maratha ministers, by Rajaram Chhatrapati in 1697.
January 1702: During this time, Durgadas Rathore, a prominent leader of the Rathore dynasty in Jodhpur State, successfully fought against the Mughal Empire for 31 years to free Marwar from their control. His efforts ultimately preserved the Rathore dynasty's rule in the region.
January 1702: During Shahu's reign, Raghoji Bhosale expanded the empire Eastwards, reaching present-day Bengal.
January 1702: Orchha was the only Bundela state not entirely subjugated by the Marathas in the 18th century.
January 1702: Khanderao Dabhade and later his son, Triambakrao, expanded Westwards into Gujarat.
January 1705: The Jagirs of Jath and Karajagi were conferred on his son in 1680. Emperor Aurangzeb confirmed these estates to the family in 1704.
January 1708: Bhopal State was founded in 1707 CE by Dost Mohammad Khan, a Pashtun soldier in the Mughal army, who became a mercenary after the Moghul Emperor Aurangzeb's death and annexed several territories to his fiefdom.
January 1708: The states of Satara and Kolhapur came into being in 1707, because of the succession dispute over the Maratha kingship.
January 1709: The ruling dynasty were descendants of Ranoji Lokhande, who was adopted by Chhattrapati Shahu, grandson of Shivaji, around the year 1708. Upon his adoption, Ranoji assumed the name 'Fatehsinh Bhonsle' and received in appenage the town of Akkalkot and surrounding areas.
January 1717: Sailana State was founded by Raja Jai Singh, great-grandson of Maharaja Ratan Singh, founder of Ratlam State. In 1716 Jai singh took revenge against his uncle for the murder of his father, he killed him in a pitched battle at sagode and secured Ratlam for his elder brother. The two brothers then divided the state between themselves. Jai singh's capital was initially at Raoti. He built Sailana as his new capital in 1736.
January 1721: Mazulipatam becomes a French possession.
January 1721: In 1720, Mahmud Hotak, the ruler of the Hotak Empire, led his Afghan forces across the deserts of Sistan and successfully captured the territory of Kerman. Mahmud Hotak was a prominent leader of the Hotak Empire, which was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire established in parts of present-day Afghanistan and Iran.
January 1722: The Baroda State was founded in 1721, when the Maratha general Pilaji Gaekwad conquered Songadh from the Mughals.
October 1722: The siege of Isfahan in 1722 was led by Mahmud Hotak, who defeated Sultan Husayn and took control of Persia, establishing the Hotak Empire. Sultan Husayn abdicated after the six-month siege, recognizing Mahmud as the new Shah of Persia.
January 1723: Bankipur was an ancient village on the Hugli river located in what is now West Bengal, north of Barrackpore, a little north of Ishapore.
January 1724: In 1722-1723, forces led by Khanthaji Kadani and Pilaji Gaekwad attempted to raid Sihor but were repelled by Maharaja Bhavsinhji Gohil. After the war Bhavsinhji realised the reason for repeated attack was the location of Sihor. In 1723, he established a new capital near Vadva village, 20 km away from Sihor, and named it Bhavnagar after himself.
January 1724: Yanaon (Yanam) became a French possession.
January 1725: The fourth Nizam Salabat Jang, a son of the Nizam al Mulk, who was indebted for his elevation to the throne to the French East India Company, granted the district of Kondavid (in the Guntur district) to the French in return for their services, and soon afterwards granted the other circars as well.
January 1725: In 1724, Raja Udot Singh of Orchha State granted Khaniadhana and several other villages to his son Amar Singh.
January 1725: Hyderabad State was founded by Mir Qamar-ud-din Khan who was the governor of Deccan under the Mughals from 1713 to 1721.
January 1727: In 1724, Jhabua was captured by Udaji Pawar, a Maratha general, and remained under his control until 1726. Jhabua State eventually regained control of the territory after Udaji Pawar's rule.
January 1728: Bahawalpur state was founded in 1727 AD by Nawab Sadiq Muhammad Khan Abbasi, who was a descendant of the Abbasid Caliphs. He established the state after breaking away from the Durrani Empire, establishing a prosperous and independent kingdom in the region.
January 1729: The seats were established in 1728 by two brothers from the Maratha clan Puar, who advanced into Malwa with the Peshwa Baji Rao. After the Maratha conquest of Central India, Dewas was divided into two states - Dewas Junior ruled by Jivaji Rao ('Dada Saheb') Puar and Dewas Senior ruled by Tukoji Rao ('Baba Saheb') Puar.
January 1730: In 1729 Anand Singh and Rai Singh, brothers of the Maharaja of Jodhpur, captured Idar by force.
January 1731: Cambay was founded as a state in 1730 by the penultimate Nawab of the Mughal Empire, Mirza Ja‘far Mu’min Khan I, the last of the Mughal governors of Gujarat, at the time of the dismemberment of Mughal rule in India.
January 1731: Jigni State was founded as a jagir in 1730 by Rao Padam Singh, a Rajput of the Bundela clan.
January 1731: Mohammad Khan Bahadur Khanji I declared independence from the Mughal governor of Gujarat subah, and founded the state of Junagarh in 1730.
January 1731: Dhar began as one of the states during Maratha dominance in India about 1730.
January 1731: Establishment of Chaudandi.
January 1732: Yanaon (Yanam) is re-occupied by the French.
January 1732: Gwalior state was a semi-autonomous Maratha state. It was centered in modern-day Madhya Pradesh, arising due to the rise of the Maratha Empire and fragmentation of the Mughal Empire.
January 1732: Panna was the capital chosen by a leader Chhatar Sal, the founder of Panna State, after leading a revolt against the Mughal Empire.
January 1732: Jaitpur state was founded in 1731 by Jagat Rai, son of the famous Bundela leader Chhatrasal, as a division of Panna State.
July 1732: On 29 July 1732, Bajirao Peshwa-I granted Holkar State by merging 28 and a half parganas to Malhar Rao Holkar, the founding ruler of the Holkar dynasty. This event took place in the region that is now part of Indore State.
January 1733: As the Mughal Empire declined and decentralized, local governors in Oudh began asserting greater autonomy, and eventually Oudh matured into an independent polity governing the fertile lands of the Central and Lower Doab.
January 1733: Jaso State was founded in 1732 by Bharti Chand, younger brother of Raja Hrideshah of Panna.
January 1734: Bantva is described as Bantva Choryashi is Ain-i-Akabari. Bantva was bestowed by Nawab Bahadur Khan (Sher Khan Babi) of Junagadh State, on his brothers Diler Khan Salabat Muhammed Khan Babi and Sher Zaman Khan in 1733 after their expulsion from Ghogha by Sohrab Khan.
January 1734: Malneta state founded.
January 1734: Kurundvad State, was founded in 1733 following a grant by the Maratha Peshwa to Trimbakrao Patwardhan.
January 1740: Ballabhgarh, is a town and a tehsil (subdistrict) in Faridabad District of Haryana, India, and is part of the National Capital Region. The town was founded by Raja Balram Singh, in 1739, who also built the Nahar Singh Mahal palace in the same year.
January 1741: As the Mughal suzerainty weakened, the Benares zamindari estate became Banaras State, thus Balwant Singh of the Narayan dynasty regained control of the territories and declared himself Maharaja of Benares in 1740.
January 1741: Vala (Vallabhipura) princely state was founded in 1740 by Thakore Sahib Akherajji of nearby Bhavnagar (also in Gohelwar prant; later a salute state under a Maharaja), a Gohil Rajput of the Suryavanshi clan, for his twin brother Visaji, who became the first Thakore.
January 1742: In 1741, Governor Joseph François Dupleix arrived in India, aiming to establish a French territorial empire. Commanded by Marquis Bussy-Castelnau, Dupleix's forces gained control over the area from Hyderabad to Cape Comorin.
February 1743: The Marathas briefly controlled Jawhar in 1742, 1758 and 1761.
January 1744: The erstwhile Princely State of Chhota Udaipur was founded in 1743 by Rawal Udeysinhji, a descendant of Patai Rawal of Champaner.
January 1751: Rairakhol was a feudatory state to Bamra until the 18th century, when the Garhjat Rajas of Patna freed it from its dependence.
January 1751: Jaora State was founded by Abdul Ghafur Muhammad Khan. 'Abdu'l Ghafur Muhammad Khan was a cavalry officer serving the Pashtun leader Muhammad Amir Khan. He later served the Holkar maharaja of Indore State. The state was confirmed by the British government in 1818.
January 1751: The foundation of the estate of Nandgaon hails back to Prahlad Das, a shawl merchant who in the 18th century had migrated from the Punjab region. When he settled in Ratanpur the area was ruled by the Bhonsle clan of Marathas.
January 1751: Beri State was founded in the mid eighteenth century by Diwan Acharju (Achharaj) Singh, a jagirdar who was the son of Diwan Mahma Rai of Karaiha in Gwalior State .
January 1751: Bhajji state founded at an uncertain date before the 19th century.
January 1751: The State of Miraj, the predecessor state, was founded before 1750 and within its limits was the former capital of the State of Sangli before the British Raj.
January 1751: The state came under the influence of the Maratha rulers of Nagpur in the 18th century, and became a princely state of British India in 1803, at the conclusion of the Second Anglo-Maratha War at Deogaon of Orissa.
January 1751: Surgana State was founded before the 1800s.
January 1751: Torawati State conquered by Maratha Empire.
January 1751: Shivaji Maharaj defeated Afzal Khan, and went on to establish an independent kingdom that evolved into the Maratha Empire.
January 1751: Savanur was conquered and made a tributary by the Marathas.
January 1751: Independence of the Suket State from Mughal Empire.
January 1751: In the 18th century Faza again fell into decline due to the rise of Pate.
January 1751: The area of Jashpur State was ruled by a Dom dynasty at the time of the Mughal Empire.
January 1751: Kothi State was founded in 1750 by Raja Keshri Singh, a Rajput ruler who expelled the former Bharr ruler of the area. The territory was located in present-day Himachal Pradesh, India.
January 1751: In the 18th century the Scindia and the Peshwa warriors took over the forested areas of Kalibhit and Charwa from Makrai.
January 1752: Kawardha State was founded in 1751.
January 1754: In 1753 Jawan Mard Khan II, son of Jawan Mard Khan I who assisted Mughal Empire in the rule of Gujarat, became independent ruler of Radhanpur, among other territories.
January 1754: The state was soon annexed by the Marathas under Damaji Gaekwad in 1753 and Anand Singh was killed in battle.
December 1754: The Governor of French India, Charles Godeheu, signed a treaty with the British on December 26, 1754, agreeing to evacuate all the territories in India conquered by his predecessor, Joseph Dupleix. The British also agreed to leave the territories of French India that they had occupied.
January 1756: Establishment of the Danish outpost of Frederiknagore (today Serampore) in Bengal.
January 1757: The region of Rajputana came under Maratha domination during this time.
June 1757: British Lieutenant Colonel Robert Clive defeated Indian and French forces in the Battle of Plassey.
January 1758: Delhi was captured by the Maratha army under Raghunath Rao in August 1757, defeating the Afghan garrison in the Battle of Delhi. This laid the foundation for the Maratha conquest of North-west India.
January 1758: The state was established in 1757 by Aman Singh, Raja of Panna State by granting the lands surrounding Alipura town to Achal Singh, son of Mukund Singh, who was the sardar of Panna at that time.
August 1758: In Lahore, as in Delhi, the Marathas were now major players. After the Battle of Attock, 1758, the Marathas captured Peshawar defeating the Afghan troops in the Battle of Peshawar on 8 May 1758.
September 1758: The State of Balasinor was a princely state in Balasinor during the era of British India and founded by Sardar Muhammed khan Babi.
January 1759: Haider Ali's victory against the Marathas at Bangalore in 1758, resulting in the annexation of their territory, made him an iconic figure. In honour of his achievements, the king gave him the title "Nawab Haider Ali Khan Bahadur".
January 1759: The maximum extent of the Kingdom of Travancore was reached at the end of Marthanda Varma's reign.
January 1759: The British East India Company, seeking an overland connection between its holdings at Madras and Bengal, sought to gain access to the Northern Circars, a series of coastal territories held by the French until 1758, when they were ousted with British military support.
January 1759: The Marathas briefly controlled Jawhar in 1742, 1758 and 1761.
January 1759: Tenganapatnam was abandoned by the Dutch in favour of Parangippettai (Porto Novo) in 1758.
February 1759: The Marathas briefly controlled Jawhar in 1742, 1758 and 1761.
April 1760: Karikal is occupied by British forces on 15 Apr 1760.
January 1761: The founder was Ranjith Singh who in 1760, profiting from the troubled times of the Maratha invasion, proclaimed his state independent and was acknowledged as a Raja by the Marathas.
January 1761: When Rai Singh got to know about his brother's death he gathered a force and once again captured Idar; he placed Anand Singh's son on the throne and became his guardian.
January 1761: The state of Kalsia was founded by Gurbaksh Singh in 1760.
December 1761: Maharaja Suraj Mal was the most prominent ruler of Bharatpur State. He captured the Mughal city of Agra on 12 June 1761, and it remained under Bharatpur's control until 1774.
January 1762: By 1760, with defeat of the Nizam in the Deccan, Maratha power had reached its zenith with a territory of over 2,500,000 square miles (6,500,000 km2).
January 1762: The Marathas briefly controlled Jawhar in 1742, 1758 and 1761.
February 1762: The Marathas briefly controlled Jawhar in 1742, 1758 and 1761.
January 1764: The princely state of Jind & Sangrur was founded in 1763 by Raja Gajpat Singh of Jind. It was a part of the Sikh Empire and later became a princely state under British suzerainty. The territory of Sangrur was added to Jind State during this time.
January 1764: Establishment of the Danish outpost in Balasore.
January 1764: By 1761, the Maratha menace had diminished and by 1763, Mysore ruler Haider Ali had captured the Keladi kingdom, defeated the rulers of Bilgi, Bednur and Gutti, invaded the Malabar in the south and conquered the Zamorin's capital Calicut with ease in 1766 and extended the Mysore kingdom up to Dharwad and Bellary in the north.
January 1764: In 1763, the territory of Nabha State was acquired by the Phulkian princely states of Punjab. The state was ruled by the Phulkian dynasty, which was founded by Baba Ala Singh. Nabha State became one of the prominent princely states in Punjab under the British Raj in India, with its capital at Nabha.
January 1766: Charkhari State was founded in 1765 by Khuman Singh.
January 1766: Ajaigarh State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. The state was founded in 1785 and its capital was located in Ajaigarh, Madhya Pradesh.
January 1766: The state takes its name from the chief town, Bijawar, which was founded by Bijai Singh, one of the Gond chiefs of Garha Mandla, in the 17th century.
January 1767: By 1761, the Maratha menace had diminished and by 1763, Mysore ruler Haider Ali had captured the Keladi kingdom, defeated the rulers of Bilgi, Bednur and Gutti, invaded the Malabar in the south and conquered the Zamorin's capital Calicut with ease in 1766 and extended the Mysore kingdom up to Dharwad and Bellary in the north.
January 1767: After Rai Singh's death in 1766, the Marathas once again threatened Idar.
January 1771: Abhai Singh, the Ruler of Khilchipur was obliged to make terms with Mahadaji Sindhia and became his tributory.
January 1771: The Garhwali forces, led by King Pradyuman Shah, defeated the Rohillas, a Pashtun tribe, in 1770. This victory allowed the Garhwal Kingdom to regain control of the Dun region, a strategic territory in present-day Uttarakhand, India.
January 1772: In 1771, the Maratha leader Mahadji Scindia recaptured Delhi from Afghan control, restoring Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II to power. In 1784, the Marathas officially became the protectors of the emperor in Delhi, solidifying their influence in the region.
January 1773: In 1772, Timur Shah, the son of Afghan ruler Ahmed Shah Durrani, lost control of Multan to Sikh forces led by Charat Singh of the Maratha Empire. This marked a significant shift in power dynamics in the region.
January 1773: In 1772, Nagvanshi became a vassal of British rule.
January 1774: Ahmad Shah Durrani, also known as Ahmad Shah Abdali, was the founder of the Durrani Empire. He lost control of Punjab to the Sikhs, who were led by leaders such as Maharaja Ranjit Singh. The Maratha Empire also took advantage of Durrani's weakened state to expand their territory.
July 1774: Rampur State was a 15 gun-salute princely state of British India. It came into existence on 7 October 1774 as a result of a treaty with Oudh.
January 1775: Maharaja Suraj Mal was the ruler of Bharatpur who captured the Mughal city of Agra on 12 June 1761. The territory remained under the control of the Bharatpur rulers until 1774 when it was taken over by the Maratha Empire.
January 1776: In 1775 Pratap Singh of Naruka family acquired Alwar fort and founded the State of Alwar.
January 1778: In 1777, Haider Ali recovered the previously lost territories of Coorg and Malabar from the Marathas.
January 1779: Foundation of Maihar State.
January 1782: The state of Bansda was founded by Virsinhji in 1781 and had its capital in Bansda.
January 1783: Establishment of Sangli State, which was a vassal of the Maratha Empire.
October 1783: The Portuguese were granted the area of Nagar Haveli on 10 June 1783 on the basis of Friendship Treaty executed on 17 December 1779 as compensation towards damage to the Portuguese frigate Santana by Maratha Navy in 1772.
January 1785: Baoni State was founded in 1784 by Imad al-Din al-Mulk Ghazi Khan, from a branch of the Asaf Jahi dynasty related to the Nizam, and Wazir of the Mughal Empire.
January 1786: The state was founded in 1785 and its capital was located in Chhatarpur, Madhya Pradesh.
January 1786: Then, in 1785 the Portuguese purchased Dadra, annexing it to Portuguese India.
January 1790: The Katoch Kings repeatedly looted Mughal controlled regions, weakening the Mughal control, aiding in the decline of Mughal power, Raja Sansar Chand II succeeded in recovering the ancient fort of his ancestors, in 1789.
June 1791: Sachin state was founded on 6 June 1791. Though over 85% of the subjects were Hindu, the state was ruled by Sunni Muslims of the Siddi dynasty of Danda-Rajpuri and Janjira State. The Siddi dynasty is of Abyssinian (Habesha) origin.
January 1795: Pathari's royal house was founded in 1794 as a jagir by a Pashtun of the Barakzai faction from Afghanistan, who rose through the ranks of the Mughal Empire.
January 1800: Ramdurg State was one of the Maratha princely states ruled by the Bhave family during the British Raj. It was administered as part of the Deccan States Agency of the Bombay Presidency, founded in 1799.
January 1800: When the British came to the Konkan area, the repeated attacks of the Marathas against Janjira ceased. Janjira State was administered as part of the Deccan States Agency of the Bombay Presidency, founded in 1799.
January 1800: With the death of Tipu Sultan in 1799, independence returned to Savanur with about a third of its original territory.
January 1801: With his fourth descendant Kumbhoji IV, the State raised itself, by acquiring the parganas of Dhoraji, Upleta, Sarai, and Patanvav.
January 1801: Sakti State's rulers were Raj Gonds. The year when the state was founded is not known. Legend says that it was founded by two twin brothers, who were soldiers of the Raja of Sambalpur. The capital was in Sakti, Janjgir-Champa district, Chhattisgarh.
January 1801: When Maharaja Ranjit Singh attacked and occupied Naraingarh in the Shivaliks in 1807, Jodh Singh was with him. In recognition of his services, Ranjit Singh presented him territories of Badala, Kameri and Chhabbal.
January 1801: Throughout the disintegration of the Mughal Empire, the armies of Jaipur were in a constant state of warfare. Towards the end of the 18th century, the Jats of Bharatpur and the Kachwaha chief of Alwar declared themselves independent from Jaipur and each annexed the eastern portion of Jaipur's territory.
January 1801: Torawati State signs a subsidiary alliance with the British Empire.
January 1802: The formal start of the Sikh Empire began with the unification of the Misls (states) by 1801, creating a unified political state.
January 1802: Khilchipur was formerly the capital of this princely state, under the Bhopal Agency of British India's Central India Agency.
January 1802: In 1801, the territories of Nawab of the Carnatic (ruler of Arcot and Nellore), Nawab of Junagarh, and Rohilkhand of Lower Doab were annexed by the British East India Company.
January 1802: Idar State signs a subsidiary alliance with the British Empire.
January 1802: Chuda is a town and Taluka headquarter of Chuda Taluka in Surendranagar district, Gujarat, India. It was formerly a Rajput princely state.
December 1802: Cambay State was ceded to the British by the Peshwa after the Treaty of Bassein in 1803.
January 1804: The state came under the influence of the Maratha rulers of Nagpur in the 18th century, and became a princely state of British India in 1803, at the conclusion of the Second Anglo-Maratha War at Deogaon of Orissa.
January 1806: British conquests in India until 1805.
January 1807: Nawab Muhammad Amir Khan (1769-1834), an adventurer and military leader of Pashtun descent, established the Tonk State. Amir Khan rose to be a military commander in the service of Yashwantrao Holkar of the Maratha Empire in 1798. In 1806, Khan received the state of Tonk from Yashwantrao Holkar.
January 1808: During the reign of his heir, Nawab Mohammad Bahadur Khanji III, Junagarh was a tributary to the Maratha Empire. However, in 1807, it came under British suzerainty under Mohammad Hamid Khanji I, who was the ruler of Junagarh State at that time.
January 1810: In 1809 Tripura became a British protectorate and in 1838 the Rajas of Tripura were recognised by the British as sovereigns.
January 1810: The Kanker State was occupied by the Marathas of Nagpur in 1809 and the Raja of Kanker was deprived of its power.
January 1812: Jamkhandi State was one of the Maratha princely states of British India. It was founded in 1811 and its capital was at Jamakhandi. It was administered as part of the Deccan States Agency of the Bombay Presidency and was one of the former states of the Southern Maratha Country.
January 1819: After the defeat of the Marathas in the Third Anglo-Maratha War, Bhopal became a British princely state in 1818.
January 1819: Piploda later benefited from the treaty of Mandsore, in which Jaora was confirmed as a princely state by the British. The Thakur of Piploda was allowed to rule in his estate on the condition that he pays Rs.28,000 as tribute to the Jaora nawab.
May 1819: In 1819, the British East India Company completed its conquest of the Maratha Empire. This marked the end of Maratha rule and the consolidation of British control over much of the Indian subcontinent.
Disestablishment
January 1819: After the defeat of the Marathas in the Third Anglo-Maratha War, Bhopal became a British princely state in 1818.
January 1819: Piploda later benefited from the treaty of Mandsore, in which Jaora was confirmed as a princely state by the British. The Thakur of Piploda was allowed to rule in his estate on the condition that he pays Rs.28,000 as tribute to the Jaora nawab.
May 1819: In 1819, the British East India Company completed its conquest of the Maratha Empire. This marked the end of Maratha rule and the consolidation of British control over much of the Indian subcontinent.
Selected Sources
Die Dänen in Indien, Südostasien und China (1620-1845), Wiesbaden (Germany), p. 236
Die Dänen in Indien, Südostasien und China (1620-1845), Wiesbaden (Germany), pp. 215-219
Hugh, C. (1911): Ranjit Singh, Encyclopædia Britannica, Vol. 22 (11th ed.), Cambridge (UK), p. 892
Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 8, p. 125 retrieved on https://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/
Larsen, K. (1940): Guvernører, Residenter, Kommadanter og Chefer samt enkele andre fremtradende personer i de tidligere Danske Tropokolonier, Copenhagen (Denmark), p. 20
Rennell, J. (1782): Map of Hindustan, London (UK)
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.235-237
 maratha empire
maratha empire