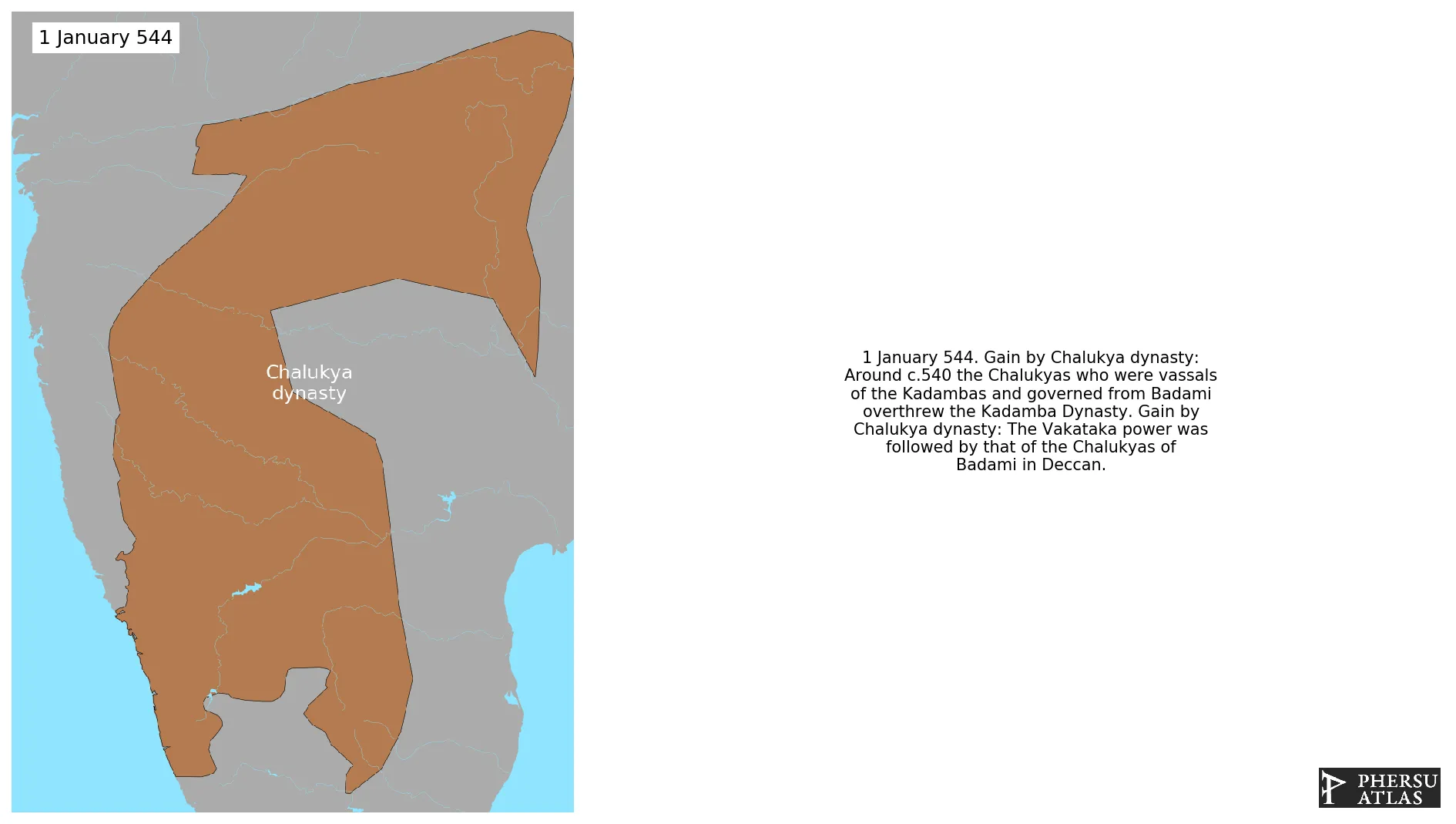
Chalukya dynasty
Chalukya dynasty
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. The Chalukya succeeded the Kadambas in the area.
Establishment
January 544: Around c.540 the Chalukyas who were vassals of the Kadambas and governed from Badami overthrew the Kadamba Dynasty.
January 544: The Vakataka power was followed by that of the Chalukyas of Badami in Deccan.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were the military campaigns by the first three Islamic Caliphates (the Caliphate of Muhammad, the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate) that led to the Islamic conquest of most of the Middle East as well as the Iberian Peninsula.
1.1.Islamic conquest of Deccan
Was the invasion of Deccan (India) initiated by the Umayyad Caliphate.
January 734: Arab invaders who had established themselves in the Sindh made a push into the Deccan.
In the VIII century Muktapida, an Indian king of the Karkota dynasty of Kashmir, created a short-lived empire covering most of India.
January 741: Karkota ruler Lalitaditya Muktapida conquered extensive territories in India and Central Asia.
January 761: Karkota ruler Lalitaditya Muktapida conquered extensive territories in India and Central Asia.
January 551: Krishnaraja (r. c. 550-575) was the earliest known ruler of the Kalachuris of Mahishmati dynasty.
January 551: The Mutharaiyar dynasty ruled the Thanjavur, Trichy, Pudukottai, Perambalur and Thiruvarur regions between from the mid VI century.
January 551: The Kalachuris conquered northern Konkan by the mid-6th century.
January 593: Chalukya ruler Kirttivarman I expanded his kingdom from the Konkan coast of present-day Maharashtra in the north to the Shimoga district of Karnataka in the south; and from the Arabian Sea in the west to the Kurnool and Guntur districts (Andhra Pradesh) in the east.
January 601: The Kalachuris of Mahishmati took control of Vidarbha in 600, succeeding the Vakataka and Vishnukundina dynasties. The Kalachuris were a powerful dynasty that ruled over central India during this time period.
May 606: After the fall of the Gupta Empire in the mid-6th century AD, northern India had again fallen apart into small republics and monarchies. Harsha of the Pushyabhuti Dynasty united the small republics from Punjab to central India and was crowned king in April 606.
January 625: Pallava Narasimhavarman was a ruler of the Pallava Dynasty who defeated the Chalukya dynasty in 642 by occupying Badami temporarily. This victory marked a significant shift in power dynamics between the two dynasties in the region.
February 625: Pallava Narasimhavarman was a powerful ruler of the Pallava dynasty in South India. Badami was the capital of the Chalukya dynasty. The Chalukya dynasty was a prominent Indian dynasty that ruled parts of southern and central India between the 6th and 12th centuries.
January 637: During the reign of Pulakeshin II (r. c. 610-642 CE), the Chalukya kingdom expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in peninsular India.
January 641: Dhruvasena II was a ruler of the Maitraka Kingdom in India during the 7th century. His rule extended to Ratlam, a town west of Ujjain, which led to the entire modern central and north Gujarat coming under the control of the Maitrakas in 640.
January 643: Buddharaja probably lost his sovereignty during a second Chalukya invasion, by Mangalesha, or by his nephew Pulakeshin II.
January 691: The Chavda was a dynasty that ruled the region of modern-day Gujarat in India, from c. 690.
January 701: After the fall of the Sharabhapuriyas in the late 6th century, Dakshina Kosala appears to have been controlled by petty chiefs until the Panduvamshis gained control of the region.
January 701: Kolathunadu was one of the 4 most powerful kingdoms on the Malabar Coast. Kolattunādu had its capital at Ezhimala and was ruled by Kolattiri Royal Family and roughly comprised the whole northern districts of Kerala state in India.
January 740: Avanijanashraya Pulakeshin, a son of Vikramaditya I's brother Jayasimhavarman who was the governor of the Lata branch (Gujarat) fought and defeated them in 739 CE.
January 741: Gurjara-Pratihara ruler Nagabhata I (730-756) extended his control east and south from Mandor, conquering Malwa as far as Gwalior and the port of Bharuch in Gujarat.
January 754: The last Chalukya king, Kirtivarman II, was overthrown by the Rashtrakuta King Dantidurga in 753.
January 758: Though he conquered the Chalukyan Empire, it is clear from the Vakkaleri inscription of 757 that the Chalukyan Emperor Kirtivarman II retained control over his southern provinces up to the year 757.
January 991: Kokalla I appears to have been the first powerful ruler of the Kalachuris of Tripuri dynasty, as he finds regular mentions in the genealogies of the later Kalachuri rulers.
January 1281: Seuna ruler Ramachandra subjugated the rulers of Vajrakara (probably modern Vairagarh) and Bhandagara.
January 1708: Bhopal State was founded in 1707 CE by Dost Mohammad Khan, a Pashtun soldier in the Mughal army, who became a mercenary after the Moghul Emperor Aurangzeb's death and annexed several territories to his fiefdom.
January 1732: Gwalior state was a semi-autonomous Maratha state. It was centered in modern-day Madhya Pradesh, arising due to the rise of the Maratha Empire and fragmentation of the Mughal Empire.
January 1754: Basoda state was established in 1753 by Muhammad Ahsanullah Khan son of Muhammad Diler Khan founder of Kurwai State.
Disestablishment
January 1843: In 1842, Mohammadgarh State was established in present-day Madhya Pradesh, India. The territory was created from parts of Basoda and Kurwai states when Ahsanullah Khan, the Nawab of Basoda, divided his state between his two sons, Bakaulla and Muhammad Khan.
Selected Sources
Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 8, p. 125 retrieved on https://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/
Schwartzberg, J. E. (1992); A Historical Atlas of South Asia, Chicago (USA), p. 146
 Chalukya dynasty
Chalukya dynasty