Congo Free State
Congo Free State
This article is about the specific polity Congo Free State and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a large state and absolute monarchy in Central Africa from 1885 to 1908. It was privately owned by and in a personal union with King Leopold II. The state included the entire area of the present Democratic Republic of the Congo and existed from 1885 to 1908, when the Belgian Federal Parliament reluctantly annexed the state as a colony belonging to Belgium after international pressure.
Establishment
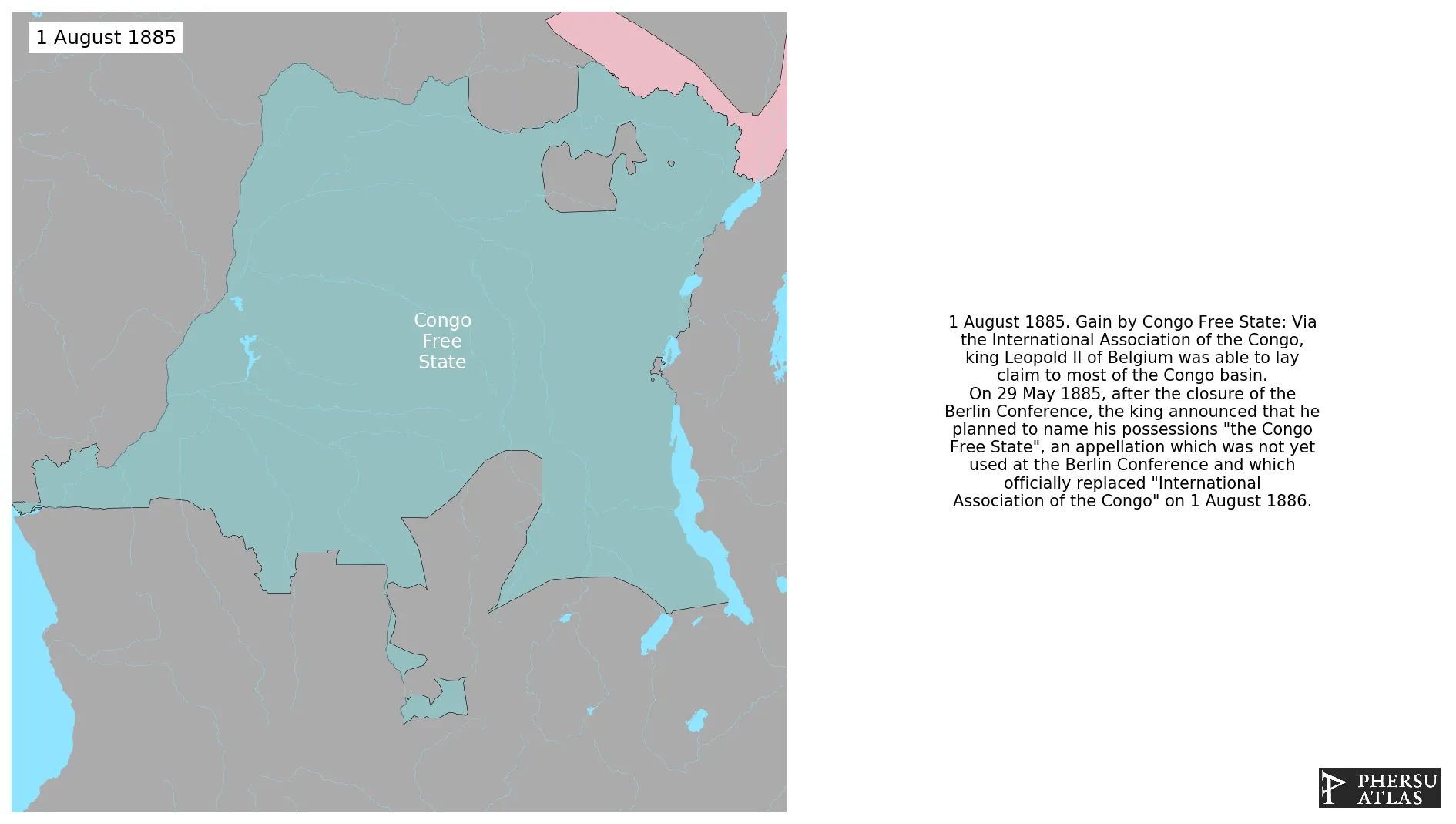
August 1885: Via the International Association of the Congo, king Leopold II of Belgium was able to lay claim to most of the Congo basin. On 29 May 1885, after the closure of the Berlin Conference, the king announced that he planned to name his possessions "the Congo Free State", an appellation which was not yet used at the Berlin Conference and which officially replaced "International Association of the Congo" on 1 August 1886.
November 1885: By the end of 1885 Ngweshe became part of Congo.
November 1885: By the end of 1885 Ruund became part of Congo.
November 1885: By the end of 1885 Buhavu became part of Congo.
November 1885: By the end of 1885 Mangbetu became part of Congo.
November 1885: By the end of 1885 Kabare became part of Congo.
November 1885: By the end of 1885 Kasongo Luunda became part of Congo.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a war fought in Central Africa between the forces of Belgian King Leopold II's Congo Free State and various Zanzibari Arab slave traders.
February 1887: Belgish autorities made Tippu Tip governor of eastern Congo (" The borders of his territories were the Aruwimi and the Lualaba River.") to eliminate his secessionist aims. However he considered himself a vassal, de facto secceeding from Congo.
January 1888: Other major slave traders like Rumaliza, the strongman of Lake Tanganyika, considered his deal with the Congo Free State to be treason. Rumaliza abolished the Congo Free State flag and swore loyalty to the red flag of the sultan of Zanzibar.
January 1892: On the 3rd of January 1892, Captain Alphonse Jacques' anti-slavery expedition founded the fortress of Albertville on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, and tried to put an end to the slave trade in the region.
March 1893: The Congo Free State forces under Francis Dhanis took control of a key river city by the name of Nyangwe.
April 1893: Dhanis advanced up the river to Kasongo.
June 1893: Commandant Pierre Ponthier arrived at the Stanley Falls from Europe. He immediately collected all the troops he could, took Captain Hubert Lothaire and some men from Bangala with him and followed the Arab units, who had fled from the Stanley Falls up the river.
October 1893: The war's last major battle occurred on 20 October 1893, on the Luama River, west of Lake Tanganyika. It was a tactical stalemate, but Sefu was killed.
February 1894: A column of Belgian Congo forces under Lothaire pursued Rumaliza to the north of Lake Tanganyika, destroying his fortified positions along the route, although Rumaliza himself managed to escape. At the lake they joined with the anti-slavery expedition led by Captain Alphonse Jacques Rumaliza took refuge in the German colony of German East Africa. The war ended in a victory for the Free State by January 1894.
The 'scramble for Katanga' was won by Leopold's Stairs Expedition, which ended the Yeke Kingdom by killing Msiri, and took over the territory for the Congo Free State.
December 1891: The 'scramble for Katanga' was won by Leopold's Stairs Expedition, which ended the Yeke Kingdom by killing Msiri, and took over the territory for the CFS, but with its own administration until it was more closely incorporated into the Belgian Congo.
January 1886: By 1885 the Congo Free State expanded up to the Congo-Zambezi rivers system.
May 1889: The colonization of Ubangi began with the establishment of the outpost Bangui in 1889 by French explorer Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza. This marked the beginning of French control over the territory, which later became known as the Colony of Ubangi-Shari.
January 1890: The Luba Empire was later absorbed into the Belgian Congo Free State.
June 1890: On 14 June, Sultan Bangassou appears at Yakoma, a post belonging to Belgian king Leopold II's empire, and signs a treaty with Captain Alphonse Vangèle which places his kingdom under the protection of the Congo Free State.
December 1894: Congo Free State protectorate over the Sultanate of Zemio.
January 1895: After 1894 Bangassou becomes subject to French control.
July 1895: French forces occupy Zemio city and Zemio North of Mbomou River according to the 12 Jul 1894 France-Congo Free State agreement.
February 1897: Belgian forces led by Chaltin continued defeated the rebels in the Battle of Rejaf, securing the Lado Enclave as a Belgian territory.
January 1900: After King Msiri's death the Kingdom of Kazembe was divided in 1894 between Britain - the eastern shores of the Luapula and Lake Mweru became part of North-Eastern Rhodesia, administered by the British South Africa Company (BSAC) - and King Leopold II of Belgium's misnamed Congo Free State (CFS) but the real control was achieved only in 1899.
November 1908: The violence and exploitation of the Congo by private militias, when the region was a personal dominion of the Belgian King, compelled the Belgian government to reluctantly annex the state following international pressure.
Disestablishment
November 1908: The violence and exploitation of the Congo by private militias, when the region was a personal dominion of the Belgian King, compelled the Belgian government to reluctantly annex the state following international pressure.

 Congo Free State
Congo Free State