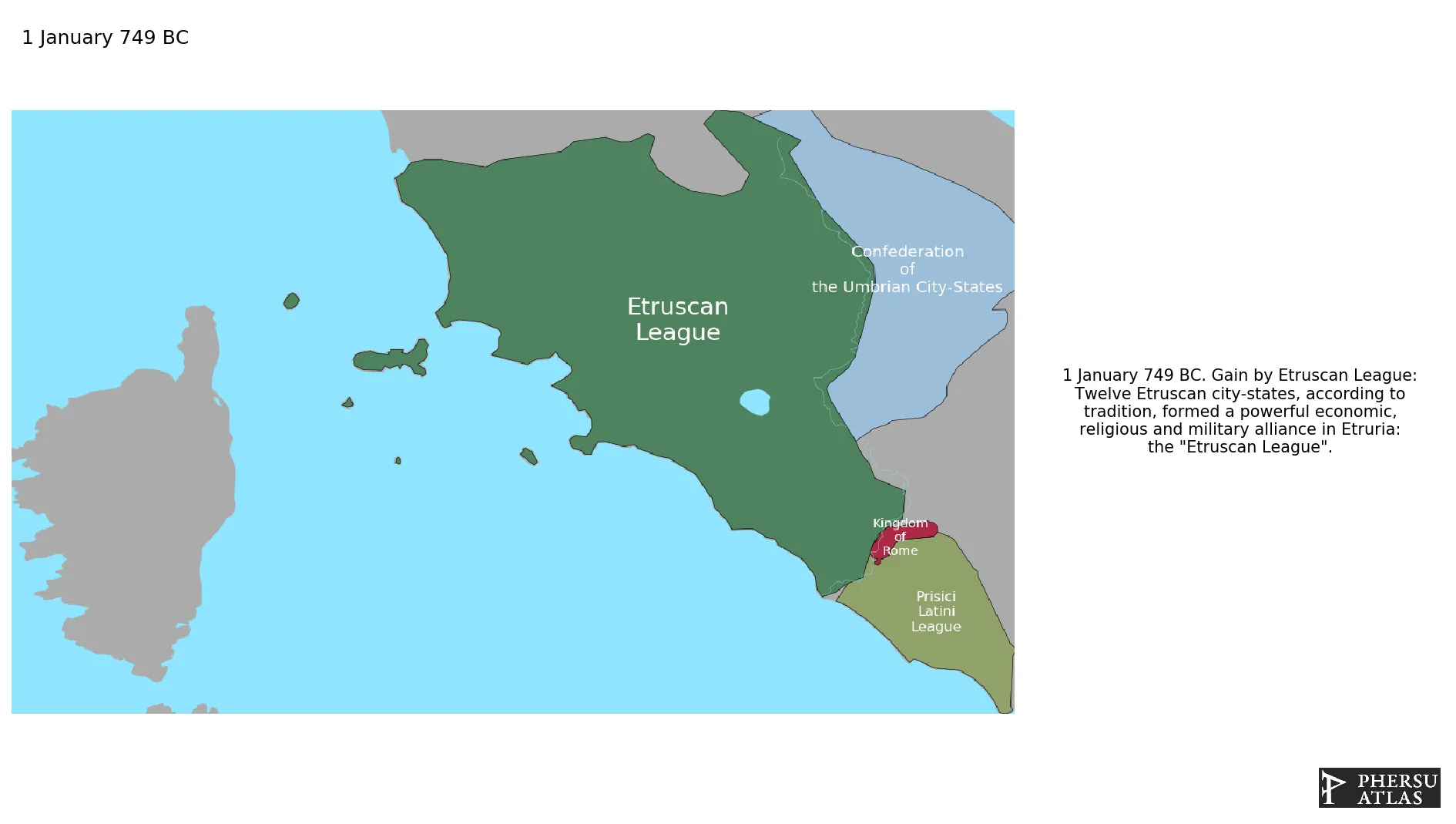
This article is about the specific polity Etruscan League and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a league of Etruscan cities during antiquity. The core of its territory was in the modern-day Italian regions of Tuscany, Umbria and northern Latium but in certain periods the league was able to extend its influence to Emilia-Romagna, Corsica, southern Latium and Campania. It was absorbed into the Roman Republic after centuries of intermittent wars.
Establishment
January 749 BC: Twelve Etruscan city-states, according to tradition, formed a powerful economic, religious and military alliance in Etruria: the "Etruscan League".
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome (in both the regal and the republican periods) and the Etruscans. The conquest of Etruria was completed in 265-264 BC.
January 745 BC: The Kingdom of Rome occupied Fidenae, a town located north of Rome.
January 615 BC: Etruscan domination in Rome (616-509 BC).
January 509 BC: Etruscan domination in Rome (616-509 BC).
January 506 BC: Siege of Rome by Lars Porsena, overlord of the city of Clusium, ca. 507 BC.
February 506 BC: End of the Siege of Rome by Lars Porsena, overlord of the city of Clusium, ca. 507 BC.
January 505 BC: Battle of Aricia: end of etruscan influence in Latium.
January 395 BC: After a long siege, the Etruscan city of Veii is conquered and sacked by the Romans.
January 395 BC: The fall of Velius is dated to approximately 396 BC.
January 385 BC: The Roman army, led by the consul Gaius Sulpicius Peticus, marched on Nepet in -386. The city was a stronghold of the Etruscans, who were in conflict with the expanding Roman Republic. The siege of Nepet was part of Rome's efforts to assert control over the region.
January 385 BC: Roman Consuls Camillus and Fabius defeat an alliance of rebel Latins, Hernici and Volsci at Sutrium.
January 294 BC: With the battle of Sentino (295 BC), Perusia and most of the rest of Umbria enter the Roman orbit, retaining the use of Etruscan.
January 294 BC: The army put together from Arezzo, Volterra and Perugia was defeated at Roselle, near Grosseto, in 295 BC. So in the III century BC Arezzo was conquered by the Romans who latinized its Etruscan name Arretium.
January 281 BC: The Battle of Lake Vadimone was fought in 283 BC. between Rome and an alliance between the Etruscans and the tribe of Galli Boi. The Roman army, led by the consul Publius Cornelius Dolabella, definitively defeated the Gallo-Etruscan army, so much so that the following year all of Etruria was now firmly controlled by Rome.
January 279 BC: Vulci was strong enough to further resist until Tiberius Coruncanius triumphed over them in 280 BC.
January 263 BC: Rome was the eventual victor in the wars and the last Etruscan resistance was crushed in 264 BC when Volsinii was defeated. The Etruscans were assimilated into Roman culture and Rome became one of the Mediterranean superpowers amongst the Greeks and the Carthaginians, though the Etruscan language survived for another 300 years.
1.1.War with Veii
Was a war between Rome and the Etruscan city of Veii.
January 719 BC: The Veientes were concerned by the increasing Roman power, and accordingly launched an incursion into Roman territory. However, they were defeated by the Romans who forced the Veientes to cede the territories of Septem Pagi and Saline.
1.2.Siege of Rome by Lars Porsena (508)
In 508 BC former Roman king Tarquin persuaded the king of the Etruscan city of Clusium, Lars Porsena, to wage war on Rome, resulting in a siege of Rome.
January 507 BC: Lars Porsenna, the king of Clusium, besieged Rome after being persuaded by former Roman King Tarquin to do so.
February 507 BC: The siege of Rome by Etruscan forces from Clusium is ended by a peace treaty.
1.3.Capture of Fidenae
Was a war of Rome against Veii that resulted in the city of Fidenae being captured by the Romans.
January 434 BC: Ancient Rome defeated Veii in the Capture of Fidenae in 435 BC.
1.4.10 Year war with Veii
After 10 years of War with Veii the Etruschian city was conquered and destroyed by the Romans.
January 405 BC: The Romans placed the Etruscan city of Veii under siege.
January 405 BC: After 10 years of War with Veii the Etruscan city is conquered and destroyed by the Romans.
1.5.War in Southern Etruria
Roman War against the Etruscans and conquest of southern Etruria.
January 385 BC: Victories in Southern Etruria, creation of 4 rustic tribes and installation of Roman colonists in this territory.
Were the events and military campaigns that led to the foundation and the expansion of the Kingdom of Rome.
January 699 BC: Expansion of the Kingdom of Rome by 700 BC.
April 587 BC: Priscus obtained a triumph over the Latins and Etruscans on 1 April 588/587 BC. He bought the cities of Corniculum and Collatia from the Roman state.
January 509 BC: Ocricoli conquered by Kingdom of Rome.
Were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome (including both the Roman Kingdom and the Roman Republic) and the Latins, from the earliest stages of the history of Rome until the final subjugation of the Latins to Rome in the aftermath of the Latin War.
3.1.Rome's first war with the Latini
Was the first war between Rome and the Latins that started when the Latins attacked the Kingdom of Rome.
January 600 BC: The Latins initially made an incursion into Roman territory. When a Roman embassy demanded compensation for the damage, the Latins gave a contemptuous reply. Ancus Martius consequently declared war on the Latins. Ancus Martius marched from Rome with a conscript army and captured the Latin city of Politorio in one attack.
January 600 BC: The war then concentrated on the Latin city of Medullia, a city which had a large garrison and was well fortified. Several clashes took place outside the city walls and the Romans were eventually victorious.
January 600 BC: Additional citizens were brought to Rome when the king captured the Latin cities of Telleni and Ficana.
3.2.War with the Latin League
Was a war waged by Roman King Tarquinius Priscus against the Latins.
January 587 BC: Tarquin's first war was waged against the Latins. Tarquinius took the Latin town of Apiolae by storm and took great booty from there back to Rome. According to the Fasti Triumphales, this war must have occurred prior to 588 BC. Subsequently, the Latin cities of Corniculum, old Ficulea, Cameria, Crustumerium, Ameriola, Medullia, and Nomentum were subdued and became Roman.
3.3.Tarquinius Priscus' wars
Were a series of wars waged by Roman King Tarquinius Priscus.
January 587 BC: When Rome was ruled by Tarquinius Priscus the Latins went to war with the city on two occasions. In the first, which according to the Fasti Triumphales took place before 588 BC, Tarquinius conquered the Latin city of Apiole.
January 579 BC: Tarquinius subjugated the whole of Lazio conquering both a series of Latin cities and those that had rebelled: Cornicolo, the ancient Ficulea, Cameria, Crustumerium, Ameriola, Medullia and Nomentum.
February 579 BC: Tarquinius subjugated the whole of Lazio conquering both a series of Latin cities and those that had rebelled: Cornicolo, the ancient Ficulea, Cameria, Crustumerium, Ameriola, Medullia and Nomentum.
3.4.War against the Latins of Tarquinius Superbus
Was a military campaign to conquer several Latin cities waged by Roman King Tarquinius Superbus.
January 509 BC: In fact, important cities of the Latium vetus were conquered under his reign, such as Suessa Pometia, Ardea, Ocricoli and Gabii.
Were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse (Sicily) over the control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean.
4.1.First Sicilian War
Was a conflict fought between ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse (Sicily) over the control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean.
4.1.1.Battle of Alalia
Took place between 540 BCE and 535 BCE off the coast of Corsica between Greeks and the allied Etruscans and Carthaginians. The Greeks evacuated Corsica, which was captured by the Etruscans, while Carthage maintained its hold on Sardinia.
January 534 BC: The naval Battle of Alalia took place ca. 535 BC off the coast of Corsica between Greeks of Phocaea and Massilia and the allied Etruscans and Carthaginians. The battle was won by the Etruscans and Carthaginians.
A political revolution replaced the then-existing Roman monarchy under Lucius Tarquinius Superbus with a republic.
January 509 BC: The first to free itself from the supremacy of the Tyrrhenians with the expulsion of the Tarquinians around 510 BC was Rome.
January 508 BC: Overthrow of the Roman monarchy. At the beginning of ist republican life the control only over the city itself. The remanant controlled territories were basically lost.
Was a War of the Roman Republic against the Sabellian people.
January 495 BC: The Romans, led by the consul Publius Servilius Priscus Strutto, destroyed the Volscian capital Suessa Pometia.
February 495 BC: The Romans, led by the consul Publius Servilius Priscus Strutto, destroyed the Volscian capital Suessa Pometia.
Were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Volsci, an ancient Italic people.
7.1.War with the Volsci
Was a War between the Roman Republic and the Volsci people.
January 492 BC: The Volsci were preparing for war. Against which it was decided to undertake yet another military action, entrusting it to the consul Postumio Cominio. The latter began the military campaign by leading the Roman army against the Volsci of Anzio, at the end of which the city was conquered. Subsequently the Roman army marched against the Volscian cities of Longula, Polusca and Corioli, which also ended up being conquered by the Romans.
Conquests by Dyonisus I "the Elder", tyrant of the Polis of Syracuse (Sicily).
January 399 BC: The legendary Portus Syracusanus is founded after the incursions of the Siceliots of Syracuse, in the 5th century BC.
January 499 BC: Expansion of the Kingdom of Rome by 700 BC.
January 299 BC: Corsica conquered by Carthage.
Disestablishment
January 263 BC: Rome was the eventual victor in the wars and the last Etruscan resistance was crushed in 264 BC when Volsinii was defeated. The Etruscans were assimilated into Roman culture and Rome became one of the Mediterranean superpowers amongst the Greeks and the Carthaginians, though the Etruscan language survived for another 300 years.
Selected Sources
Cornell, T. (1982): Atlas of the Roman world, New York : Facts on File, p. 27
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXII
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.29
Venning, T. (2011): A chronology of the Roman Empire, Continuum International Publishing Group, p.39
Venning, T. (2011): A chronology of the Roman Empire, Continuum International Publishing Group, p.60
 Etruscan League
Etruscan League