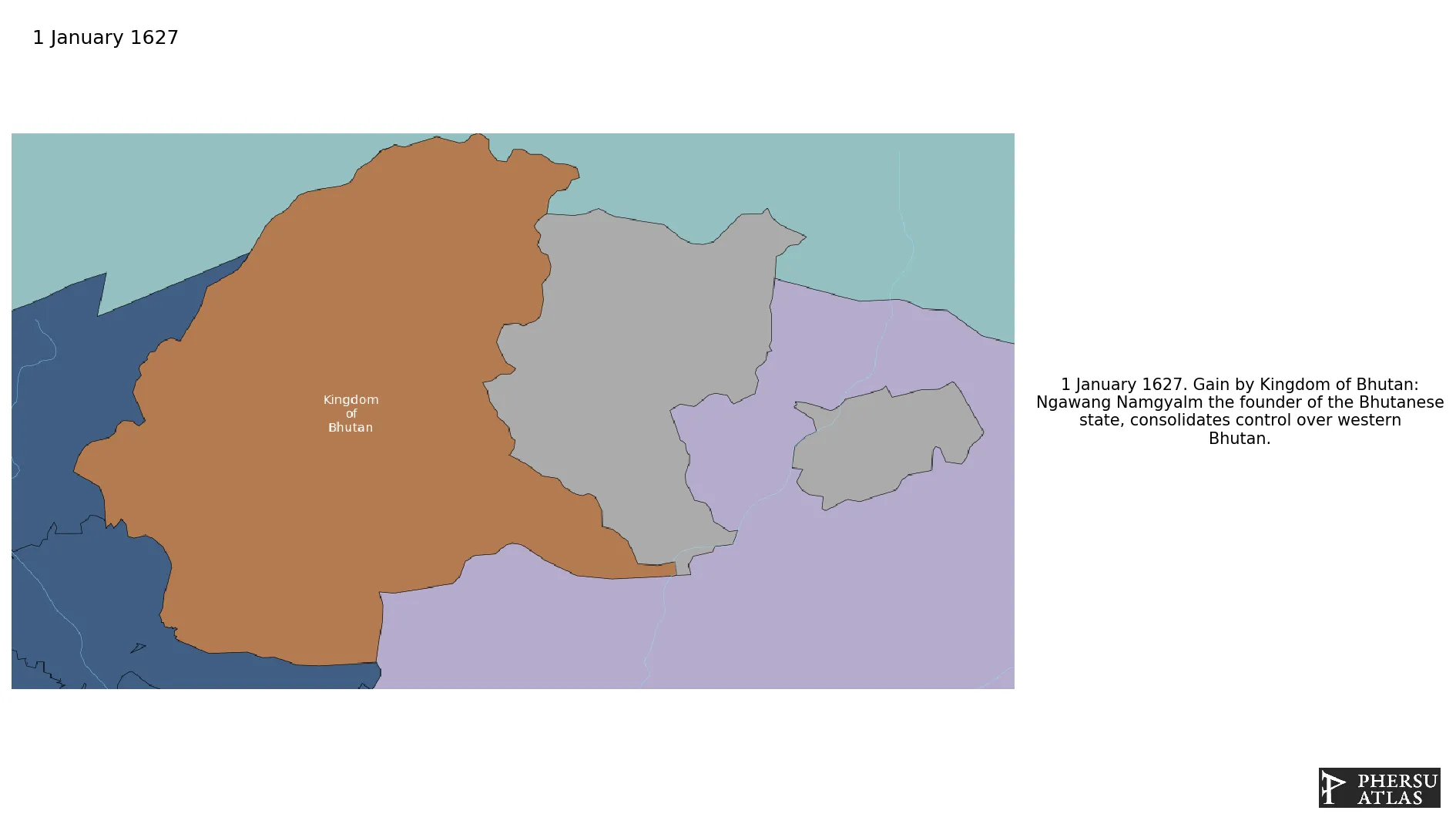
Kingdom of Bhutan
Kingdom of Bhutan
This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Bhutan and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Is a landlocked country in South Asia.
Establishment
January 1627: Ngawang Namgyalm the founder of the Bhutanese state, consolidates control over western Bhutan.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars fought by the British East India Company in the Indian Subcontinent that resulted in the British conquest and colonial rule of the region.
1.1.Anglo-Nepalese War
Was a war between the Kingdom of Nepal and the British East India Company. .
1.1.1.Treaty of Sugauli
Was the treaty that ended the Anglo-Nepali War. Nepal lost one-third of its territory.
March 1816: The Treaty of Sugauli, signed following the Anglo-Nepalese War of 1814-16, established the boundary line of Nepal.
Was a war fought between British India and Bhutan from 1864 to 1865.
2.1.Treaty of Sinchula
Was the treaty that ended the Bhutan War. Under the terms of the Treaty, signed 11 November 1865, Bhutan ceded territories in the Assam Duars and Bengal Duars, as well as the 83 km² of territory of Dewangiri in southeastern Bhutan to British India.
November 1865: Under the terms of the Treaty of Sinchula, signed 11 November 1865, Bhutan ceded territories in the Assam Duars and Bengal Duars, as well as the 83 km² of territory of Dewangiri in southeastern Bhutan.
January 1630: Tibetan armies invaded Bhutan around 1629.
February 1630: Tibetan armies invaded Bhutan around 1629.
January 1632: In 1631, Bhutan was occupied by Tibet under the military leadership of the Tibetan ruler, Ngawang Namgyal.
February 1632: In 1631, Bhutan was occupied by Tibet under the rule of the Tibetan ruler, Ngawang Namgyal. However, in 1632, the territory was liberated and returned to the Kingdom of Bhutan under the leadership of Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal.
January 1635: In 1634, Ngawang Namgyal, the founder of Bhutan, defeated Karma Tenkyong's army in the Battle of Five Lamas. This victory solidified Ngawang Namgyal's power and influence in the region, leading to the territory of Bhutan coming under Tibetan military occupation.
February 1635: In 1634 Ngawang Namgyal defeated Karma Tenkyong's army in the Battle of Five Lamas.
January 1640: bhutan conquered by tibet.
February 1640: Bhutan is freed from Tibetan control.
January 1641: The unification of Bhutan, during the reign of Ngawang Namgyal, occurred by unifying the various warring fiefdoms of the region.
January 1641: By 1640 Bhutan reached its current borders.
January 1644: In 1643, a joint Mongol-Tibetan force led by Gushri Khan sought to destroy Nyingmapa refugees who had fled to Bhutan and thus invaded the region.
February 1644: The Mongol-Tibetan forces leave Bhutan.
January 1648: Tibetan invasion of Bhutan.
February 1648: The Tibetan invasion in 1647, led by the 5th Dalai Lama and his Mongol allies, failed to conquer Bhutan.
January 1715: In 1714, Tibetan forces, led by Lhazang Khan of the Khoshut Khanate, with support from Mongolia, invaded Bhutan. Despite their efforts, they were unable to gain control of the territory.
February 1715: In 1714, Tibetan forces, led by the 5th Dalai Lama, invaded Bhutan with the support of Mongolia. However, they were ultimately unsuccessful in gaining control of the territory, as the Bhutanese forces, under the leadership of the Zhabdrung Rinpoche, successfully defended their kingdom.
January 1773: British invasion and occupation of Bhutan (1772).
February 1773: The British forces left Bhutan.
January 1785: In 1784, the British East India Company, represented by Warren Hastings, turned over the Bengal Duars territory to the Kingdom of Bhutan. The boundaries of the territory were poorly defined, leading to disputes between the two parties.
January 1835: British demands for payment led to several military incursions into Bhutan between 1834 and 1835, resulting in defeat for Bhutan's forces and a temporary loss of territory.
February 1835: British demands for payment led to several military incursions into Bhutan between 1834 and 1835, resulting in defeat for Bhutan's forces and a temporary loss of territory.
January 1836: British demands for payment led to several military incursions into Bhutan between 1834 and 1835, resulting in defeat for Bhutan's forces and a temporary loss of territory.
February 1836: British demands for payment led to several military incursions into Bhutan between 1834 and 1835, resulting in defeat for Bhutan's forces and a temporary loss of territory.
November 1865: The Kingdom of Bhutan becomes a protectorate of British India.
August 1949: When India gained independence in, the new Indian Government recognized Bhutan as an independent country.
August 1949: Indo-Bhutan Treaty. Under this agreement, India returned the land around Deothang to Bhutan. The region had been lost by Bhutan after the 1865 Anglo-Bhutanese War.

 Kingdom of Bhutan
Kingdom of Bhutan