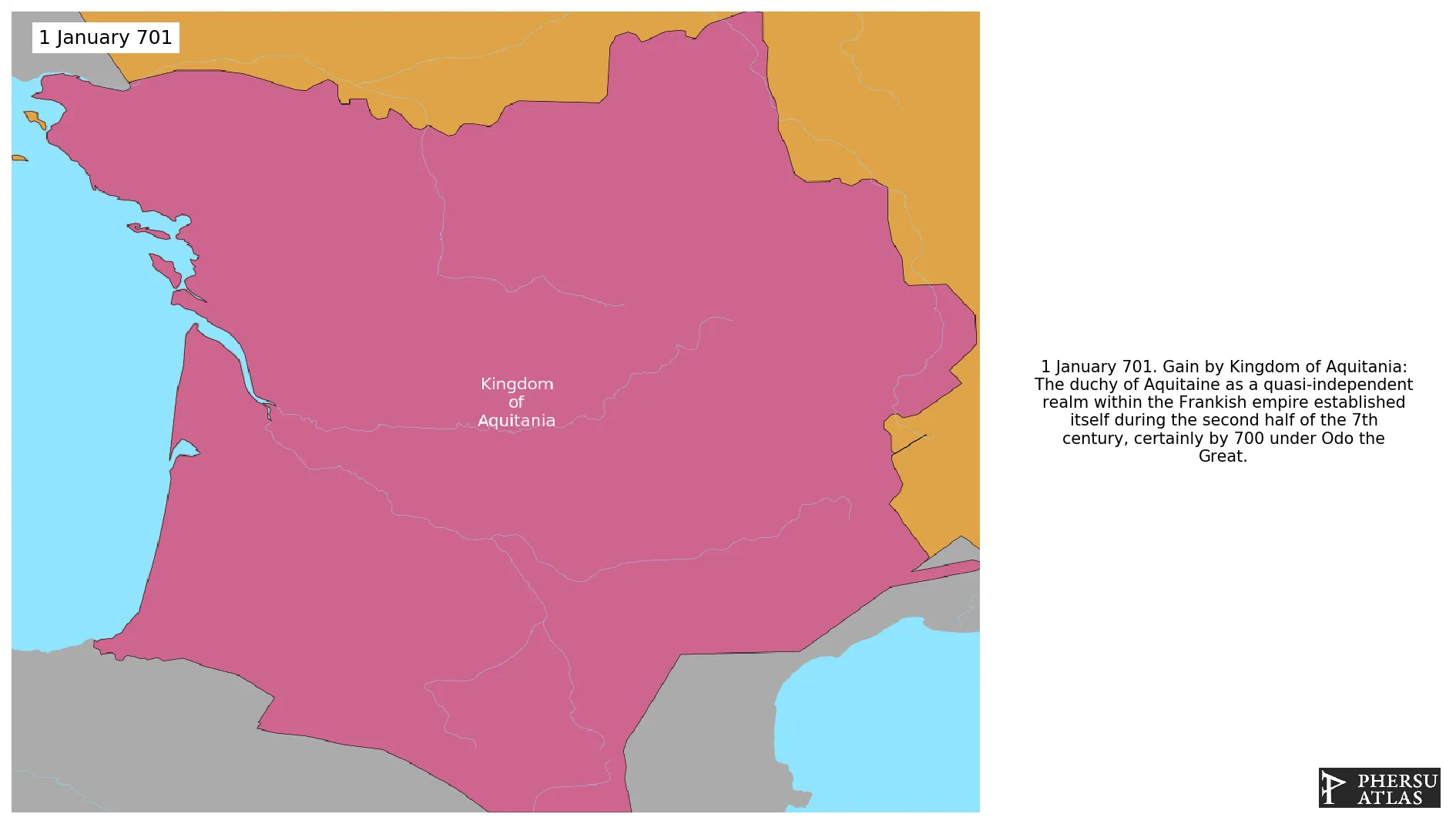
Kingdom of Aquitania
Kingdom of Aquitania
This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Aquitania and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
A de facto independent polity in western France that was a nominal Frankish vassal.
Establishment
January 701: The duchy of Aquitaine as a quasi-independent realm within the Frankish empire established itself during the second half of the 7th century, certainly by 700 under Odo the Great.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The duchy of Aquitaine as a quasi-independent realm within the Frankish empire established itself by 700 under Odo the Great.
The Frankish Kingdom was partitioned and reuinited several times as the Frankish rulers used to divide their territories equally among their heirs. This lead also to a number of wars and revolts.
January 716: In 715 Odo the great declared himself independent during the civil war raging in Gaul. No other time seems reasonable for the acquisition of Potiers and neighboring territories since an attempt to conquer limoges by Wolf I was unsuccessful in 673.
2.1.Frankish Civil War
Was a war between Teilreiche of the Frankish Kingdom (polities emerging from the hereditary divisions of the Frankish Kingdom that repeatedly divided and reunited). After their defeat at the Battle of Vincy, Chilperic and Ragenfrid allied with Odo the Great, the independent duke of Aquitaine, and marched on Soissons. .
October 719: After their defeat at the Battle of Vincy, Chilperic and Ragenfrid allied with Odo the Great, the independent duke of Aquitaine, and marched on Soissons. Unfortunately, Charles had anticipated this, and was awaiting them. That army easily defeated the allied forces of Odo, Chilperic, and Ragenfrid near Soissons. The war was over and Charles was undisputed dux Francorum.
Were a series of military campaigns by Frankish king Pepin the short against Aquitania.
January 760: In 759-760, Pippin the Short, King of the Franks, clashed with Waifer, Duke of Aquitaine, over rebellious Franks and church issues. Waifer sent ambassadors and hostages to secure peace with Pippin, maintaining control over Aquitaine.
February 760: In 759-760, Pippin the Short, King of the Franks, clashed with Waifer, Duke of Aquitaine, over rebellious Franks and church issues. Waifer sent ambassadors and hostages to secure peace with Pippin, maintaining control over Aquitaine.
January 761: In 761, Pippin the Short, King of the Franks, intervened in the Kingdom of Aquitania due to Waifer's support for Frankish rebels and disputes with the French church. Waifer sent ambassadors and hostages to negotiate peace with Pippin, agreeing to his conditions to avoid conflict.
February 761: In 761, Pippin the Short, King of the Franks, intervened in the Kingdom of Aquitania due to Waifer's support for Frankish rebels and disputes with the French church. Waifer sent ambassadors and hostages to negotiate peace with Pippin, agreeing to his conditions to avoid conflict.
January 762: Pippin, also known as Pepin the Short, was the King of the Franks. In 761, he launched a military campaign and ravaged Aquitaine, a territory ruled by Duke Waifer. This event marked the expansion of the Kingdom of the Franks into Aquitania.
February 762: Pippin the Short, King of the Franks, ravaged Aquitaine in 762. This military campaign was part of Pippin's efforts to expand the Frankish kingdom and assert his authority over the region, which was ruled by Duke Waiofar. The Kingdom of Aquitania was eventually absorbed into the Frankish Empire.
January 763: Pippin returned the following year and laid siege to Bituricam (modern Bourges) and captured it, allowing any defenders sent by Waifer who had been captured to return to their lands, while the rebuilt Bitorica was occupied by the Franks.
February 763: Pippin returned the following year and laid siege to Bituricam (modern Bourges) and captured it, allowing any defenders sent by Waifer who had been captured to return to their lands, while the rebuilt Bitorica was occupied by the Franks.
January 766: In the years 765 and 766, Pepin invaded Aquitaine.
February 766: End of Frankish invasion of Aquitaine.
January 767: In the years 765 and 766, Pepin invaded Aquitaine.
February 767: End of Frankish invasion of Aquitaine.
January 768: In 767, Pepin the Short, King of the Franks, traveled to Aquitaine with his wife Queen Bertrada to capture Waifer, who had rebelled and taken control of part of the duchy. Pepin's intervention ultimately led to Aquitaine being incorporated into the Kingdom of the Franks.
February 768: In 767, Pepin the Short, King of the Franks, traveled to Aquitaine with Queen Bertrada to capture Waifer, who had rebelled and taken control of part of the Kingdom of Aquitania. Pepin's intervention aimed to restore his authority over the region.
January 736: Odo was succeeded by his son Hunald, who reverted to former independence, so defying the Frankish Mayor of the Palace Charles Martel's authority.
Disestablishment
January 770: The autonomous and troublesome duchy of Aquitaine was conquered by the Franks in 769, after a series of revolts against their suzerainty. In order to avoid a new demonstration of Aquitain particularism, Charlemagne decided to organize the land within his kingdom.

 Kingdom of Aquitania
Kingdom of Aquitania