If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the countries established by the Vandals during Antiquity and the Middle Ages.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
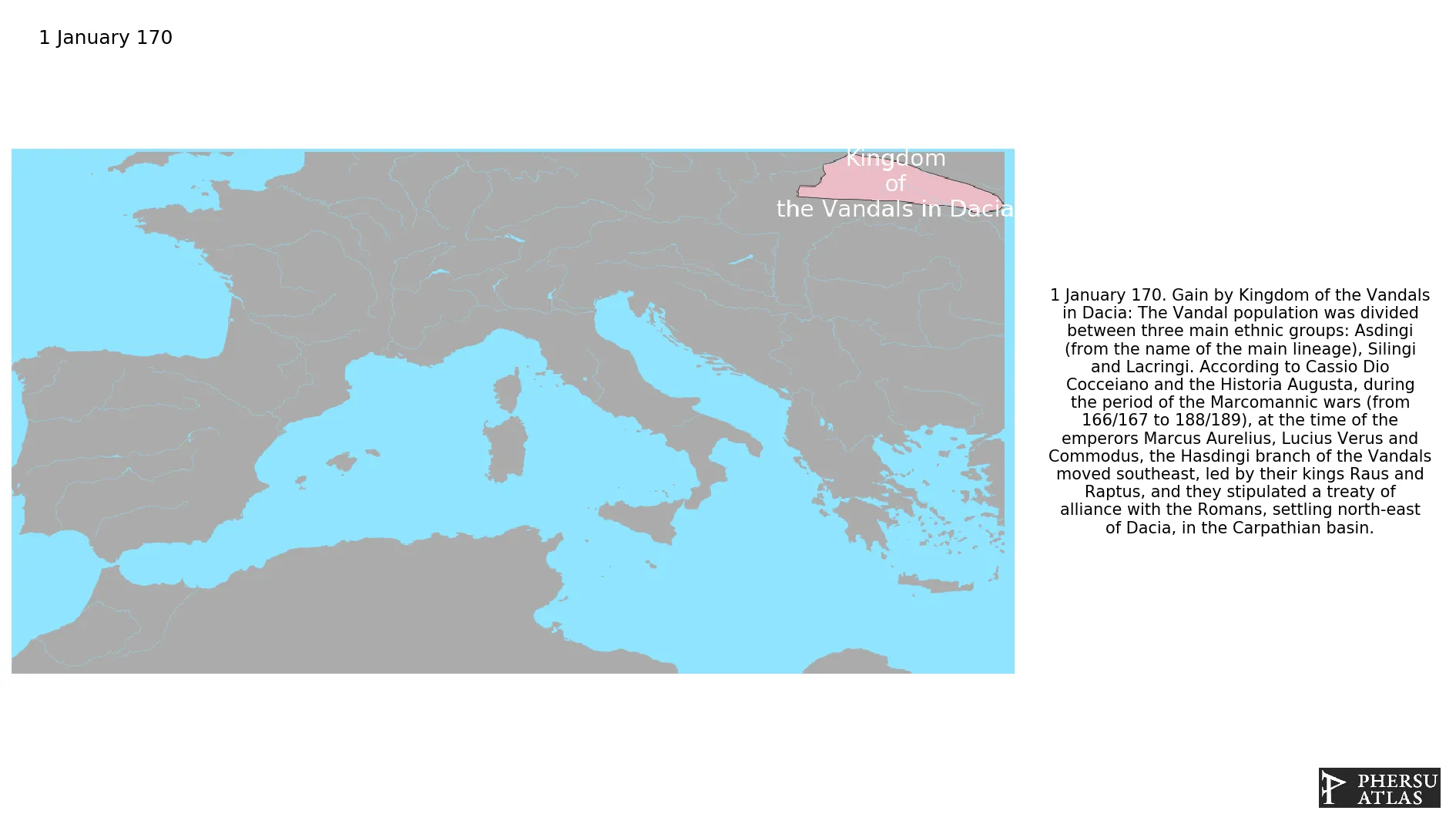
Kingdom of the Vandals in Dacia
Kingdom of the Vandals in Pannonia
Kingdom of the Vandals Silingi in Spain
Kingdom of the Vandals Hasdingi in Spain
Kingdom of the Vandals in Betica
Kingdom of the Vandals
Establishment
January 170: The Vandal population was divided between three main ethnic groups: Asdingi (from the name of the main lineage), Silingi and Lacringi. According to Cassio Dio Cocceiano and the Historia Augusta, during the period of the Marcomannic wars (from 166/167 to 188/189), at the time of the emperors Marcus Aurelius, Lucius Verus and Commodus, the Hasdingi branch of the Vandals moved southeast, led by their kings Raus and Raptus, and they stipulated a treaty of alliance with the Romans, settling north-east of Dacia, in the Carpathian basin.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Germanic Tribe of the Hasdingi Vandals settled down in the Carpathian Basin after a treaty with the Romans.
In 335 AD the Vandals, that had established north to the Banat region, were defeated by the Ostrogoths and expelled.
January 336: In 340 the raids started again and conquered the Vandal kingdom (which was located in Dacia before the conquest of North Africa) and took this populous region. In 335, the Vandals, who inhabited the region between the Marisus river and the Danube (perhaps just northwest of the Banat), under the leadership of Visimar, clashed with the Goths of Geberic and were defeated.
After their expulsion from the Danube area by the invading Visigoths, the Vandals established themselves in Pannonia as Roman foederati.
January 336: The Vandals obtained the permission by the Roman emperor to settle in Pannonia, where they remained peaceful for at least forty years, obeying the laws of the Empire like the other inhabitants of the region. They were thus incorporated as foederati, maintaining their buffer function between the empire and the other barbarian tribes of the Sarmatian plain.
The Gepids invaded Dacia and created their own kingdom in the area.
January 351: The Lazyges retake back the territories in the Carpathian Basin that were previously lost to the Roman Empire. The Iazyges were a nomadic tribe of Sarmatian origin.
January 351: The Gepids settle in the Carpathian Basin. No archaeological evidence substantiates the Gepids' presence before around 350.
Were a series of conflicts that saw the Huns, an invading tribe probably from Central Asia, fighting against the Romans as well as the Germanic tribes of Europe.
5.1.Hunnic Invasion of Europe
The Huns invaded Europe starting with the Ukrainian Steppe.
5.1.1.The Kingdom of the Goths is absorbed by the Huns
The Huns invaded and annexed the Kingdom of the Goths.
January 377: The Huns expelled the Goth from eastern Europe and expanded between the Danube and the Black Sea.
The Hasdingi Vandals left their territoris in Pannonia to flee the Hunnic invasion.
January 401: The Hasdingi Vandals left Pannonia around 400, driven to colonize new lands by the advance of Hun troops.
The Alans, Suebi and Vandals occupied and partitioned the Iberian Peninsula.
November 409: In the last months of 409 Vandals, Alans and Suebi, entered Spain, subjecting it for the most part. According to the testimony of the Spanish chronicler Hydatius, the Vandals, the Alans and the Swabians divided up the territories conquered in Spain by drawing lots.
Was a military campaign by emperor Honorus to reconquer the Iberian peninsula from the Alans, Suebi and Vandals.
January 415: After a war with the Romans the Goths were sent to the Iberian peninsula to wipe out the barbarian kingdoms created there. Once these successes were achieved, the Hispanic provinces of Lusitania, Carthaginian and Baetica returned to precarious Roman control.
Was a Roman military campaign against the Vandals and the Alans that had occupied Galicia.
January 421: A new Vandal-Alana coalition attempted to expand into Galicia to the detriment of the Swabians, forcing the Romans to intervene in 420: the Vandals were forced to abandon Galicia, migrating to Baetica.
January 421: The Hispanic problem had not yet been resolved, also because after the defeat, the Vandals Silingi and Alani joined forces with the Vandals Hasdingi, whose king, Gunderic, became king of the Vandals and Alani. The new Vandal-Alana coalition immediately attempted to expand into Galicia to the detriment of the Swabians, forcing the Romans to intervene in 420: the Vandals were forced to abandon Galicia, migrating to Baetica.
January 423: In 422, the Roman-Visigothic coalition, led by General Castino, attempted to annihilate the Vandals-Alani in a pitched battle, but the defection of the comes Africae Bonifacio due to a quarrel with Castino and an alleged betrayal by the Visigoths resulted in a catastrophic defeat . When the expedition failed, Castino was forced to retire to Terragona and, subsequently, to return to Italy.
February 423: In 422, the Roman-Visigothic coalition, led by General Castino, attempted to annihilate the Vandals-Alani in a pitched battle, but the defection of the comes Africae Bonifacio due to a quarrel with Castino and an alleged betrayal by the Visigoths resulted in a catastrophic defeat . When the expedition failed, Castino was forced to retire to Terragona and, subsequently, to return to Italy.
The Vandals occupied the southern Iberian peninsula.
January 426: The struggles for obtaining the rank of general of the Empire between Aetius, Boniface and Felix (which lasted until 433) partially distracted the central government from the fight against the Barbarians, facilitating their successes. The Vandals thus had the green light to raid and occupy southern Spain, with the capture of Seville and Cartagena and the devastation of the Balearic Islands (425).
The Vandals invaded North Africa.
January 430: In the meantime the rivalry between Felice (magister militum praesentialis in Italy) and Bonifacio (comes d'Africa) began to produce deleterious effects for the Empire. When in 428 an army landed in Africa, Boniface, in difficulty, would have asked for help from the Vandals of Genseric, who crossed the Strait of Gibraltar to move to his aid. Some modern scholars, however, have believed that the Vandals would have invaded Africa on their own initiative, having the need to settle in a more protected place from the attacks of the Visigoths allies of the Romans.
January 430: The Vandals crossed the Strait of Gibraltar subdued Mauretania (429).
January 431: Numidia conquered by Kingdom of the Vandals.
August 431: The Kingdom of the Vandals captured Hippo.
The Vandals conquered Carthage, in modern-day Tunisia.
October 439: While Aetius was restoring order in Gaul, in Africa Genseric on 19 October 439 took Carthage, the capital of the Praetorian Prefecture of Africa, definitively putting an end to any semblance of imperial power in the region. Having taken control of the numerous African ports, Genserico also set up his own fleet with which he began to practice piracy.
The Vandals occupied Sicily.
January 441: The Vandalic Kingdom took advantage of the weakness of the Western Roman Empire of Valentinian III, engaged in the wars in Gaul, to plunder and occupy Sicily in 440.
Theodosius II, emperor of the Eastern Roman Empire, dispatched an expedition to deal with the Vandals in 441.
January 442: Theodosius II, emperor of the Eastern Roman Empire, dispatched an expedition to deal with the Vandals in 441, however it only progressed as far as Sicily.
Was a military campaign of Western Roman Emperor against the Vandals in Sicily and southern Italy.
January 456: Ricimer was a Germanic general and de facto ruler of the Western Roman Empire. The Vandals were a Germanic tribe led by King Genseric. The pirate raids were part of the Vandals' conquest of North Africa and Mediterranean territories.
February 456: Ricimer was a Germanic general and de facto ruler of the Western Roman Empire. The Vandals were a Germanic tribe known for their piracy and raids in the Mediterranean. Ricimer's successful defense against the Vandals helped maintain control over Sicily and southern Italy for the Western Roman Empire in 456.
Gaiseric, King of the Vandals and Alans, attacked and occupied several Mediterranean islands.
January 457: In 456, Genseric, with his fleet, took possession of Sardinia, Corsica and the Balearic Islands.
Western Roman Emoperor Majorian was assassinated and overthrown by Ricimer.
September 461: Upon his return to Italy, Majoran was assassinated by order of Ricimer in August 461. Majorian's death meant the definitive loss to the Vandals of Africa, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica and the Balearic Islands, as well as of Spain to the Visigoths: in fact , after Majorian's withdrawal from Spain, no other Roman official is attested in the sources in the Iberian peninsula, making it clear that after 460 Spain was no longer de facto part of the Empire.
Was an military expedition of the Vandals in the Peloponnese.
January 470: After capturing the western fleet and destroying the eastern one, the Vandals attempted to invade the Peloponnese, but were driven back to sea near the Maina peninsula with very heavy losses. Taking 500 Roman hostages on Zakynthos, they hacked them to pieces on the way back to Carthage, throwing the remains overboard.
February 470: After capturing the western fleet and destroying the eastern one, the Vandals attempted to invade the Peloponnese, but were driven back to sea near the Maina peninsula with very heavy losses. Taking 500 Roman hostages on Zakynthos, they hacked them to pieces on the way back to Carthage, throwing the remains overboard.
Odoacer received eastern Sicily from the Vandals.
January 477: In 476, the Kingdom of Odoacer, led by the Germanic chieftain Odoacer, gained control of central-eastern Sicily from the Vandals, a Germanic tribe led by King Genseric. This acquisition was made possible through the payment of a tribute.
Odoacer conquered western Sicily from the Vandals.
January 478: In 476 Odoacer, king of the Heruli, began a bloody war against the Vandals, redeeming however almost all of Sicily with a tribute. With Hunneric the only Vandal stronghold remained Lilybaeum.
Was an unsuccesfull Vandalic military expedition to Sicily.
January 492: Taking advantage of the conflict between Odoacer and Theodoric, Vandal king Gunthamund tried to regain possession of Sicily.
February 492: The Vandalic troops sent to the Sicily in 491 were driven back by the Ostrogoths. The Vandals also lost the contribution that Odoacer paid to the king of the Vandals, starting in 476, for the possession of the island.
The Kingdom of the Ostrogoths conquered the last Vandalic territories in Sicily.
January 497: Under Gutemondo, nephew of Genseric, between 484 and 496, Sicily was entirely conquered by the Ostrogoths.
The Kingdom of the Ostrogoths donated the Sicilian city of Lilibeo to the Kingdom of the Vandals after the marriage of Amalfrid, the sister of Theodoric King of the Ostrogoths, with the King of the Vandals.
January 501: The vandal king Thrasamund made an alliance with the Ostrogoths, and in his second marriage, in 500, he married the sister of their king Theodoric, Amalafrida, who arrived in Carthage escorted by 1,000 notables and 5,000 slaves skilled in arms, bringing as a dowry the Sicilian city of Lilybaeum and its district (the western end of the island).
Were a series of wars initiated by Eastern Roman Emperor Justinian I to reconquer former territories of the Western Roman Empire. Although Justinian was not able to conquer back all these territories, he was succesful in conquering most of them.
24.1.Vandalic War
Was a war by Eastern Roman Emperor Juistinian I against the Vandalic Kingdom, which was conquered by the Romans.
September 533: Syllectum was captured by a Roman detachment under Boriades.
September 533: The Battle of Ad Decimum against the Vandals ended in a crushing Roman victory.
September 533: On the morning of September 15th, Belisarius drew up the army for battle before the city walls, but as no enemy appeared, he led his army into the city, after again exhorting his troops to show discipline. .
October 533: The Romans advanced through Thapsus, Leptis Parva and Hadrumetum to Grasse.
October 533: The Romans reached Cape Caputvada on the eastern shore of modern Tunisia.
November 533: Belisarius also demanded the return of the port of Lilybaeum in western Sicily from the Ostrogoths, who had captured it during the war.
December 533: Belisarius was a Byzantine general who led the Eastern Roman Empire's campaign to reconquer the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Hippo Regius was a city where the Vandals sought refuge but eventually surrendered to Belisarius in 533.
April 534: Gelimer surrendered to the Eastern Roman Empire, led by General Belisarius, in March 534 after negotiations that ensured his safety.
April 534: Belisarius was a Byzantine general under Emperor Justinian I. In 534, he sent armies to occupy various vandal regions outside Africa, including Sardinia, Corsica, Caesarea, Septem, Gadira, Balearic islands, and Tropolitania. This marked a significant expansion of the Eastern Roman Empire's territory.
24.1.1.Surrender of Gelimer
Was the surrender of the king of the Vandals Gelimer to the Eastern Roman invading troops.
January 535: Gelimer continued to resist on Mount Pappua, besieged by Fara, a Herulian general in the service of the Byzantines, to whom he surrendered in 534. With Gelimer's capture, the Kingdom of the Vandals dissolved.
24.2.Byzantine reconquest of Spania
Was a Byzantine military campaign against the Kingdom of the Visigoths to reconquer the Iberian Peninsula. The Byzantine were able to slowly occupy the southern coast of the Peninsula.
January 535: Ceuta was seized by an expedition dispatched by Belisarius.
Disestablishment
January 535: Ceuta was seized by an expedition dispatched by Belisarius.
January 535: Gelimer continued to resist on Mount Pappua, besieged by Fara, a Herulian general in the service of the Byzantines, to whom he surrendered in 534. With Gelimer's capture, the Kingdom of the Vandals dissolved.
 vandals
vandals