If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
Hafsid Kingdom
Hafsid Kingdom (Spain)
French Tunisia
French Tunisia (Vichy France)
Kingdom of Tunisia
Republic of Tunisia
Establishment
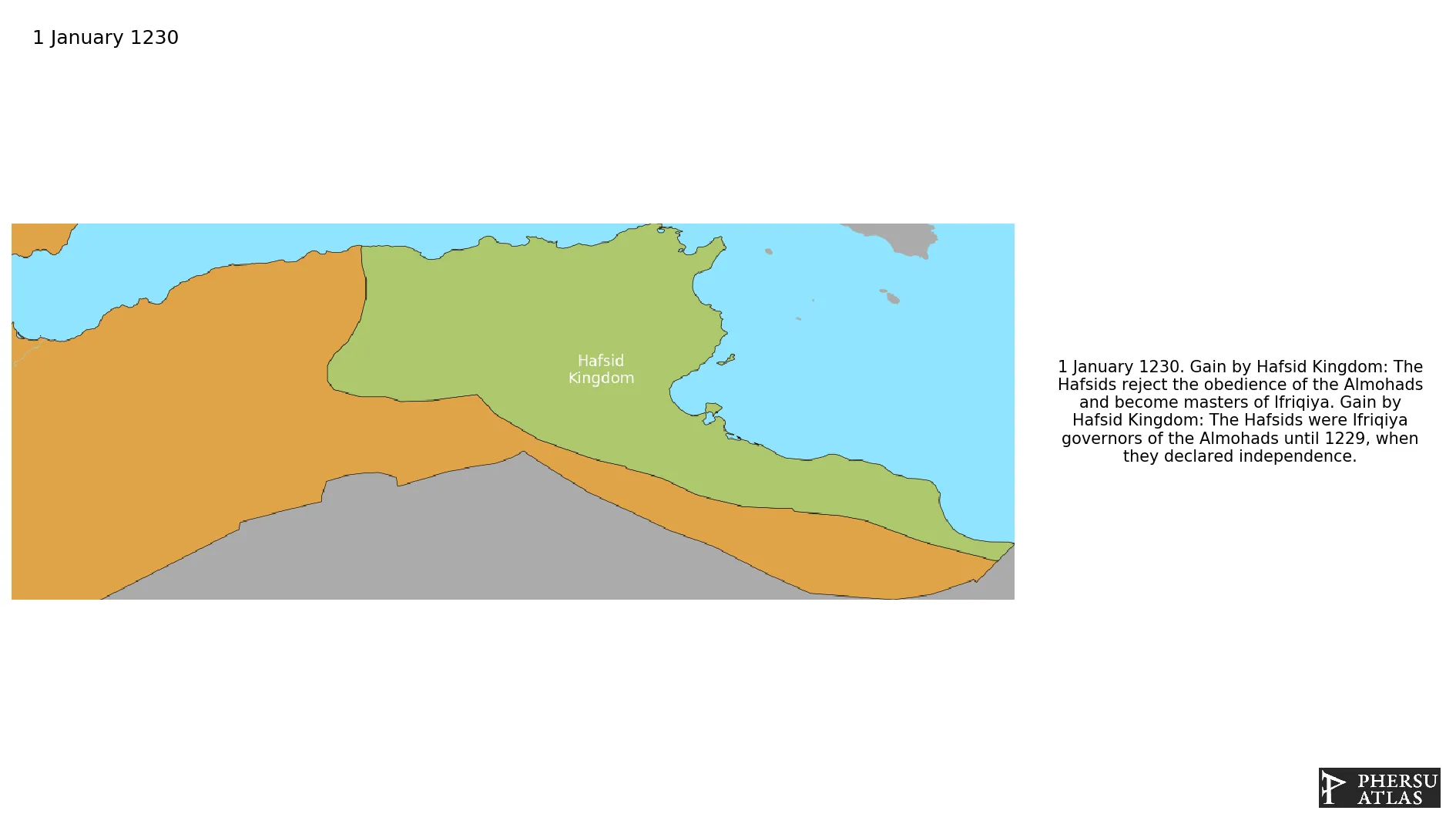
January 1230: The Hafsids were Ifriqiya governors of the Almohads until 1229, when they declared independence.
January 1230: The Hafsids reject the obedience of the Almohads and become masters of Ifriqiya.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the Medieval period. The best known of these military expeditions are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291.
1.1.Eighth Crusade
Was a Crusade led by Louis IX of France against the Hafsids of Tunisia.
July 1270: The Crusaders landed on the Tunisian coast on 18 July without facing much resistance. The crusaders built a camp near a fort built over Carthage and awaited the arrival of the Sicilian contingent under Charles of Anjou.
October 1270: Because of diseases the siege of Tunis was abandoned on 30 October with the Treaty of Tunis.
Conquests and wars with Ottoman involvement during the rule of Suleiman I.
January 1521: Kheireddine Barbarossa seizes the city of Collo with the help of the locals.
January 1522: Constantine conquered by Ottoman Empire.
January 1523: Annaba conquered by Ottoman Empire.
August 1534: The Ottomans conquered Tunis in 1534.
January 1542: In 1541, the city of Biskra was conquered by the Ottoman Empire under the leadership of Hayreddin Barbarossa, a famous Ottoman admiral and privateer.
January 1557: In 1556, the Turkish corsair Dragut, who ruled in Tripoli, attacked Tunisia from the east. He successfully entered Kairouan in 1558, further expanding the Ottoman Empire's territory in North Africa.
January 1562: Tripoli was besieged and conquered by famed Ottoman admirals Sinan Pasha and Turgut Reis. Declared as Bey and later Pasha of Tripoli, Turgut Reis submitted the tribes of the interior and several cities like Misrata, Zuwara, Gharyan, and Gafsa in the next decade.
Expansion during the rule of Selim II in the Ottoman Empire.
January 1570: The Ottomans again conquered Tunis in 1569 and held it for four years.
September 1574: The Conquest of Tunis in 1574 marked the final conquest of Tunis by the Ottoman Empire over the Spanish Empire.
Was the French conquest of Tunisia that became a French protectorate.
4.1.Conquest of Tunisia
Was the French military invasion and occupation of Tunisia.
May 1881: The Treaty of Bardo established a French protectorate over the Beylik of Tunis.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
5.1.World War II (All other Vichy France Colonies)
Refers to the events that happened in French Colonies that decided to be loyal to the German puppet state of Vichy France.
July 1940: With the creation of Vichy France, initially all French colonies were aligned with Vichy.
5.2.World War II (North African Theatre)
Was the North African theatre of World War II.
5.2.1.Allied invasion of French North Africa
Was the Allied invasion of French North Africa during World War II.
5.2.1.1.Tunisian campaign
Was a series of battles that took place in Tunisia during the North African campaign of the Second World War, between Axis and Allied.
November 1942: British and American forces reach Tabarka (Tunisia), which is occupied.
November 1942: The 509th U.S. Parachute Regiment occupies Gafsa airfield in Tunisia.
November 1942: British forces make contact with German forces at Djebel Abiod (Tunisia).
November 1942: French and U.S. Troops occupy Gafsa (Tunisia).
December 1942: Allied forces reach Medjez el Bab where they are attacked by German tank-infantry columns.
December 1942: The Allies reached the outskirts of Djedeida.
December 1942: In Tunisia, the Allies were forced to withdraw to Medjez, and by 26 December 1942 the Allies had withdrawn to the line they had set out from two weeks earlier.
February 1943: Axis forces evacuate Sidi Bou Zid (Tunisia).
February 1943: Frontline between allied and axis forces in Tunisia on that date.
March 1943: Frontline between allied and axis forces in Tunisia on that date.
April 1943: Frontline between allied and axis forces in Tunisia on that date.
May 1943: Allied conquest of Tunisi.
May 1943: With the surrender of German General Messe, Tunisia is liberated by the allied.
Occurred in July 1961 when Tunisia imposed a blockade on the French naval base at Bizerte, Tunisia, hoping to force its evacuation. The crisis culminated in a three-day battle between French and Tunisian forces that left some 630 Tunisians and 24 French dead and eventually led to France ceding the city and naval base to Tunisia in 1963.
October 1963: It occurred in July 1961 when Tunisia imposed a blockade on the French naval base at Bizerte, Tunisia, hoping to force its evacuation. The crisis culminated in a three-day battle between French and Tunisian forces that left some 630 Tunisians and 24 French dead and eventually led to France ceding the city and naval base to Tunisia in 1963.
January 1243: The Hafsids conquered the Kingdom of Tlemcen in 1242.
January 1243: The region of Silves passed to the Hafsid Kingdom.
January 1273: Oujda and Sijilmasa lost to Marinids.
January 1285: In 1284, the Aragonese ruler Frederick III, who had recently taken control of Sicily, invaded Djerba and maintained control of the territory until 1333. This marked a period of Aragonese dominance in the region.
January 1300: The Marinid Abu Yaqub Yusuf an-Nasr was the sultan of the Marinid Dynasty, a Berber Muslim dynasty. Tlemcen was a city in North Africa, known for its strategic importance and wealth. The siege lasted for 8 years, from 1299 to 1307, as the Marinids sought to expand their territory.
January 1308: End of the Marinid siege of Tlemcen.
January 1321: Most of the intenal area of the Hafsid Kingdom is conquered by the Kingdom of Tlemcen.
January 1334: In 1284, Frederick III of Aragon, who was the ruler of Sicily, invaded Djerba and held control of the territory until 1333. This marked a period of Aragonese dominance in the region before the territory was eventually taken over by the Hafsid Kingdom.
January 1354: Bejaia conquered by Marinid Dynasty.
January 1358: Kingdom of Tlemcen conquered by Marinid Dynasty.
January 1360: The Zayyanid king Abu Hammu Musa II (r. 1359-1389) took the throne of Tlemcen.
January 1390: Djerba was retaken for Sicily by Manfredi Chiaramonte, who became lord of the island, and also seized the Kerkennah Islands.
January 1393: The Sicilian garrison abandoned Kerkennah Islands and Djerba in 1392.
January 1425: In 1424, the territory of Tlemcen came under the control of the Hafsid dynasty.
January 1466: In 1465, the city of Tuggurt came under the rule of the Sultanate of Tuggurt, which was established in the 15th century. The territory was previously under the authority of the Hafsid dynasty, like other cities in eastern Algeria.
January 1501: The Zayyanids of Tlemcen recognize Hafsid suzerainty.
January 1511: Tripoli (1510-1530), then ceded to the Knights Hospitaller, was lost in 1551.
January 1511: Spanish Béjaïa (Bugia) (1510-1555).
January 1515: Called by the inhabitants of Algiers, the brothers Arudj and Khayr ad-Din landed in Jijel in 1514 and made the city their rear base.
January 1519: The French bought right of possession over El Kala, in North Africa, from the Arabas.
January 1522: The Tunisian Island of Djerba was controlled by Spanish forces from 1521 to 1524 and from 1559 to 1560. The Spanish called the Island Yerba.
January 1525: The Tunisian Island of Djerba was controlled by Spanish forces from 1521 to 1524 and from 1559 to 1560. The Spanish called the Island Yerba.
July 1535: A year later the King of Spain and Holy Roman Emperor Charles I and V seized Tunis, drove the Ottomans out and restored Muley Hassan as a Hapsburg tributary.
July 1535: In 1535, the Spanish forces captured Tunis from the Ottoman Empire. The territory remained under Spanish control until 1574, when it was returned to the local rulers of Tunis. This event marked a significant period of Spanish presence in North Africa.
January 1536: In 1535, the Spanish conquered La Goulette (La Goleta) from the Ottoman Empire.
January 1536: In 1535, the Spanish under the command of Pedro Navarro captured the city of Annaba, known as Bona at the time.
January 1536: Spanish forces captured the city of Bizerte in present-day Tunisia.
January 1538: In 1537, the Spanish forces under the command of Charles V captured the city of Sousse in present-day Tunisia. The territory was then ruled by the Spanish until 1574. This marked a period of Spanish control in the region, with Sousse becoming an important strategic outpost in the Mediterranean.
January 1541: In 1540, Tabarka was taken over by the Genoese, who also controlled Jijel in Algeria. The Genoese held Tabarka until 1742, maintaining control over the territory for over two centuries.
September 1550: Mahdiya conquered by austria.
January 1551: In 1550, Mahdia was captured by the Ottoman Empire under the leadership of Turgut Reis, also known as Dragut. The territory of Mahdia was then incorporated into the Ottoman province of Mehdya.
January 1551: In 1550, the Spanish took control of Monastir, a city in present-day Tunisia. The territory was then governed by the Spanish for four years until 1554. This period marked a significant chapter in the history of Monastir as it was under Spanish rule during this time.
January 1554: In 1553, Mahdia was captured by the Hafsid Kingdom of Spain. The city was previously under the control of the Ottoman Empire. The Hafsid Kingdom was ruled by the Hafsid dynasty, a Berber Muslim dynasty that controlled parts of North Africa.
January 1555: In 1554, the territory of Monastir was under Spanish control as part of the Hafsid Kingdom. Monastir was a strategic location in North Africa, and its control was contested by various powers including the Spanish Empire and the Hafsid Kingdom.
January 1556: Charles V, who was King of Spain and Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, left the Spanish Empire to his son Philip and the Austrian Lands to his brother Ferdinand I.
January 1560: The Tunisian Island of Djerba was controlled by Spanish forces from 1521 to 1524 and from 1559 to 1560. The Spanish called the Island Yerba.
January 1560: Tolga and Biskra conquered by Kingdom of Ait Abbas.
January 1560: In 1559, the Kingdom of Ait Abbas gained control of Touggourt. El Hadj Khichan el Merbaï, a member of the loyal Hachem tribe, was appointed as Sheikh of Touggourt by the Kingdom.
January 1574: Spanish Bizerte fell to the Hafsid Kingdom.
January 1574: Hafsid Kingdom conquered by Spain.
January 1574: Ahmed Amokrane, a prominent leader of the Kingdom of Ait Abbas, conquered the territory of the Ouled Naïl from Bou Saâda to Djelfa.
March 1956: The Tunisian independence movement was already active before World War I, and continued to gain strength against mixed French opposition. Its ultimate aim was achieved in 1956 when Tunisia gained independence becoming a sovereign state.
March 1956: Due to Bizerte's strategic location on the Mediterranean, France retained control of the city and their naval base after Tunisian independence in 1956.
July 1957: Declaration of the Republic of Tunisia on 25 July 1957.
Selected Sources
U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/brochures/tunisia/p22-23(map).jpg
U.S. Army Center of Military History. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/brochures/tunisia/p16(map).jpg
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.110
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.67
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.68
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.69
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.74
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.93

 tunisia
tunisia