This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Rome and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
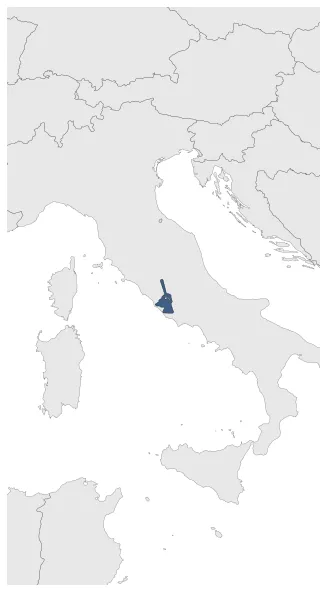
According to oral accounts, the Roman Kingdom began with the city's founding c. 753 BC. It was the earliest form of the Roman state. During this period Rome controlled just the territory around the city.
Summary
The origins of Rome are shrouded in myth and legend, but it is believed that the city was founded by Latin villagers and refugees who sought safety behind the wooden palisades on the Palatine Hill overlooking the Tiber River. According to legend, the twins Romulus and Remus, descendants of the Trojan hero Aeneas, were the first kings of Rome.
Under the early kings, Rome grew in power and influence, gradually conquering its neighbors and establishing itself as a dominant force in the region. The Etruscan monarchy was overthrown in 510 BC and a republic was established, governed by a patrician oligarchy.
Establishment
April 753 BC: Foundation of Rome.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were the events and military campaigns that led to the foundation and the expansion of the Kingdom of Rome.
January 749 BC: Romulus, the legendary founder and first king of Rome, managed to conquer Medullia.
January 699 BC: Expansion of the Kingdom of Rome by 700 BC.
April 587 BC: Priscus obtained a triumph over the Latins and Etruscans on 1 April 588/587 BC. He bought the cities of Corniculum and Collatia from the Roman state.
January 509 BC: Ocricoli conquered by Kingdom of Rome.
Was a war between the Kingdom of Rome and several nearby peoples and city-states.
January 750 BC: The Ceninensi who invaded the Roman territories, but they were beaten by the ordered ranks of the Romans. After Romulus had conquered their city it was the turn of the Antemnati. Their city was stormed and occupied, leading Romulus to celebrate a second ovation. Only the Crustumini city remained, whose resistance lasted even less than their allies.
Were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome (in both the regal and the republican periods) and the Etruscans. The conquest of Etruria was completed in 265-264 BC.
January 745 BC: The Kingdom of Rome occupied Fidenae, a town located north of Rome.
January 615 BC: Etruscan domination in Rome (616-509 BC).
January 509 BC: Etruscan domination in Rome (616-509 BC).
3.1.War with Veii
Was a war between Rome and the Etruscan city of Veii.
January 719 BC: The Veientes were concerned by the increasing Roman power, and accordingly launched an incursion into Roman territory. However, they were defeated by the Romans who forced the Veientes to cede the territories of Septem Pagi and Saline.
Was the Roman conquest of the ancient city of Alba Longa.
January 672 BC: According to tradition, the friendly relations between the Romans and the population of Alba Longa had broken down and continuous disputes had arisen. The Roman king's response to the Albani's complaints was that the initiation of the quarrel had been their doing. And since both peoples had equal strength, and continued to weaken with frequent fighting, to shorten the war it was decided to resolve the dispute with a challenge between three twin brothers who represented on one side the Romans (the Horatii) and on the other the Albani (the Curiazi). Alba Longa was defeated and subjected to the Roman state.
Were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome (including both the Roman Kingdom and the Roman Republic) and the Latins, from the earliest stages of the history of Rome until the final subjugation of the Latins to Rome in the aftermath of the Latin War.
5.1.Rome's first war with the Latini
Was the first war between Rome and the Latins that started when the Latins attacked the Kingdom of Rome.
January 600 BC: The war then concentrated on the Latin city of Medullia, a city which had a large garrison and was well fortified. Several clashes took place outside the city walls and the Romans were eventually victorious.
January 600 BC: The Latins initially made an incursion into Roman territory. When a Roman embassy demanded compensation for the damage, the Latins gave a contemptuous reply. Ancus Martius consequently declared war on the Latins. Ancus Martius marched from Rome with a conscript army and captured the Latin city of Politorio in one attack.
January 600 BC: Additional citizens were brought to Rome when the king captured the Latin cities of Telleni and Ficana.
5.2.War with the Latin League
Was a war waged by Roman King Tarquinius Priscus against the Latins.
January 587 BC: Tarquin's first war was waged against the Latins. Tarquinius took the Latin town of Apiolae by storm and took great booty from there back to Rome. According to the Fasti Triumphales, this war must have occurred prior to 588 BC. Subsequently, the Latin cities of Corniculum, old Ficulea, Cameria, Crustumerium, Ameriola, Medullia, and Nomentum were subdued and became Roman.
5.3.Tarquinius Priscus' wars
Were a series of wars waged by Roman King Tarquinius Priscus.
January 587 BC: When Rome was ruled by Tarquinius Priscus the Latins went to war with the city on two occasions. In the first, which according to the Fasti Triumphales took place before 588 BC, Tarquinius conquered the Latin city of Apiole.
January 579 BC: Tarquinius subjugated the whole of Lazio conquering both a series of Latin cities and those that had rebelled: Cornicolo, the ancient Ficulea, Cameria, Crustumerium, Ameriola, Medullia and Nomentum.
February 579 BC: Tarquinius subjugated the whole of Lazio conquering both a series of Latin cities and those that had rebelled: Cornicolo, the ancient Ficulea, Cameria, Crustumerium, Ameriola, Medullia and Nomentum.
5.4.War against the Latins of Tarquinius Superbus
Was a military campaign to conquer several Latin cities waged by Roman King Tarquinius Superbus.
January 509 BC: In fact, important cities of the Latium vetus were conquered under his reign, such as Suessa Pometia, Ardea, Ocricoli and Gabii.
A political revolution replaced the then-existing Roman monarchy under Lucius Tarquinius Superbus with a republic.
January 509 BC: The first to free itself from the supremacy of the Tyrrhenians with the expulsion of the Tarquinians around 510 BC was Rome.
January 508 BC: Overthrow of the Roman monarchy. At the beginning of ist republican life the control only over the city itself. The remanant controlled territories were basically lost.
January 508 BC: A political revolution replaced the then-existing Roman monarchy under Lucius Tarquinius Superbus with a republic.
January 749 BC: Twelve Etruscan city-states, according to tradition, formed a powerful economic, religious and military alliance in Etruria: the "Etruscan League".
Disestablishment
January 508 BC: Overthrow of the Roman monarchy. At the beginning of ist republican life the control only over the city itself. The remanant controlled territories were basically lost.
January 508 BC: A political revolution replaced the then-existing Roman monarchy under Lucius Tarquinius Superbus with a republic.
Selected Sources
Cornell, T. (1982): Atlas of the Roman world, New York : Facts on File, p. 27
 Kingdom of Rome
Kingdom of Rome




























